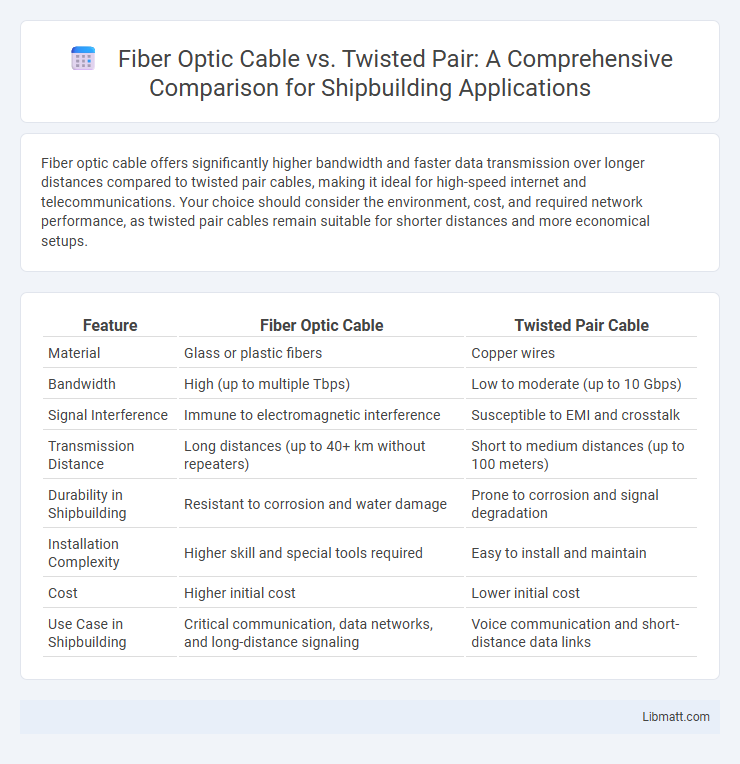
Fiber optic cable offers significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission over longer distances compared to twisted pair cables, making it ideal for high-speed internet and telecommunications. Your choice should consider the environment, cost, and required network performance, as twisted pair cables remain suitable for shorter distances and more economical setups.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiber Optic Cable | Twisted Pair Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass or plastic fibers | Copper wires |
| Bandwidth | High (up to multiple Tbps) | Low to moderate (up to 10 Gbps) |
| Signal Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Transmission Distance | Long distances (up to 40+ km without repeaters) | Short to medium distances (up to 100 meters) |
| Durability in Shipbuilding | Resistant to corrosion and water damage | Prone to corrosion and signal degradation |
| Installation Complexity | Higher skill and special tools required | Easy to install and maintain |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Use Case in Shipbuilding | Critical communication, data networks, and long-distance signaling | Voice communication and short-distance data links |
Introduction to Fiber Optic and Twisted Pair Cables
Fiber optic cables use glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light signals, offering high bandwidth and long-distance communication with minimal signal loss. Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference, commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and telephone systems. Your choice between these cables depends on factors like data speed requirements, distance, and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Fiber Optic and Twisted Pair
Fiber optic cables transmit data as light pulses through glass or plastic fibers, offering higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to twisted pair cables, which use electromagnetically shielded copper wires to transmit electrical signals. Fiber optic cables provide superior immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for high-speed, long-distance communication in environments with heavy electrical noise, while twisted pair cables are cost-effective and commonly used for short-distance applications like local area networks (LANs). Installation complexity and overall cost are higher for fiber optic systems due to specialized connectors and equipment, whereas twisted pair cables allow easier handling and maintenance.
Construction and Material Comparison
Fiber optic cables consist of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that transmit data as light pulses, providing high bandwidth and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Twisted pair cables use pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce crosstalk and interference but have limited bandwidth and shorter transmission distances compared to fiber optics. Your choice between these cables depends on the need for speed, distance, and resistance to interference in your network infrastructure.
Data Transmission Speed and Bandwidth
Fiber optic cables deliver significantly higher data transmission speeds and greater bandwidth capacity compared to twisted pair cables, making them ideal for high-speed internet and large data transfers. Fiber optics can support speeds up to 100 Gbps or more over long distances without signal degradation, whereas twisted pair cables typically max out at 1 Gbps over shorter distances due to electromagnetic interference and signal loss. The superior bandwidth of fiber optic cables enables simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams, supporting advanced applications in telecommunications and data centers.
Signal Attenuation and Interference Resistance
Fiber optic cables exhibit significantly lower signal attenuation compared to twisted pair cables, allowing data to travel longer distances without loss of quality. Their core made of glass or plastic fibers resists electromagnetic interference, ensuring cleaner and more reliable transmission, unlike twisted pair cables which are susceptible to noise and crosstalk from nearby electrical devices. Choosing fiber optic technology can enhance Your network performance by reducing signal degradation and improving interference immunity.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fiber optic cables require specialized skills and equipment for installation, including precise splicing and handling of delicate glass fibers, which can increase upfront costs. Maintenance is generally lower due to their resistance to electromagnetic interference and environmental factors, resulting in fewer repairs and signal degradation compared to twisted pair cables. Your choice should consider whether you need a long-term, low-maintenance solution or a more cost-effective, easier-to-install option like twisted pair cables.
Cost Analysis: Fiber Optic vs Twisted Pair
Fiber optic cables generally have higher initial costs due to expensive materials and installation processes, making twisted pair cables a more budget-friendly option for short-distance or less data-intensive applications. However, fiber optic cables offer lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan, which can reduce total cost of ownership over time, especially in enterprises requiring high-speed data transmission. Your choice should consider both upfront expenses and long-term operational savings to determine the most cost-effective solution for your network infrastructure.
Use Cases and Applications
Fiber optic cable excels in high-speed data transmission over long distances, making it ideal for internet backbones, data centers, and telecommunications networks. Twisted pair cables are widely used for shorter-distance applications such as local area networks (LANs), telephone lines, and home networking due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Your choice depends on bandwidth requirements and distance, with fiber optic preferred for high-performance needs and twisted pair suited for everyday connectivity.
Security and Reliability Considerations
Fiber optic cables offer superior security compared to twisted pair cables due to their immunity to electromagnetic interference and difficulty in signal tapping, making data breaches less likely. Reliability is enhanced with fiber optics as they resist corrosion and signal degradation over long distances, unlike twisted pair cables which are prone to interference and physical wear. Your network's security and uptime significantly benefit from choosing fiber optic technology in environments demanding high data integrity and minimal downtime.
Future Trends in Network Cabling
Fiber optic cable is rapidly becoming the preferred choice for future network cabling due to its higher bandwidth capacity, longer transmission distances, and immunity to electromagnetic interference compared to twisted pair cables. Emerging technologies such as 5G, IoT, and data-intensive applications will increasingly rely on fiber optics to support ultra-fast, reliable connectivity. Your network infrastructure will benefit from investing in fiber optic cabling to future-proof against growing data demands and evolving technological standards.
Fiber optic cable vs twisted pair Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com