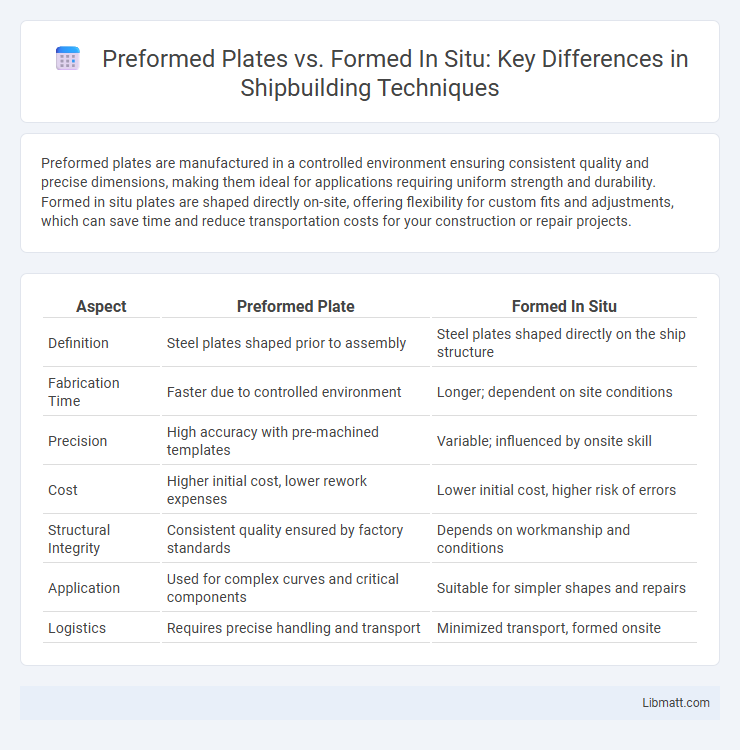
Preformed plates are manufactured in a controlled environment ensuring consistent quality and precise dimensions, making them ideal for applications requiring uniform strength and durability. Formed in situ plates are shaped directly on-site, offering flexibility for custom fits and adjustments, which can save time and reduce transportation costs for your construction or repair projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Preformed Plate | Formed In Situ |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steel plates shaped prior to assembly | Steel plates shaped directly on the ship structure |
| Fabrication Time | Faster due to controlled environment | Longer; dependent on site conditions |
| Precision | High accuracy with pre-machined templates | Variable; influenced by onsite skill |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower rework expenses | Lower initial cost, higher risk of errors |
| Structural Integrity | Consistent quality ensured by factory standards | Depends on workmanship and conditions |
| Application | Used for complex curves and critical components | Suitable for simpler shapes and repairs |
| Logistics | Requires precise handling and transport | Minimized transport, formed onsite |
Introduction to Preformed Plates and Formed In Situ
Preformed plates are prefabricated structural elements manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, ensuring consistent quality and precise dimensions. Formed in situ refers to structural components cast directly at the construction site, allowing greater flexibility to adapt to specific project requirements and complex geometries. Both methods are widely used in construction, with preformed plates offering efficiency and quality assurance, while formed in situ provides customization and on-site adaptability.
Definition and Overview of Preformed Plates
Preformed plates are prefabricated structural elements manufactured under controlled conditions to achieve precise dimensions and consistent material properties, commonly used in construction and engineering projects. These plates offer improved quality control, reduced on-site labor, and faster installation compared to formed in situ plates, which are cast or shaped directly at the construction site. Preformed plates typically exhibit enhanced durability and uniformity, making them ideal for applications requiring high strength and accuracy.
Definition and Overview of Formed In Situ Structures
Formed in situ structures are constructed directly at the site by pouring or molding materials like concrete into pre-designed molds or formwork, allowing for customized shapes and seamless integration with existing components. Unlike preformed plates, which are manufactured offsite and then transported, formed in situ elements offer greater adaptability to complex architectural designs and improved monolithic strength. Your construction project can benefit from enhanced durability and reduced joint vulnerabilities by choosing formed in situ methods over preformed plates.
Key Differences Between Preformed and In Situ Methods
Preformed plates are manufactured in controlled environments ensuring consistent quality and structural integrity, while formed in situ plates are shaped directly at the construction site, allowing for customization but potentially introducing variability. Preformed plates offer faster installation and reduced labor costs compared to in situ methods, which require on-site forming, curing, and often longer project timelines. The choice between preformed and in situ techniques depends on factors like project scale, site conditions, material specifications, and desired mechanical properties.
Advantages of Preformed Plate Systems
Preformed plate systems offer superior quality control due to factory manufacturing, ensuring consistent strength and durability compared to formed in situ plates. These systems reduce on-site labor time and minimize construction errors, leading to faster project completion and lower overall costs. Their precise dimensions and engineered properties improve structural performance and simplify installation processes in various construction applications.
Benefits of Formed In Situ Construction
Formed in situ construction offers significant benefits such as enhanced structural integrity due to the monolithic nature of the concrete, which minimizes joints and potential weak points. This method allows for greater flexibility in design and customization, adapting easily to unique site conditions and complex shapes. Your project benefits from improved durability and reduced risk of leaks compared to preformed plates, which rely on connections between separate components.
Limitations and Challenges of Preformed Plates
Preformed plates face limitations such as reduced adaptability to irregular bone defects and potential mismatches with patient-specific anatomy, leading to suboptimal fixation. Their standard sizes restrict customization, which can compromise surgical outcomes in complex fractures or anatomical variations. Material rigidity may also cause stress shielding, hindering natural bone healing compared to formed in situ plates that conform precisely to the surgical site.
Drawbacks and Issues with Formed In Situ Approach
Formed in situ plates often present challenges such as increased installation time and labor costs due to on-site molding and curing requirements. Variability in quality can occur because of inconsistent environmental conditions and human error during formation. Additionally, formed in situ methods may suffer from lower structural uniformity and reduced durability compared to preformed plates, leading to potential long-term maintenance issues.
Applications and Suitability for Different Projects
Preformed plates offer consistent quality and are ideal for projects requiring precise load-bearing elements, such as bridge decks and high-rise buildings, where uniformity and strength are critical. Formed in situ components provide greater flexibility on site, making them suitable for customized architectural projects or repairs where adaptation to existing structures is necessary. Your project's specific structural demands and site conditions will determine the most suitable approach.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
When deciding between preformed plates and formed in situ options, consider factors such as material strength, installation time, and long-term durability. Preformed plates offer consistent quality and quicker installation, while formed in situ allows for customized shaping to fit complex structures. Your choice should align with project requirements, budget constraints, and the specific mechanical demands of the application.
Preformed plate vs formed in situ Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com