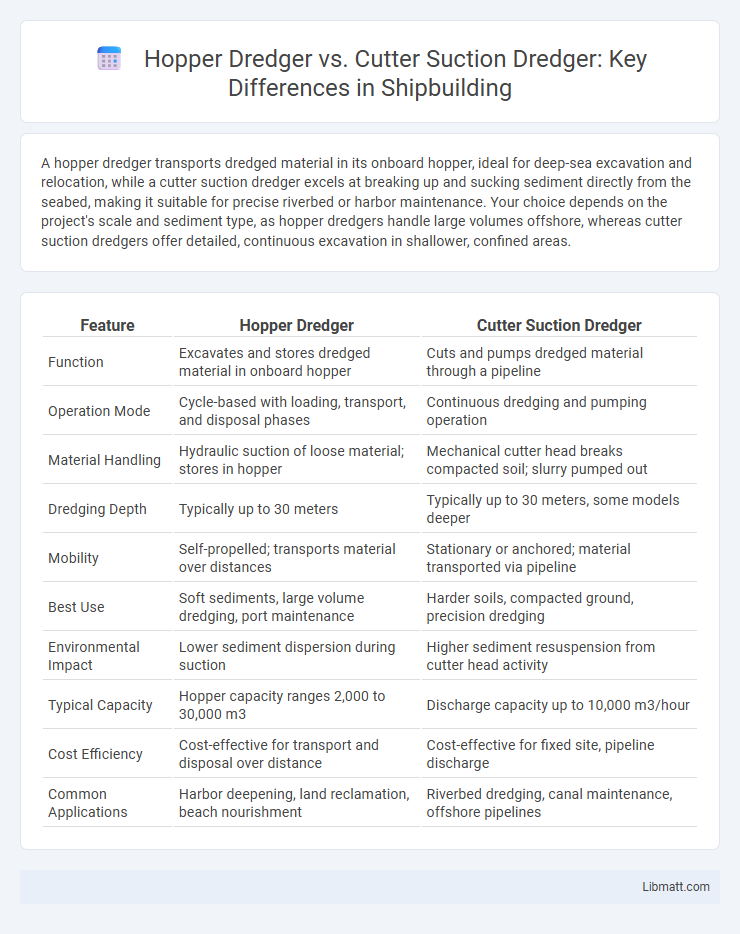
A hopper dredger transports dredged material in its onboard hopper, ideal for deep-sea excavation and relocation, while a cutter suction dredger excels at breaking up and sucking sediment directly from the seabed, making it suitable for precise riverbed or harbor maintenance. Your choice depends on the project's scale and sediment type, as hopper dredgers handle large volumes offshore, whereas cutter suction dredgers offer detailed, continuous excavation in shallower, confined areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hopper Dredger | Cutter Suction Dredger |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Excavates and stores dredged material in onboard hopper | Cuts and pumps dredged material through a pipeline |
| Operation Mode | Cycle-based with loading, transport, and disposal phases | Continuous dredging and pumping operation |
| Material Handling | Hydraulic suction of loose material; stores in hopper | Mechanical cutter head breaks compacted soil; slurry pumped out |
| Dredging Depth | Typically up to 30 meters | Typically up to 30 meters, some models deeper |
| Mobility | Self-propelled; transports material over distances | Stationary or anchored; material transported via pipeline |
| Best Use | Soft sediments, large volume dredging, port maintenance | Harder soils, compacted ground, precision dredging |
| Environmental Impact | Lower sediment dispersion during suction | Higher sediment resuspension from cutter head activity |
| Typical Capacity | Hopper capacity ranges 2,000 to 30,000 m3 | Discharge capacity up to 10,000 m3/hour |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for transport and disposal over distance | Cost-effective for fixed site, pipeline discharge |
| Common Applications | Harbor deepening, land reclamation, beach nourishment | Riverbed dredging, canal maintenance, offshore pipelines |
Introduction: Understanding Dredging Vessels
Hopper dredgers and cutter suction dredgers serve distinct roles in marine excavation, with hopper dredgers designed to collect and transport loose sediment in their onboard hoppers, ideal for deep-water dredging and sediment relocation. Cutter suction dredgers employ a rotating cutter head to loosen compacted seabed materials, effectively suctioning and pumping sediments through pipelines directly to disposal sites or reclamation areas. Your choice between these vessels depends on project depth, sediment type, and operational flexibility required for optimal dredging performance.
Overview of Hopper Dredgers
Hopper dredgers are specialized vessels designed to excavate and transport sediment in a single operation, using a large onboard hopper to store dredged materials. They excel in deep-sea dredging and land reclamation projects where sediment needs to be moved over long distances without continuous pumping. Your choice of a hopper dredger depends on factors like dredging depth, sediment type, and disposal requirements, offering significant advantages in efficiency and versatility compared to cutter suction dredgers.
Overview of Cutter Suction Dredgers
Cutter suction dredgers (CSDs) are highly efficient dredging vessels equipped with a rotating cutter head to loosen hard materials such as clay, rock, and compacted soil before suctioning the slurry through a pipeline. These dredgers excel in underwater excavation, especially in precise trenching and deep dredging projects, with cutter diameters ranging typically from 0.5 to 2 meters and suction pipe diameters between 300 mm and 1,200 mm. Compared to hopper dredgers, which transport sediment onboard for disposal, CSDs pump dredged material directly through pipelines, enabling continuous discharge and reduced material handling time.
Key Differences in Operational Mechanism
Hopper dredgers operate by using a suction pipe to collect sediment and store it in an onboard hopper for transport, making them ideal for deep-water dredging and transporting materials over long distances. Cutter suction dredgers use a rotating cutter head to loosen seabed material, which is then suctioned through a pipe and pumped directly to the disposal site or reclamation area, suited for precise excavation and continuous dredging. The primary difference lies in hopper dredgers' reliance on onboard storage for sediment transport versus cutter suction dredgers' direct pipeline discharge system.
Applications and Ideal Use Cases
Hopper dredgers excel in deep-sea dredging and sediment transport, making them ideal for port construction, land reclamation, and offshore mining where large volumes of material need to be transported over long distances. Cutter suction dredgers are preferred for precise excavation in shallow to medium depths, often used in riverbed maintenance, canal deepening, and pipeline trenching due to their ability to cut hard soils and rocks efficiently. The choice between hopper and cutter suction dredgers depends on project scale, sediment type, and specific environmental conditions.
Material Handling Capabilities
Hopper dredgers excel in transporting loose, unconsolidated sediments by suctioning material and storing it onboard for efficient relocation, making them ideal for deepening or widening waterways. Cutter suction dredgers use a rotating cutter head to break up harder, compacted materials like clay, rock, or compacted sand, then suction the dislodged material through a pipeline for immediate disposal or land reclamation. Your choice depends on the dredging project's material composition and the required method of material handling and transport.
Comparative Efficiency and Productivity
Hopper dredgers excel in transporting large volumes of dredged material over long distances due to their onboard storage capacity, making them highly efficient for offshore and deep-water projects. Cutter suction dredgers offer superior precision and continuous excavation capabilities, ideal for maintaining waterways and shallow water operations with steady material removal rates. Your choice depends on project scale and site conditions, where hopper dredgers maximize bulk transfer efficiency while cutter suction dredgers provide consistent productivity in sediment removal.
Environmental Considerations
Hopper dredgers generate less turbidity by transporting sediment directly onboard, minimizing sediment dispersion compared to cutter suction dredgers that agitate the seabed during suction operations. Cutter suction dredgers can cause higher suspension of fine particles, potentially impacting aquatic ecosystems and water quality. Sediment containment by hopper dredgers reduces environmental disturbance, making them preferable in sensitive marine habitats.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Hopper dredgers require higher initial investment and operational costs due to their large capacity and complex hopper systems, while cutter suction dredgers generally offer lower upfront expenses and more affordable fuel consumption. Maintenance for hopper dredgers is often more intensive and costly because of their mechanical and hydraulic systems associated with hopper operation, whereas cutter suction dredgers demand regular maintenance of cutter heads and suction pipes but typically incur lower repair costs. You should weigh the total lifecycle costs and maintenance needs of each dredger type to determine the most economical choice for your project.
Choosing the Right Dredger for Your Project
Choosing the right dredger for your project depends on factors such as the type of material to be excavated and project location. Hopper dredgers are ideal for deepwater dredging and handling loose sediments, offering high mobility and large material capacity. Cutter suction dredgers excel in excavating compacted soils or clay in shallow to medium depths, providing precision and continuous operation for infrastructure projects.
Hopper dredger vs cutter suction dredger Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com