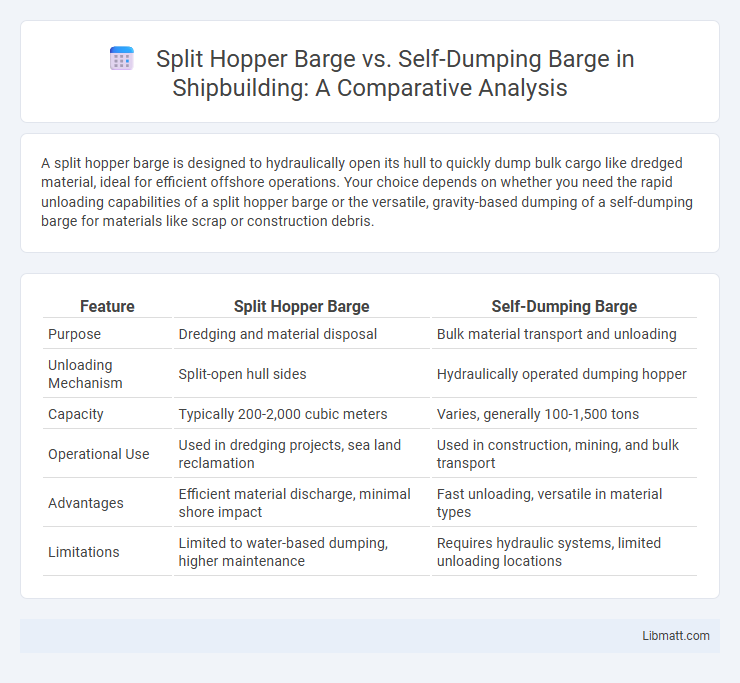
A split hopper barge is designed to hydraulically open its hull to quickly dump bulk cargo like dredged material, ideal for efficient offshore operations. Your choice depends on whether you need the rapid unloading capabilities of a split hopper barge or the versatile, gravity-based dumping of a self-dumping barge for materials like scrap or construction debris.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Split Hopper Barge | Self-Dumping Barge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Dredging and material disposal | Bulk material transport and unloading |
| Unloading Mechanism | Split-open hull sides | Hydraulically operated dumping hopper |
| Capacity | Typically 200-2,000 cubic meters | Varies, generally 100-1,500 tons |
| Operational Use | Used in dredging projects, sea land reclamation | Used in construction, mining, and bulk transport |
| Advantages | Efficient material discharge, minimal shore impact | Fast unloading, versatile in material types |
| Limitations | Limited to water-based dumping, higher maintenance | Requires hydraulic systems, limited unloading locations |
Overview of Split Hopper Barges and Self-Dumping Barges
Split hopper barges feature a clam-shell bottom that splits open to efficiently deposit bulk materials such as dredged sediment or construction debris into water bodies, optimizing precise unloading in marine operations. Self-dumping barges are designed with a hinged mechanism allowing for quick tipping and automatic dumping of cargo like scrap metal and waste, enhancing productivity in industrial and construction environments. The distinct operational mechanisms of split hopper and self-dumping barges cater to specialized tasks, with split hoppers excelling in controlled underwater material release and self-dumpers optimizing rapid land-based material discharge.
Design and Structural Differences
Split hopper barges feature a unique hinged bottom design that allows the two halves of the hull to open and release cargo directly into the water, optimizing sediment disposal and dredging operations. Self-dumping barges employ a hydraulic tilting mechanism that lifts the entire barge bed to efficiently unload bulk materials onto docks or shorelines without external assistance. Your choice between these barges depends on operational needs, with split hopper barges offering precision underwater dumping, while self-dumping barges provide versatile tilt-based unloading for diverse cargo types.
Operational Mechanisms Explained
Split hopper barges operate by opening their two side hulls inward or outward, allowing bulk materials like dredged sediment or aggregate to be discharged directly into the water or onto a designated site with precision. Self-dumping barges utilize a hydraulic lifting mechanism that tilts the entire hopper to one side or the rear, enabling rapid unloading of heavy loads such as construction debris or waste without manual intervention. Understanding these operational mechanisms helps you select the ideal barge for efficient material handling in marine or construction environments.
Load Capacity and Cargo Handling
Split hopper barges offer specialized load capacity management by allowing bulk materials to be unloaded through split hull sections that open, enabling efficient and rapid cargo handling ideal for dredging and bulk material transport. Self-dumping barges prioritize ease of cargo discharge by using a tipping mechanism to unload materials such as construction debris or scrap, with load capacities typically optimized for heavier, dense materials. While split hopper barges provide precise control over bulk cargo distribution and discharge, self-dumping barges excel in handling mixed or bulky waste with simplified unloading, impacting operational efficiency based on cargo type and project requirements.
Efficiency in Dredging Operations
Split hopper barges offer enhanced efficiency in dredging operations by allowing precise, controlled dumping of dredged material through their split hull design, minimizing spillage and environmental impact. Self-dumping barges improve operational speed by automatically releasing cargo through a hinged hull or side, reducing unloading time and labor costs on-site. Your choice depends on project needs, with split hopper barges excelling in accuracy and environmental control, while self-dumping barges prioritize quick, straightforward material discharge.
Advantages of Split Hopper Barges
Split hopper barges offer precise cargo discharge by using a clam-shell mechanism that splits the hull for rapid unloading, ideal for dredging and construction projects. Their design minimizes spillage and environmental impact, ensuring efficient sediment management and offshore material transport. These barges also reduce turnaround time compared to self-dumping barges, enhancing operational productivity in marine work.
Benefits of Self-Dumping Barges
Self-dumping barges provide efficient material handling by automatically releasing loads, reducing manual labor and increasing operational safety on construction sites. Their robust design supports heavy payloads and quick unloading, making them ideal for waste management and debris removal in challenging environments. You benefit from faster turnaround times and improved productivity compared to split hopper barges, which require more complex discharge mechanisms.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Split hopper barges excel in handling dredged materials and bulk cargoes in marine construction and port maintenance projects, efficiently facilitating sediment transport and disposal. Self-dumping barges are primarily used in industrial and construction settings for managing heavy waste, scrap materials, and debris, offering quick unloading through their hydraulic or gravity-assisted dumping mechanisms. Your project requirements determine the optimal barge type, ensuring effective handling of either marine sediments or onsite bulk waste.
Cost Considerations and Maintenance
Split hopper barges generally incur higher initial costs due to their complex design and specialized unloading mechanism, while self-dumping barges offer a more budget-friendly option with simpler construction. Maintenance for split hopper barges demands regular inspections and repairs of hydraulic systems and hopper doors, increasing operational expenses. Your choice depends on balancing upfront investment and ongoing maintenance to optimize cost efficiency for your project needs.
Choosing the Right Barge for Your Project
Choosing the right barge for your project depends on material type and unloading efficiency; split hopper barges offer precise control for sediment or dredged material deposition, while self-dumping barges excel in rapid unloading of bulk materials like gravel or debris. Your decision should consider site conditions and project timeline, as split hopper barges are suitable for controlled dumping in aquatic environments, whereas self-dumping barges provide quicker discharge on land or near shores. Evaluating these factors ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness for your marine or construction operations.
Split hopper barge vs self-dumping barge Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com