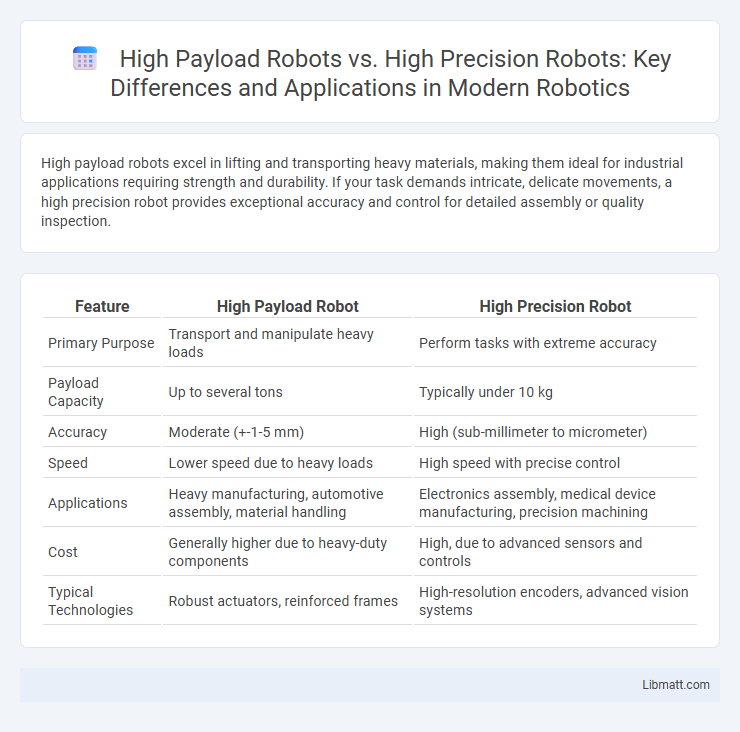
High payload robots excel in lifting and transporting heavy materials, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring strength and durability. If your task demands intricate, delicate movements, a high precision robot provides exceptional accuracy and control for detailed assembly or quality inspection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Payload Robot | High Precision Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Transport and manipulate heavy loads | Perform tasks with extreme accuracy |
| Payload Capacity | Up to several tons | Typically under 10 kg |
| Accuracy | Moderate (+-1-5 mm) | High (sub-millimeter to micrometer) |
| Speed | Lower speed due to heavy loads | High speed with precise control |
| Applications | Heavy manufacturing, automotive assembly, material handling | Electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing, precision machining |
| Cost | Generally higher due to heavy-duty components | High, due to advanced sensors and controls |
| Typical Technologies | Robust actuators, reinforced frames | High-resolution encoders, advanced vision systems |
Introduction to High Payload and High Precision Robots
High payload robots are engineered to handle heavy loads exceeding 100 kilograms, making them essential in industries like automotive and aerospace for tasks such as material handling and assembly. High precision robots offer exceptional accuracy with repeatability often within micrometers, crucial in electronics manufacturing and medical device production where exact movements are mandatory. Understanding the distinct capabilities of high payload versus high precision robots enables tailored automation solutions for complex industrial applications.
Key Differences Between High Payload and High Precision Robots
High payload robots are designed to handle and manipulate heavy loads, equipped with robust motors and strong frames to maximize lifting capacity, often exceeding hundreds of kilograms. High precision robots prioritize accuracy and repeatability, featuring advanced sensors and control systems to perform tasks with micron-level precision, ideal for delicate assembly or semiconductor manufacturing. The key difference lies in their primary function: payload capacity versus accuracy, influencing their applications, mechanical design, and control complexity.
Applications Suited for High Payload Robots
High payload robots excel in industries requiring heavy material handling, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace assembly, and large-scale welding operations. These robots are designed to lift and maneuver substantial weights with stability, making them ideal for transporting bulky components and performing tasks that demand robust force. Your choice of a high payload robot enhances efficiency and safety when working with heavy-duty applications that exceed the capacity of high precision robots.
Use Cases for High Precision Robots
High precision robots excel in applications requiring exact movements and intricate assembly, such as electronics manufacturing, medical device production, and microchip fabrication. Their ability to perform tasks with micron-level accuracy ensures consistent quality and reduces material waste in sectors like semiconductor and pharmaceutical industries. Your production lines benefit from enhanced reliability and product consistency when incorporating high precision robots in tasks demanding meticulous attention to detail.
Technical Specifications: Payload vs. Precision
High payload robots are engineered to handle heavy loads typically ranging from 100 kg to over 1000 kg, emphasizing robust mechanical structures and high-torque actuators to maximize lifting capacity while maintaining operational stability. In contrast, high precision robots prioritize positional accuracy often within the range of micrometers (+-0.01 mm to +-0.1 mm), utilizing fine-tuned sensors, advanced control algorithms, and rigid kinematic designs to achieve exact movement and repeatability. While payload capacity is crucial for applications like material handling and heavy assembly, precision robots excel in tasks requiring intricate manipulation such as electronics manufacturing and micro-assembly.
Advantages of High Payload Robots
High payload robots excel in handling heavy-duty tasks, enabling efficient material transport and assembly in industrial settings. Their robust build supports large-scale manufacturing processes, reducing operational downtime and increasing productivity. These robots often accommodate diverse tooling options, enhancing versatility across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors.
Benefits of High Precision Robots
High precision robots deliver unparalleled accuracy and repeatability, essential for tasks requiring meticulous detail and consistent quality in manufacturing, electronics, and medical device assembly. Their advanced sensors and control systems minimize errors, reduce waste, and enhance product reliability, significantly boosting operational efficiency. Your production processes benefit from these robots by achieving tighter tolerances and superior craftsmanship, elevating overall performance and competitiveness.
Industry Trends: Demand for Payload and Precision
Industry trends reveal a growing demand for both high payload and high precision robots across manufacturing and logistics sectors. High payload robots are crucial for automotive and heavy machinery industries, supporting tasks like lifting and assembly with enhanced efficiency. Your choice depends on whether your operation prioritizes load capacity or exacting accuracy, as precision robots dominate electronics and medical device manufacturing where meticulous detail is essential.
Decision Factors: Choosing the Right Robot
Selecting between a high payload robot and a high precision robot depends on the specific application requirements, such as load capacity and accuracy demands. Industrial sectors like automotive manufacturing prioritize high payload robots for handling heavy components, while electronics assembly lines demand high precision robots for delicate and intricate tasks. Evaluating factors like cycle time, workspace constraints, and the nature of the materials involved ensures optimal robot selection for operational efficiency.
Future Developments in Robotics: Payload and Precision Enhancements
Future developments in robotics will emphasize increasing payload capacity while maintaining or improving high precision capabilities, enabling robots to handle heavier loads without sacrificing accuracy. Advances in materials science, sensor technology, and AI-driven control systems will drive these enhancements, allowing for more versatile applications in manufacturing and automation. Your choice between high payload and high precision robots will increasingly depend on integrated capabilities, balancing strength and exactness to meet evolving industry demands.
High Payload Robot vs High Precision Robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com