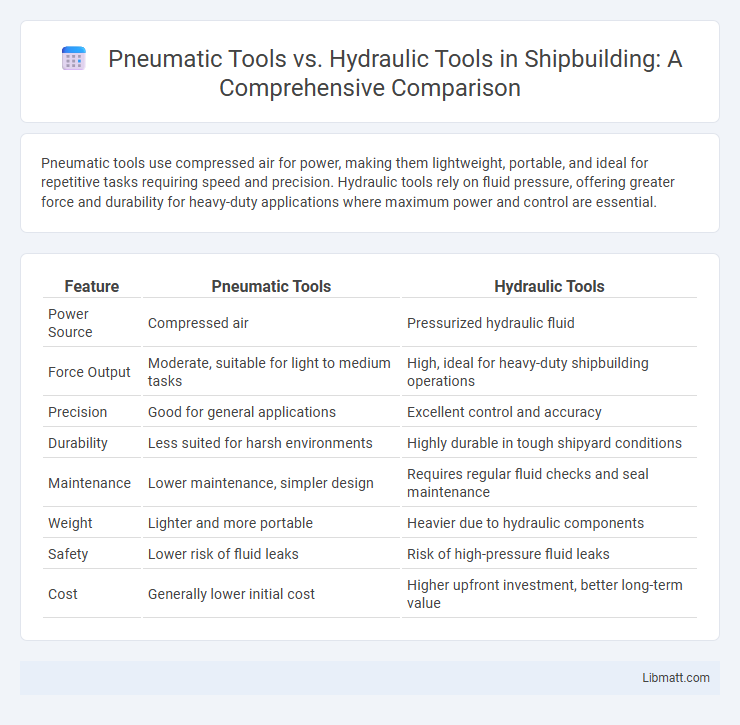
Pneumatic tools use compressed air for power, making them lightweight, portable, and ideal for repetitive tasks requiring speed and precision. Hydraulic tools rely on fluid pressure, offering greater force and durability for heavy-duty applications where maximum power and control are essential.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Tools | Hydraulic Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Pressurized hydraulic fluid |
| Force Output | Moderate, suitable for light to medium tasks | High, ideal for heavy-duty shipbuilding operations |
| Precision | Good for general applications | Excellent control and accuracy |
| Durability | Less suited for harsh environments | Highly durable in tough shipyard conditions |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, simpler design | Requires regular fluid checks and seal maintenance |
| Weight | Lighter and more portable | Heavier due to hydraulic components |
| Safety | Lower risk of fluid leaks | Risk of high-pressure fluid leaks |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment, better long-term value |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Hydraulic Tools
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, offering lightweight, portable solutions ideal for various industrial and construction applications. Hydraulic tools rely on pressurized fluid to deliver high force and precision, making them suitable for heavy-duty tasks requiring substantial power. Both systems transform energy into mechanical motion but differ in efficiency, power output, and maintenance requirements.
Core Mechanisms: How Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Tools Work
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air to generate force, driving pistons or rotary motors for tasks requiring moderate power with rapid movement. Hydraulic tools rely on pressurized fluids, typically oil, to create strong, consistent force through fluid displacement, ideal for heavy-duty applications demanding precise control and high torque. Your choice between pneumatic and hydraulic tools depends on the required force, application environment, and maintenance preferences.
Power Output and Force Comparison
Pneumatic tools generate power by compressing air, delivering moderate force suited for rapid, repetitive tasks, typically producing output pressures up to 120 psi. Hydraulic tools utilize incompressible fluid under high pressure, often exceeding 3000 psi, resulting in significantly higher force output ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring precise and sustained power. The difference in fluid compressibility and operating pressure makes hydraulic tools more powerful and capable of handling tasks with greater resistance compared to pneumatic tools.
Common Applications in Various Industries
Pneumatic tools are widely used in automotive repair, assembly lines, and construction for tasks such as tightening bolts, sanding, and cutting due to their lightweight and high-speed operation. Hydraulic tools find common applications in heavy machinery maintenance, mining, and aerospace industries where high force and precise control are essential for lifting, bending, and pressing. Both tool types are integral in manufacturing processes, with pneumatic tools favored for rapid, repetitive tasks and hydraulic tools preferred for power-intensive operations.
Efficiency and Performance Differences
Pneumatic tools excel in applications requiring high-speed operation and lightweight handling, driven by compressed air that offers consistent power output and rapid tool cycling. Hydraulic tools deliver superior force and torque due to fluid pressure, making them ideal for heavy-duty tasks demanding maximum power and precise control. Efficiency in pneumatic tools is often higher for repetitive, moderate-force tasks, while hydraulic tools provide enhanced performance in strength-intensive operations with improved load control and stability.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Pneumatic tools typically require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts and less susceptibility to fluid contamination, resulting in a longer operational lifespan under standard conditions. Hydraulic tools, while offering higher power density, demand regular inspection and replacement of seals, hoses, and fluid to prevent leaks and maintain performance, which can increase maintenance frequency. Proper upkeep significantly influences the lifespan of both tools, with pneumatic tools generally lasting longer in high-use environments when maintained appropriately.
Safety Considerations and Potential Hazards
Pneumatic tools operate using compressed air, reducing fire hazards but posing risks such as air pressure accidents and tool ejection. Hydraulic tools rely on fluid pressure, which can cause leaks leading to slips or exposure to high-pressure fluid injection injuries. Ensuring your workspace has proper maintenance, protective gear, and regular inspections minimizes safety risks associated with both pneumatic and hydraulic tools.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Expenses
Pneumatic tools generally require a lower initial investment compared to hydraulic tools due to simpler design and widespread availability. Operating expenses for pneumatic tools tend to be higher over time because of energy consumption and air compressor maintenance, whereas hydraulic tools, while more costly upfront, offer greater energy efficiency and durability, leading to reduced long-term operating costs. Evaluating the total cost of ownership must consider application requirements, usage frequency, and maintenance infrastructure to determine the most cost-effective option.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Pneumatic tools, powered by compressed air, generally consume more energy due to the inefficiencies in air compression and heat loss, whereas hydraulic tools operate with fluid pressure, offering higher energy efficiency and lower operational emissions. The environmental impact of pneumatic tools is elevated by the electricity required for air compressors, often sourced from fossil fuels, while hydraulic systems can leverage renewable energy sources more effectively due to their consistent pressure delivery and reduced energy waste. Proper maintenance and advanced technology in hydraulic tools further minimize fluid leakage and contamination, enhancing their sustainability compared to the higher noise pollution and potential air leaks associated with pneumatic tools.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Pneumatic tools offer lightweight design and rapid operation, ideal for repetitive tasks requiring speed and portability. Hydraulic tools deliver higher force and precision, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications and industrial environments. Evaluating your project's power requirements and operational environment ensures you select the most efficient tool for optimal performance.
Pneumatic tools vs hydraulic tools Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com