Delta robots offer high-speed precision through their parallel-arm design, making them ideal for tasks requiring fast, repetitive movements. Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints, providing greater flexibility and a wider range of motion suited for complex, multi-axis operations in varied industrial applications.
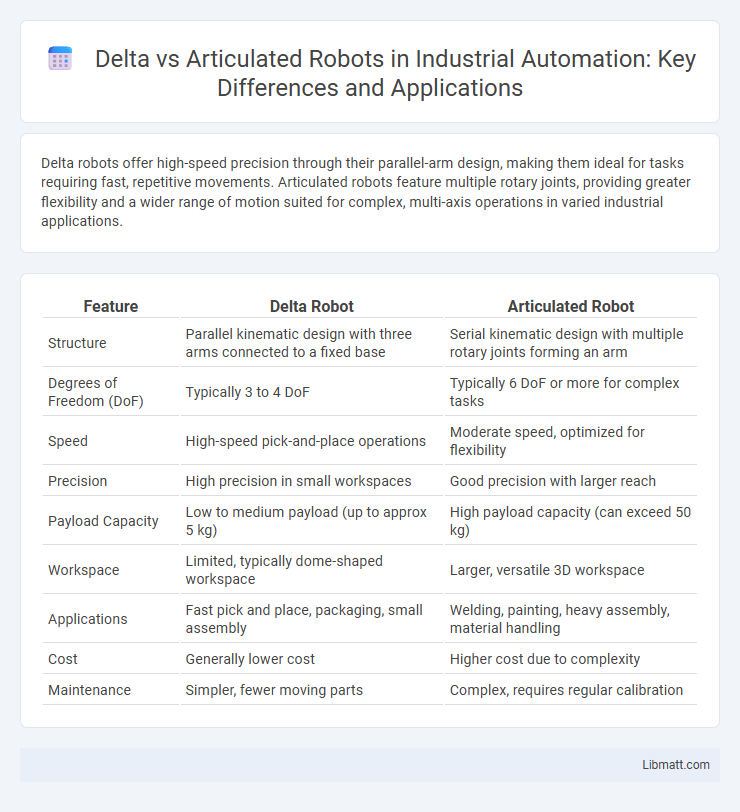
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Delta Robot | Articulated Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Parallel kinematic design with three arms connected to a fixed base | Serial kinematic design with multiple rotary joints forming an arm |
| Degrees of Freedom (DoF) | Typically 3 to 4 DoF | Typically 6 DoF or more for complex tasks |
| Speed | High-speed pick-and-place operations | Moderate speed, optimized for flexibility |
| Precision | High precision in small workspaces | Good precision with larger reach |
| Payload Capacity | Low to medium payload (up to approx 5 kg) | High payload capacity (can exceed 50 kg) |
| Workspace | Limited, typically dome-shaped workspace | Larger, versatile 3D workspace |
| Applications | Fast pick and place, packaging, small assembly | Welding, painting, heavy assembly, material handling |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Maintenance | Simpler, fewer moving parts | Complex, requires regular calibration |
Overview of Delta and Articulated Robots
Delta robots feature three parallel arms connected to a common base, enabling high-speed and precise movements ideal for pick-and-place tasks in manufacturing and packaging industries. Articulated robots consist of rotary joints allowing a wide range of motion and flexibility, making them suitable for complex assembly, welding, and material handling applications. Both types optimize automation workflows by balancing speed, accuracy, and versatility based on specific industrial requirements.
Key Differences Between Delta and Articulated Robots
Delta robots feature a parallel arm structure offering high-speed, precise pick-and-place operations, ideal for lightweight tasks in packaging and assembly lines. Articulated robots have rotary joints providing greater flexibility and a wider range of motion, suitable for complex manufacturing applications involving welding, painting, and heavy lifting. The key difference lies in Delta robots' speed and precision for repetitive tasks versus articulated robots' versatility and reach in diverse industrial environments.
Structural Design Comparison
Delta robots feature a parallel kinematic structure with three arms connected to a fixed base, providing high-speed and precise movements ideal for pick-and-place tasks. Articulated robots use multiple rotary joints arranged in a serial chain, offering greater flexibility and a wider range of motion suitable for complex assembly and welding operations. Understanding your application's requirements will help determine whether the compact, fast Delta design or the versatile, adaptive articulated structure is the better choice.
Movement and Range of Motion
Delta robots excel in high-speed, precise parallel movements, offering exceptional repeatability within a limited but highly controlled workspace, typically suited for light assembly and pick-and-place tasks. Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints enabling a broader range of motion and greater flexibility, capable of complex tasks requiring extensive reach and varied orientations. The delta's parallel linkage provides rapid, smooth linear movements, whereas articulated arms offer enhanced maneuverability with their multi-axis rotational capabilities.
Speed and Precision Analysis
Delta robots excel in high-speed pick-and-place tasks due to their lightweight parallelogram arms and fixed base, achieving speeds up to 300 picks per minute with precision around +-0.1 mm. Articulated robots, featuring rotary joints and flexible arm segments, offer greater reach and complex motion but typically operate at slower speeds near 60 cycles per minute with precision tolerance around +-0.2 mm. Your choice depends on whether application demands prioritize rapid, precise movements or versatile, multi-axis articulation.
Load Capacity and Application Suitability
Delta robots excel in high-speed pick-and-place tasks due to their lightweight design but typically have lower load capacity, usually under 5 kg. Articulated robots offer greater load capacity, often exceeding 20 kg, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like welding and material handling. Your choice depends on whether speed and precision or strength and versatility are more critical for your specific operational needs.
Workspace and Footprint Considerations
Delta robots offer a compact footprint with a fixed base and parallel arms that allow high-speed operations in a limited workspace, making them suitable for pick-and-place tasks in tight production lines. Articulated robots feature multi-jointed arms that provide a larger, more flexible workspace with a wider range of motion, ideal for complex assembly or welding processes requiring reach and dexterity. When optimizing workspace and footprint, delta robots excel in environments where floor space is constrained and rapid, repetitive movements are essential, whereas articulated robots require more room but deliver superior versatility and reach.
Typical Industries and Use Cases
Delta robots excel in high-speed pick-and-place applications commonly found in food packaging, pharmaceutical sorting, and electronics assembly due to their lightweight arms and precision. Articulated robots are favored in automotive manufacturing, metal fabrication, and complex welding tasks where a wider range of motion and heavy payload capacity are required. Delta robots thrive in environments demanding rapid, repetitive tasks, whereas articulated robots suit versatile operations involving three-dimensional manipulation and heavy-duty processes.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Type
Delta robots offer high-speed performance and excellent repeatability, making them ideal for packaging and pick-and-place applications, but their limited payload capacity and restricted workspace can be drawbacks. Articulated robots provide greater flexibility and a wider range of motion with multiple axes, suitable for complex assembly and welding tasks, though they typically have slower speeds and higher maintenance requirements. Understanding these advantages and limitations is critical for selecting the right robot type based on specific industrial needs and operational constraints.
How to Choose: Delta vs Articulated Robots
Choosing between delta and articulated robots depends on your specific application requirements such as precision, speed, and workspace layout. Delta robots excel in high-speed, lightweight pick-and-place tasks with a compact design, making them ideal for packaging and assembly lines. Articulated robots offer greater flexibility and reach, suitable for complex tasks like welding, painting, and material handling in larger work envelopes, allowing you to optimize your production efficiency based on the task complexity.
Delta vs Articulated Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com