Linear robots excel in precise, straight-line movements ideal for pick-and-place tasks or assembly operations, offering high speed and repeatability along linear axes. Articulated robots provide greater flexibility with multiple rotary joints, enabling complex and versatile motions suitable for welding, painting, and intricate manipulation tasks that require a wide range of movement.
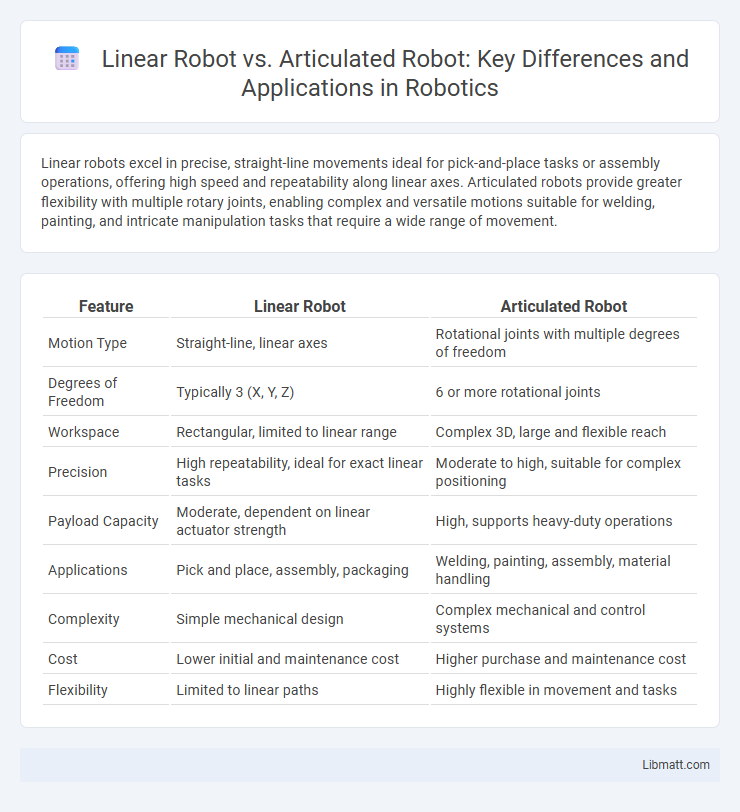
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Linear Robot | Articulated Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Type | Straight-line, linear axes | Rotational joints with multiple degrees of freedom |
| Degrees of Freedom | Typically 3 (X, Y, Z) | 6 or more rotational joints |
| Workspace | Rectangular, limited to linear range | Complex 3D, large and flexible reach |
| Precision | High repeatability, ideal for exact linear tasks | Moderate to high, suitable for complex positioning |
| Payload Capacity | Moderate, dependent on linear actuator strength | High, supports heavy-duty operations |
| Applications | Pick and place, assembly, packaging | Welding, painting, assembly, material handling |
| Complexity | Simple mechanical design | Complex mechanical and control systems |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost | Higher purchase and maintenance cost |
| Flexibility | Limited to linear paths | Highly flexible in movement and tasks |
Introduction to Linear and Articulated Robots
Linear robots operate on a single axis, moving back and forth in a straight line, ideal for simple, repetitive tasks with high precision. Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints, resembling a human arm, and offer greater flexibility and range of motion for complex applications such as welding, assembly, and material handling. Understanding these differences helps you select the right robot type based on your automation needs and workspace constraints.
Key Differences Between Linear and Articulated Robots
Linear robots move along straight paths on a fixed axis, providing high precision and speed in repetitive tasks such as pick-and-place operations. Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints, enabling complex, multi-directional movements ideal for welding, assembly, and intricate manipulation. Your choice depends on whether you require straightforward linear motion or flexible, multi-axis articulation for complex applications.
Design and Structural Comparison
Linear robots feature a straightforward design with axes arranged in a straight line, enabling precise, high-speed linear motions ideal for pick-and-place tasks. Articulated robots utilize rotary joints similar to a human arm, offering multiple degrees of freedom and enhanced flexibility for complex movements in three-dimensional space. Structurally, linear robots are simpler and generally more compact, while articulated robots have more intricate mechanical components allowing for versatile positioning and orientation.
Movement and Range of Motion
Linear robots offer precise, straight-line movement along one or more axes, making them ideal for tasks requiring high-speed and repetitive linear motion with a limited range of motion. Articulated robots feature rotary joints that provide a wide range of motion, allowing complex movements and flexibility similar to a human arm, ideal for intricate assembly or welding tasks. Your selection should consider whether the application demands straightforward, high-speed linear travel or versatile, multi-directional maneuvering.
Precision and Accuracy
Linear robots excel in precision and accuracy due to their straightforward, single-axis movement, minimizing positioning errors and ensuring consistent repeatability. Articulated robots offer versatile motion but may introduce slight deviations in precision because of their multiple joints and complex kinematics. Your choice should depend on whether the task requires high linear accuracy or flexible, multi-axis maneuverability.
Typical Applications in Industry
Linear robots excel in precision tasks such as pick-and-place operations, assembly, and packaging in electronics and automotive manufacturing due to their straightforward, linear motion. Articulated robots, with their multi-jointed arms, dominate in complex industrial applications including welding, painting, and heavy material handling, offering superior flexibility and reach for automotive and aerospace industries. Both types enhance manufacturing efficiency, but linear robots are preferred for repetitive, high-speed tasks while articulated robots are essential for intricate, multi-axis movements.
Advantages of Linear Robots
Linear robots offer exceptional precision and speed due to their straightforward, straight-line movements, making them ideal for tasks requiring high repeatability and accuracy. Their simple design results in lower maintenance costs and increased reliability compared to articulated robots. Linear robots excel in space-saving applications and can be easily integrated into automated production lines for efficient material handling and assembly processes.
Advantages of Articulated Robots
Articulated robots offer greater flexibility and a wider range of motion compared to linear robots, making them ideal for complex tasks requiring multi-axis movement. Their multiple rotary joints provide enhanced precision and adaptability in tight or irregular spaces, especially in automotive assembly and intricate manufacturing processes. Articulated robots also excel in tasks requiring varying reach and orientation, improving productivity and reducing cycle times in dynamic industrial environments.
Selection Criteria: Which Robot Fits Your Needs?
Linear robots excel in tasks requiring precise, repetitive motion along a single axis, making them ideal for applications like pick-and-place or conveyor systems. Articulated robots offer greater flexibility and multi-axis movement, suited for complex assembly, welding, or packaging operations. Selecting the right robot depends on factors such as workspace size, payload capacity, degree of freedom needed, and task complexity.
Future Trends in Industrial Robotics
Future trends in industrial robotics emphasize the growing integration of AI and machine learning, which enhances the precision and adaptability of both linear and articulated robots. Linear robots excel in high-speed, repetitive tasks with straightforward paths, while articulated robots offer superior flexibility and reach for complex assembly and processing operations. Your manufacturing processes can benefit from hybrid systems combining these robots to optimize efficiency and accommodate evolving production demands.
Linear robot vs Articulated robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com