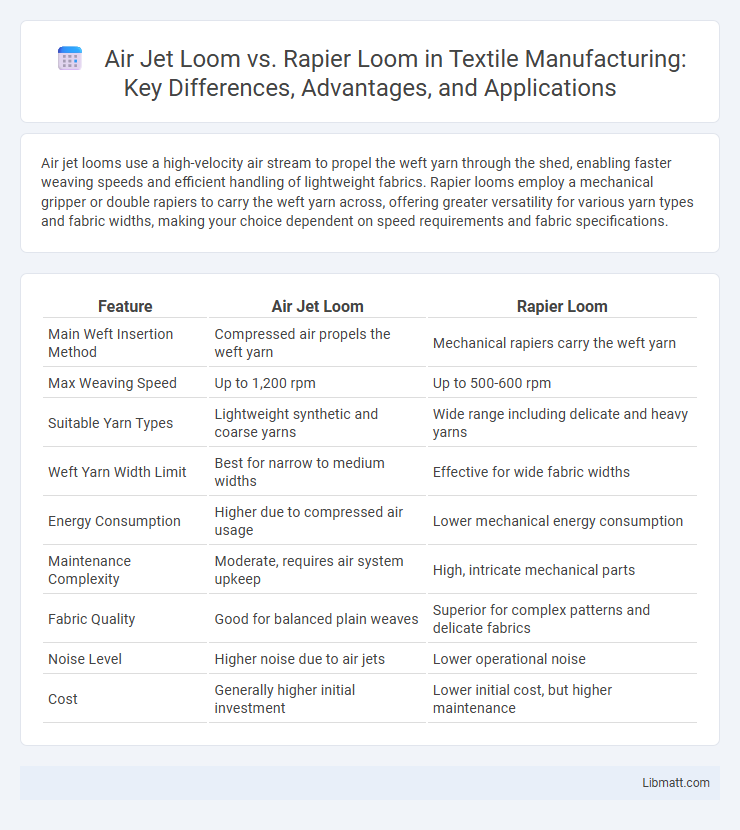
Air jet looms use a high-velocity air stream to propel the weft yarn through the shed, enabling faster weaving speeds and efficient handling of lightweight fabrics. Rapier looms employ a mechanical gripper or double rapiers to carry the weft yarn across, offering greater versatility for various yarn types and fabric widths, making your choice dependent on speed requirements and fabric specifications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Air Jet Loom | Rapier Loom |
|---|---|---|
| Main Weft Insertion Method | Compressed air propels the weft yarn | Mechanical rapiers carry the weft yarn |
| Max Weaving Speed | Up to 1,200 rpm | Up to 500-600 rpm |
| Suitable Yarn Types | Lightweight synthetic and coarse yarns | Wide range including delicate and heavy yarns |
| Weft Yarn Width Limit | Best for narrow to medium widths | Effective for wide fabric widths |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to compressed air usage | Lower mechanical energy consumption |
| Maintenance Complexity | Moderate, requires air system upkeep | High, intricate mechanical parts |
| Fabric Quality | Good for balanced plain weaves | Superior for complex patterns and delicate fabrics |
| Noise Level | Higher noise due to air jets | Lower operational noise |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Lower initial cost, but higher maintenance |
Introduction to Air Jet Looms and Rapier Looms
Air jet looms and rapier looms represent two advanced weaving technologies used in textile manufacturing. Air jet looms utilize high-speed air jets to propel the weft yarn across the warp, offering rapid production for medium to high-density fabrics. Rapier looms employ a mechanical rapier that carries the weft yarn through the shed, providing versatility in handling a wide range of yarn types and fabric structures.
Basic Working Principles
Air jet looms use a powerful jet of compressed air to propel the weft yarn through the shed, allowing for high-speed weaving and minimal yarn tension. Rapier looms employ a mechanical rapier arm or gripper to carry the weft yarn across the loom, providing precise control over different yarn types and fabric patterns. Understanding these basic working principles enables you to select the optimal weaving technology tailored to your production needs and fabric specifications.
Key Differences in Mechanism
Air jet looms use a powerful blast of air to propel the weft yarn through the shed, offering high-speed weaving suited for lightweight fabrics. Rapier looms employ a mechanical gripper system where a rapier arm carries the weft yarn across the width of the fabric, allowing for precise control over a wide range of yarn types. The air jet mechanism excels in speed but can be limited by yarn type, while rapier looms provide versatility for heavier and delicate yarns with moderate speed.
Yarn and Fabric Compatibility
Air jet looms excel in weaving fine and medium yarns, particularly cotton, polyester, and blended fabrics, due to their high-speed and gentle yarn handling, which minimizes yarn breakage and produces high-quality, lightweight textiles. Rapier looms accommodate a wider range of yarn types, including coarse, delicate, and textured yarns such as wool, silk, and technical fibers, offering superior fabric versatility and the ability to handle complex weaves with varying yarn thicknesses. This adaptability in yarn and fabric compatibility makes rapier looms ideal for diverse textile applications, while air jet looms are preferred for fast production of uniform, smooth fabrics.
Speed and Productivity Comparison
Air jet looms achieve weaving speeds of up to 1,200 picks per minute, outperforming rapier looms that typically operate between 300 and 600 picks per minute. The high-speed air jet technology significantly enhances productivity, especially in lightweight and medium-weight fabric manufacturing. Although rapier looms offer versatility in fabric types, air jet looms provide superior efficiency and throughput in mass production environments.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Air jet looms consume significantly more energy compared to rapier looms due to the high air pressure required to propel the weft yarn across the shed. Rapier looms demonstrate greater energy efficiency by using mechanical means to insert the weft, reducing overall power demand. Your textile production benefits from choosing rapier looms when aiming for lower energy costs and higher operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Air jet looms typically incur higher maintenance costs due to their complex pneumatic systems requiring regular servicing and precise calibration. Rapier looms offer lower operational expenses as their mechanical components are more durable and easier to maintain, reducing downtime and repair costs. Energy consumption is generally higher in air jet looms, further increasing operational costs compared to the more energy-efficient rapier looms.
Fabric Quality and Versatility
Air jet looms produce fabrics with a smooth surface and reduced yarn tension, enhancing fabric quality for lightweight and fine textiles. Rapier looms excel in versatility, handling a wide range of yarn types and complex patterns, making them suitable for diverse fabric constructions. Your choice depends on prioritizing superior fabric finish or adaptability to various weaving requirements.
Applications in Textile Industry
Air jet looms excel in producing lightweight fabrics such as polyester and nylon, making them ideal for technical textiles, sportswear, and home furnishings due to their high-speed weaving and low energy consumption. Rapier looms offer versatility in handling a wide range of yarn types and fabric densities, suitable for denim, upholstery, and complex patterned textiles that require precise control and high fabric quality. Textile manufacturers select air jet looms for mass production of smooth, fine fabrics, while rapier looms serve specialized applications demanding diverse materials and intricate weaves.
Choosing the Right Loom: Factors to Consider
When choosing between an air jet loom and a rapier loom, consider fabric type, production speed, and energy efficiency. Air jet looms excel in weaving medium to heavy fabrics at high speeds with lower maintenance costs but require consistent compressed air supply. Rapier looms offer versatility for a wide range of yarn types and complex patterns, making them ideal for lightweight or delicate fabrics despite slower speeds and higher initial investment.
Air jet loom vs Rapier loom Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com