A shaft generator converts mechanical energy from a ship's engine into electrical power, offering fuel efficiency and reducing emissions compared to diesel generators, which burn fuel directly to produce electricity and are typically used as backup power sources. Choosing the right generator depends on your energy needs, operational costs, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
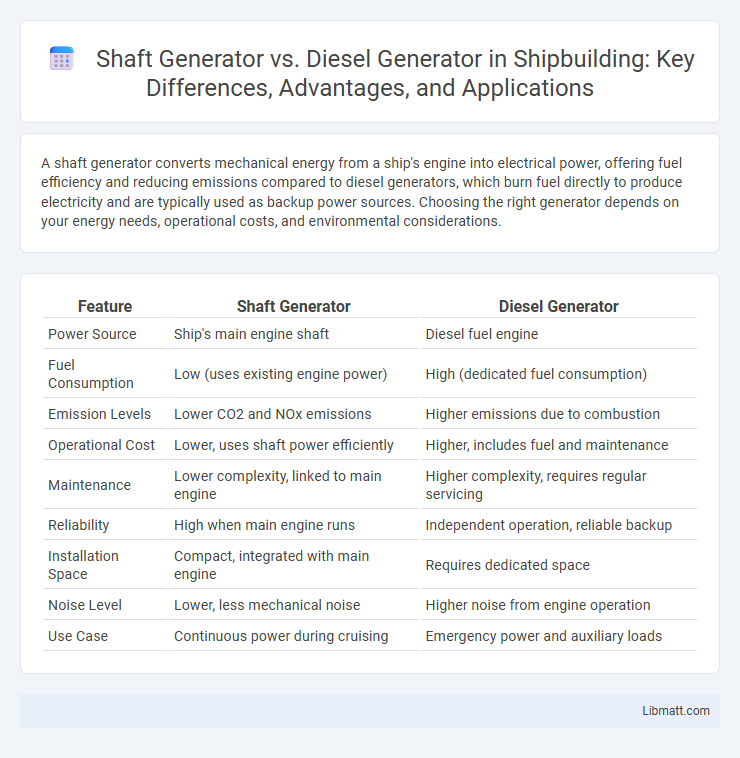
| Feature | Shaft Generator | Diesel Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Ship's main engine shaft | Diesel fuel engine |
| Fuel Consumption | Low (uses existing engine power) | High (dedicated fuel consumption) |
| Emission Levels | Lower CO2 and NOx emissions | Higher emissions due to combustion |
| Operational Cost | Lower, uses shaft power efficiently | Higher, includes fuel and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, linked to main engine | Higher complexity, requires regular servicing |
| Reliability | High when main engine runs | Independent operation, reliable backup |
| Installation Space | Compact, integrated with main engine | Requires dedicated space |
| Noise Level | Lower, less mechanical noise | Higher noise from engine operation |
| Use Case | Continuous power during cruising | Emergency power and auxiliary loads |
Introduction to Shaft and Diesel Generators
Shaft generators convert mechanical energy from a ship's main engine into electrical power, providing efficient energy generation during vessel operation and reducing fuel consumption. Diesel generators use separate engines fueled by diesel to produce electricity independently of the main engine, offering reliable power supply especially when the ship is docked or main engines are off. Shaft generators are preferred for continuous onboard power with lower emissions, while diesel generators provide essential backup and auxiliary power capabilities.
How Shaft Generators Work
Shaft generators convert mechanical energy from a ship's main engine shaft into electrical power, providing a continuous and efficient source of electricity while reducing fuel consumption. They operate by coupling a generator to the propulsion shaft, enabling electricity generation coinciding with the vessel's operational speed. Unlike diesel generators, shaft generators rely on the engine's rotation, eliminating the need for separate fuel consumption and lowering emissions during connected operations.
Diesel Generators: Basic Principle
Diesel generators operate on the principle of converting chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion, which drives an engine connected to an electrical generator. The combustion process ignites diesel fuel in the engine's cylinders, causing pistons to move and subsequently rotate the generator's rotor, producing electrical power. Diesel generators are widely used for emergency power supply and remote locations due to their reliability and efficiency in generating electricity independently of external sources.
Key Differences Between Shaft and Diesel Generators
Shaft generators utilize the mechanical energy from a ship's main engine to produce electrical power, making them more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly compared to diesel generators, which rely on internal combustion engines fueled by diesel. Diesel generators provide independent power supply, essential for standby or emergency use, with flexible deployment even when the main engine is off, whereas shaft generators depend on the propulsion system's operation. Maintenance complexity and operational costs are generally higher for diesel generators due to fuel consumption and engine wear, while shaft generators have lower emissions and operational costs but limited functionality when the vessel is stationary.
Efficiency Comparison: Shaft vs Diesel Generators
Shaft generators deliver higher efficiency by directly converting mechanical energy from the main engine into electrical power, reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to diesel generators. Diesel generators rely on fuel combustion, which results in lower overall efficiency due to energy losses during the conversion process. Choosing a shaft generator can optimize your vessel's power generation by leveraging existing propulsion energy, enhancing operational cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Shaft generators produce significantly lower emissions compared to diesel generators by utilizing the ship's main engine power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprint. Diesel generators emit higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and environmental harm. Implementing shaft generators enhances compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations on sulfur emissions and supports sustainable shipping practices.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Shaft generators integrate directly with a ship's main engine, resulting in simpler installation with fewer electrical components compared to diesel generators, which require dedicated engines and fuel systems. Maintenance for shaft generators is generally less frequent but demands specialized knowledge due to their mechanical linkage to the vessel's propulsion, whereas diesel generators require regular checks on fuel, oil, and cooling systems. Your choice depends on available space, ease of access for routine servicing, and the technical expertise of your maintenance crew.
Operational Costs and Fuel Consumption
Shaft generators leverage the ship's main engine to produce electrical power, significantly reducing operational costs and fuel consumption compared to diesel generators, which rely on separate engines running on additional fuel. Diesel generators incur higher fuel expenses and maintenance costs due to independent operation and more frequent usage of fuel oil. You can optimize your vessel's fuel efficiency and lower overall operating expenses by utilizing a shaft generator system where feasible.
Applications in the Maritime Industry
Shaft generators and diesel generators serve critical roles in the maritime industry by providing essential electrical power to vessels. Shaft generators harness mechanical energy from the ship's main engine to produce electricity efficiently during navigation, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Diesel generators supplement power needs when the main engine is off or during peak demand, ensuring your vessel's systems remain operational under all conditions.
Future Trends and Technological Developments
Shaft generators are increasingly integrated with hybrid and electric propulsion systems, enhancing energy efficiency by recovering power directly from the ship's main engine shaft. Diesel generators continue to evolve with advancements in fuel injection technology, emission reduction systems, and the adoption of alternative fuels like LNG and biodiesel to meet stricter environmental regulations. Emerging trends favor the combination of shaft generators with energy storage solutions and smart grid technologies to optimize power management and reduce operational costs on maritime vessels.
Shaft generator vs diesel generator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com