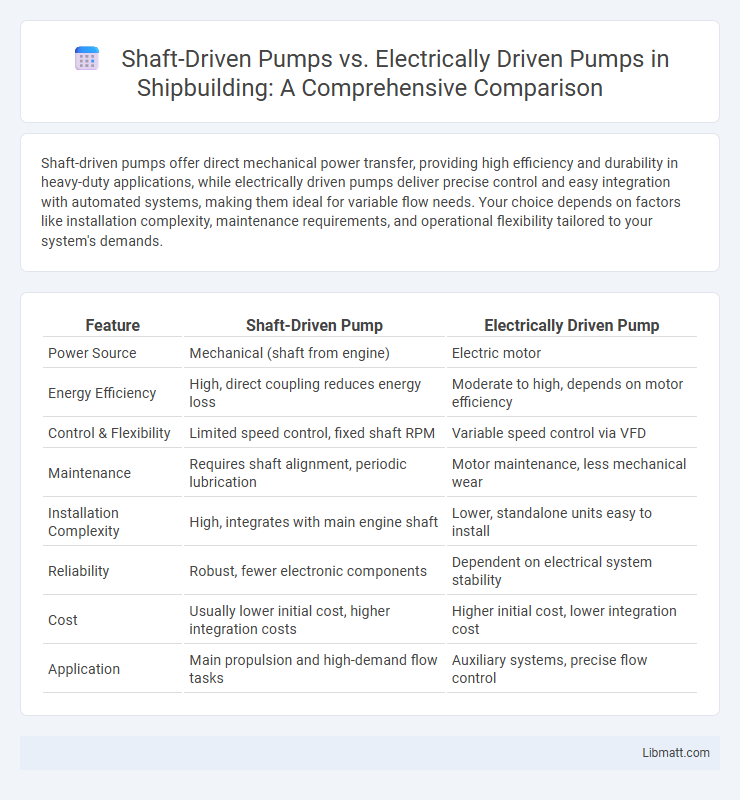
Shaft-driven pumps offer direct mechanical power transfer, providing high efficiency and durability in heavy-duty applications, while electrically driven pumps deliver precise control and easy integration with automated systems, making them ideal for variable flow needs. Your choice depends on factors like installation complexity, maintenance requirements, and operational flexibility tailored to your system's demands.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shaft-Driven Pump | Electrically Driven Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Mechanical (shaft from engine) | Electric motor |
| Energy Efficiency | High, direct coupling reduces energy loss | Moderate to high, depends on motor efficiency |
| Control & Flexibility | Limited speed control, fixed shaft RPM | Variable speed control via VFD |
| Maintenance | Requires shaft alignment, periodic lubrication | Motor maintenance, less mechanical wear |
| Installation Complexity | High, integrates with main engine shaft | Lower, standalone units easy to install |
| Reliability | Robust, fewer electronic components | Dependent on electrical system stability |
| Cost | Usually lower initial cost, higher integration costs | Higher initial cost, lower integration cost |
| Application | Main propulsion and high-demand flow tasks | Auxiliary systems, precise flow control |
Overview of Shaft-Driven and Electrically Driven Pumps
Shaft-driven pumps transmit mechanical energy from an engine or motor to the pump via a rotating shaft, offering high reliability and durability in heavy-duty industrial applications such as oil refining and water treatment. Electrically driven pumps utilize electric motors directly coupled to the pump, providing precise control, energy efficiency, and ease of automation in residential, commercial, and light industrial settings. Key performance metrics include the shaft-driven pump's robustness and torque capacity versus the electrically driven pump's variable speed capabilities and lower operational noise.
Working Principles of Shaft-Driven Pumps
Shaft-driven pumps operate by transferring mechanical energy directly from a rotating shaft connected to an engine or motor, causing the pump impeller to rotate and move fluid through the system. The shaft transmits torque, which turns the internal pump components, resulting in fluid displacement based on centrifugal or positive displacement principles. This direct mechanical linkage ensures efficient energy transfer and precise control of pump speed and flow rate in industrial applications.
How Electrically Driven Pumps Operate
Electrically driven pumps operate by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through an electric motor to create fluid movement. The motor directly powers the pump shaft, enabling precise control over flow rates and pressure through variable frequency drives or speed controllers. This design offers high efficiency, ease of automation, and reduced maintenance compared to shaft-driven pumps connected via gearboxes or belts.
Efficiency Comparison: Shaft vs Electric Pumps
Shaft-driven pumps typically offer higher mechanical efficiency due to direct energy transfer from the motor to the pump shaft, minimizing energy loss compared to electrically driven pumps that may encounter additional conversion losses. Electric pumps, however, provide precise speed control and can optimize efficiency under variable load conditions through variable frequency drives (VFDs). Understanding these efficiency dynamics helps you select the ideal pump type for energy savings and operational performance in your specific application.
Installation Requirements and Complexity
Shaft-driven pumps typically require precise mechanical alignment during installation, including coupling alignment between the pump and the driving motor, which adds complexity and demands skilled labor. Electrically driven pumps often feature integrated motor-pump designs that simplify installation by reducing the number of components and alignment steps needed. The installation of shaft-driven pumps tends to be more time-consuming and requires more detailed setup compared to electrically driven pumps, which generally offer plug-and-play capability, minimizing setup challenges.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity
Shaft-driven pumps generally require more frequent maintenance due to mechanical wear on bearings and seals, which can affect overall longevity. Electrically driven pumps benefit from fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance demands and extending operational life. Choosing the right pump for your system depends on balancing maintenance capabilities with the expected service duration.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational Expenses
Shaft-driven pumps generally incur lower initial costs due to their simpler design and fewer electrical components, making them cost-effective for long-term use in industries with existing power systems. Electrically driven pumps often require higher upfront investment due to motors and control systems but provide greater energy efficiency, leading to reduced operational expenses over time. Maintenance costs for shaft-driven pumps tend to be lower, while electrically driven pumps may demand specialized servicing and can benefit from automation, impacting overall lifecycle costs.
Performance in Different Industrial Applications
Shaft-driven pumps excel in high-pressure, continuous-operation industrial applications such as oil refineries and chemical plants due to their robust mechanical efficiency and low maintenance requirements. Electrically driven pumps offer greater flexibility and precise control, making them ideal for variable flow processes in water treatment and HVAC systems. Performance differences hinge on factors like energy consumption, responsiveness, and suitability for specific fluid types or operational conditions.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Shaft-driven pumps generally exhibit higher mechanical efficiency with lower energy loss compared to electrically driven pumps, resulting in reduced overall energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint. Electrically driven pumps often rely on grid electricity, which may come from non-renewable sources, increasing their environmental impact unless paired with green energy solutions. Selecting shaft-driven pumps can optimize energy use in applications where mechanical energy is readily available, thereby minimizing environmental harm.
Choosing the Right Pump for Your Needs
Shaft-driven pumps offer high durability and are ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring consistent torque and reliability. Electrically driven pumps provide greater energy efficiency and precise speed control, making them suitable for variable flow rates and automated systems. Evaluate your specific operational requirements, including maintenance capabilities and power availability, to select the most efficient and cost-effective pump for your needs.
Shaft-driven pump vs electrically driven pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com