An inert gas system prevents oxidation and contamination by displacing oxygen with inert gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide, commonly used in industrial processes and storage tanks. Your choice between an inert gas system and a nitrogen blanket depends on the specific application, where nitrogen blankets are a simpler method providing a protective nitrogen layer to inhibit oxidation in storage vessels.
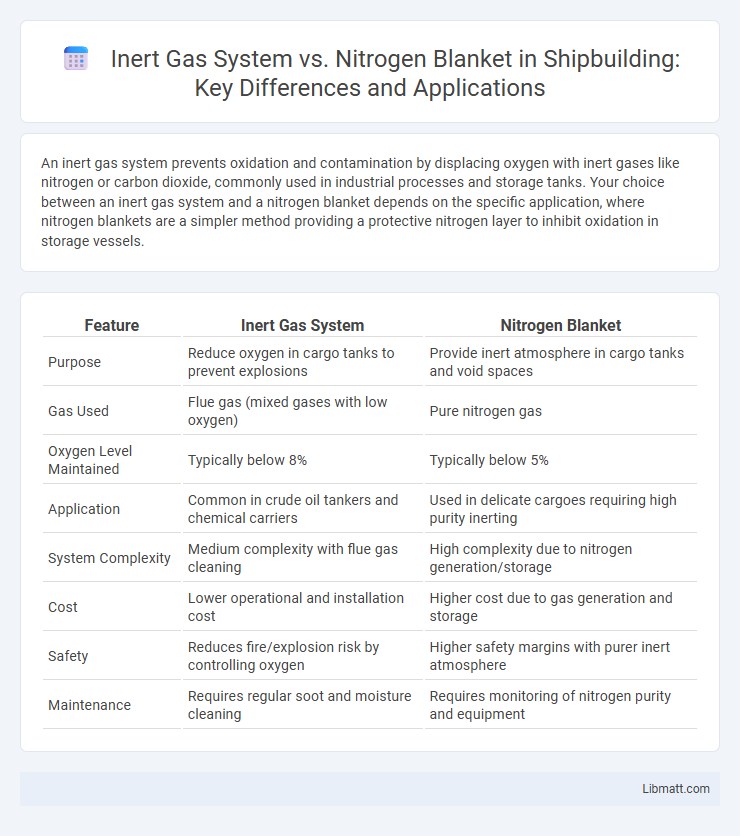
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Inert Gas System | Nitrogen Blanket |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduce oxygen in cargo tanks to prevent explosions | Provide inert atmosphere in cargo tanks and void spaces |
| Gas Used | Flue gas (mixed gases with low oxygen) | Pure nitrogen gas |
| Oxygen Level Maintained | Typically below 8% | Typically below 5% |
| Application | Common in crude oil tankers and chemical carriers | Used in delicate cargoes requiring high purity inerting |
| System Complexity | Medium complexity with flue gas cleaning | High complexity due to nitrogen generation/storage |
| Cost | Lower operational and installation cost | Higher cost due to gas generation and storage |
| Safety | Reduces fire/explosion risk by controlling oxygen | Higher safety margins with purer inert atmosphere |
| Maintenance | Requires regular soot and moisture cleaning | Requires monitoring of nitrogen purity and equipment |
Introduction to Inert Gas Systems and Nitrogen Blanketing
Inert Gas Systems use gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide to reduce oxygen levels, preventing combustion and corrosion in storage tanks and vessels. Nitrogen Blanketing specifically involves maintaining a protective nitrogen layer on liquid surfaces to avoid contamination and oxidation. Your choice between these systems depends on factors such as the stored material, safety requirements, and operational conditions.
Fundamental Principles of Inert Gas Systems
Inert gas systems operate by introducing non-reactive gases, such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, to displace oxygen and prevent combustion or oxidation in storage tanks and processing equipment. These systems rely on maintaining an oxygen concentration below the limiting oxygen concentration (LOC) to inhibit fire hazards and chemical reactions. Your choice between an inert gas system and a nitrogen blanket depends on factors like application requirements, gas availability, and desired pressure control.
What is Nitrogen Blanketing?
Nitrogen blanketing is a technique used to protect sensitive materials by filling the vapor space above liquids in storage tanks or vessels with nitrogen gas, minimizing oxidation and contamination. Unlike general inert gas systems that may use various gases, nitrogen blanketing specifically maintains a controlled nitrogen atmosphere to prevent chemical reactions and ensure product stability. Understanding how nitrogen blanketing works helps you optimize safety and preserve the quality of your stored substances.
Key Differences Between Inert Gas Systems and Nitrogen Blanketing
Inert gas systems typically use combustion or atmospheric gases such as flue gas to reduce oxygen levels in tanks, while nitrogen blanketing specifically employs pure nitrogen to create a protective layer above the liquid. Inert gas systems are commonly used in large-scale applications like oil tankers and refineries for fire prevention, whereas nitrogen blanketing is favored in chemical and pharmaceutical industries for preventing oxidation and contamination. The key differences lie in gas composition, application scale, and the targeted purpose of maintaining product integrity versus fire hazard control.
Applications in Industrial Processes
Inert gas systems and nitrogen blankets are critical in industrial processes for preventing oxidation, combustion, and contamination. Inert gas systems, often using argon or CO2, are widely applied in petrochemical refining, chemical manufacturing, and food packaging to create oxygen-free environments. Nitrogen blankets are commonly utilized in pharmaceutical production and storage tanks to maintain product integrity by displacing reactive gases and moisture.
Safety Considerations and Risk Management
Inert gas systems and nitrogen blankets both enhance safety by minimizing oxygen levels to prevent combustion in storage tanks and process vessels. Inert gas systems utilize gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide to displace oxygen, reducing explosion risks, while nitrogen blankets specifically maintain a protective nitrogen layer over flammable liquids to inhibit vapor formation. Your risk management strategy should prioritize continuous monitoring, proper system maintenance, and adherence to safety standards to ensure effective oxygen displacement and prevent hazardous atmospheres.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Maintenance
Inert gas systems typically incur higher installation costs due to complex equipment such as gas generators and control units, whereas nitrogen blanket systems have simpler setups with lower initial expenses. Maintenance for inert gas systems requires regular checks of gas purity and generator operation, leading to increased operational costs, while nitrogen blankets demand less frequent maintenance, mainly focused on gas supply and pressure monitoring. Over time, nitrogen blanket systems offer cost advantages in both installation and maintenance, especially for applications with less stringent gas quality requirements.
Efficiency and Performance Metrics
Inert gas systems provide rapid oxygen displacement with efficiency metrics such as a 95-99% reduction in oxygen levels, enhancing fire prevention and product preservation in storage tanks. Nitrogen blankets maintain a consistently low oxygen environment with performance measured by oxygen content below 5%, optimizing protection for sensitive materials. Both systems show high efficiency, but inert gas systems excel in large-scale industrial applications due to faster gas delivery and broader coverage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Inert gas systems often utilize industrial gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide to displace oxygen and prevent combustion, with nitrogen blankets specifically using nitrogen to create an oxygen-free atmosphere. Nitrogen blankets reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to inert gases like CO2, supporting sustainability by minimizing environmental footprint during storage and transportation of flammable products. Both methods enhance process safety, but nitrogen's inertness and abundance make nitrogen blankets a more eco-friendly choice for long-term environmental impact and sustainable industrial practices.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Facility
Selecting the ideal inert gas system or nitrogen blanket depends on your facility's specific safety, operational, and cost requirements. Inert gas systems, commonly using nitrogen or other gases, effectively prevent oxidation and combustion by displacing oxygen in storage tanks or pipelines. Your choice should consider factors such as application type, gas purity needs, maintenance complexity, and regulatory compliance to ensure optimal protection and efficiency.
Inert gas system vs nitrogen blanket Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com