Battery-powered robots offer greater mobility and flexibility, allowing you to operate them in areas without access to power outlets. Plug-in robots rely on continuous external power, which can limit their range but often provides longer operational time and consistent performance.
Table of Comparison
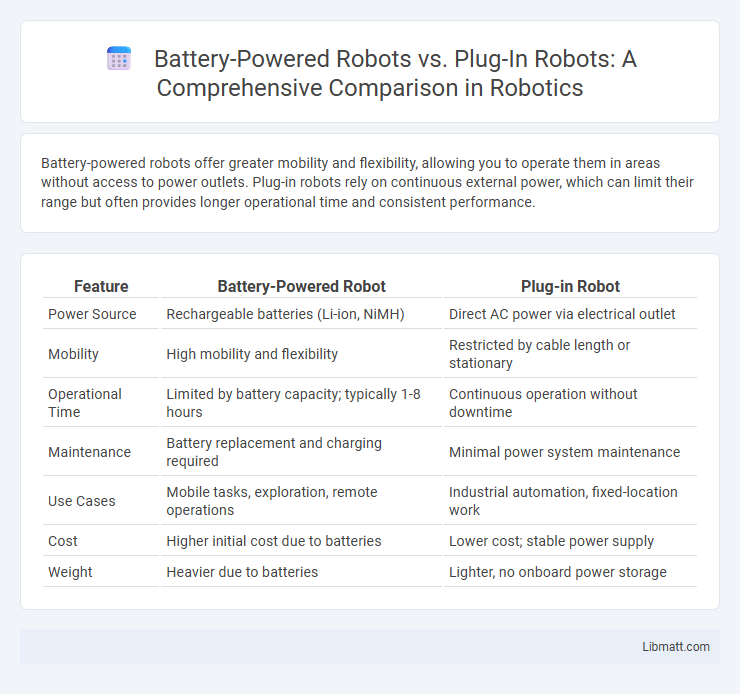
| Feature | Battery-Powered Robot | Plug-in Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Rechargeable batteries (Li-ion, NiMH) | Direct AC power via electrical outlet |
| Mobility | High mobility and flexibility | Restricted by cable length or stationary |
| Operational Time | Limited by battery capacity; typically 1-8 hours | Continuous operation without downtime |
| Maintenance | Battery replacement and charging required | Minimal power system maintenance |
| Use Cases | Mobile tasks, exploration, remote operations | Industrial automation, fixed-location work |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to batteries | Lower cost; stable power supply |
| Weight | Heavier due to batteries | Lighter, no onboard power storage |
Introduction to Battery-Powered and Plug-in Robots
Battery-powered robots operate autonomously using rechargeable lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride batteries, enabling mobility without constant access to external power sources. Plug-in robots rely on direct electrical connections to power grids, ensuring continuous operation but limiting their range and mobility due to tethering. Key applications of battery-powered robots include warehouse automation and outdoor surveillance, while plug-in models are often used in fixed manufacturing lines and laboratory environments.
Power Source Overview: Battery vs Plug-in
Battery-powered robots rely on rechargeable lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride batteries, providing cordless mobility and increased operational flexibility for your tasks. Plug-in robots draw continuous power from an external electrical source via a cable, ensuring uninterrupted operation but limiting movement range and requiring proximity to power outlets. Choosing between these power sources depends on your need for portability versus consistent power availability during robot deployment.
Mobility and Flexibility Comparison
Battery-powered robots offer superior mobility by operating wirelessly, allowing them to navigate various environments without being tethered to a fixed power source. Plug-in robots, however, rely on continuous external power, limiting their movement to areas near power outlets and reducing operational flexibility. The absence of cables in battery-powered robots enhances their adaptability for tasks requiring dynamic positioning and movement across diverse locations.
Energy Efficiency and Consumption
Battery-powered robots offer higher energy efficiency by utilizing rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that provide consistent power with minimal energy loss during storage and operation. Plug-in robots rely on continuous external power sources, which can lead to energy waste through power conversion and idle consumption when not actively moving. Optimizing battery capacity and power management systems in battery-powered robots reduces overall energy consumption and enhances operational autonomy compared to plug-in models.
Maintenance Requirements
Battery-powered robots require regular battery checks, occasional replacements, and monitoring of charge cycles to maintain optimal performance. Plug-in robots generally have lower maintenance demands since they stay connected to a constant power source, but their electrical components and wiring need periodic inspections for safety. Understanding these maintenance requirements helps you select the right robot type for your operational needs and long-term reliability.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term
Battery-powered robots typically have higher upfront costs due to the need for advanced battery systems and charging infrastructure, whereas plug-in robots benefit from lower initial investment by relying on continuous external power sources. Long-term expenses for battery-powered robots include battery replacements and potential efficiency loss over time, increasing maintenance costs, while plug-in robots incur minimal energy storage maintenance but may face higher operational costs if fixed power outlets limit mobility and productivity. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires analyzing both energy costs and maintenance frequency to determine which solution offers the best balance for specific industrial applications.
Performance and Reliability
Battery-powered robots offer enhanced mobility and flexibility, operating independently without the constraints of power cords, which improves performance in dynamic environments. However, their reliability can be affected by battery life limitations and the need for regular recharging or battery replacement. Plug-in robots deliver consistent power supply ensuring extended operation time and stable performance but are limited by tether length and reduced maneuverability, impacting their adaptability in complex tasks.
Application Suitability
Battery-powered robots excel in applications requiring mobility and flexibility, such as warehouse inventory management or outdoor inspections, where tethering would limit their operational range. Plug-in robots are ideal for tasks demanding continuous power and high precision, like assembly line operations or laboratory automation, where consistent energy supply ensures uninterrupted performance. Your choice should align with the environment and task duration to maximize efficiency and productivity.
Environmental Impact
Battery-powered robots rely on rechargeable lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride batteries, which raise concerns regarding resource extraction, battery disposal, and energy consumption during charging. Plug-in robots draw continuous power from the grid, often leading to higher carbon footprints depending on the electricity generation mix, especially in regions reliant on fossil fuels. Evaluating environmental impact requires considering factors such as battery lifecycle emissions, electricity source sustainability, and energy efficiency during operation.
Choosing the Right Robot for Your Needs
When selecting between a battery-powered robot and a plug-in robot, consider your operational flexibility and duration requirements. Battery-powered robots offer mobility and freedom from cords, ideal for environments needing frequent movement or temporary workspaces. Plug-in robots provide continuous power for long-running tasks without interruptions, making them suitable for stationary applications where consistent energy supply is crucial.
Battery-Powered Robot vs Plug-in Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com