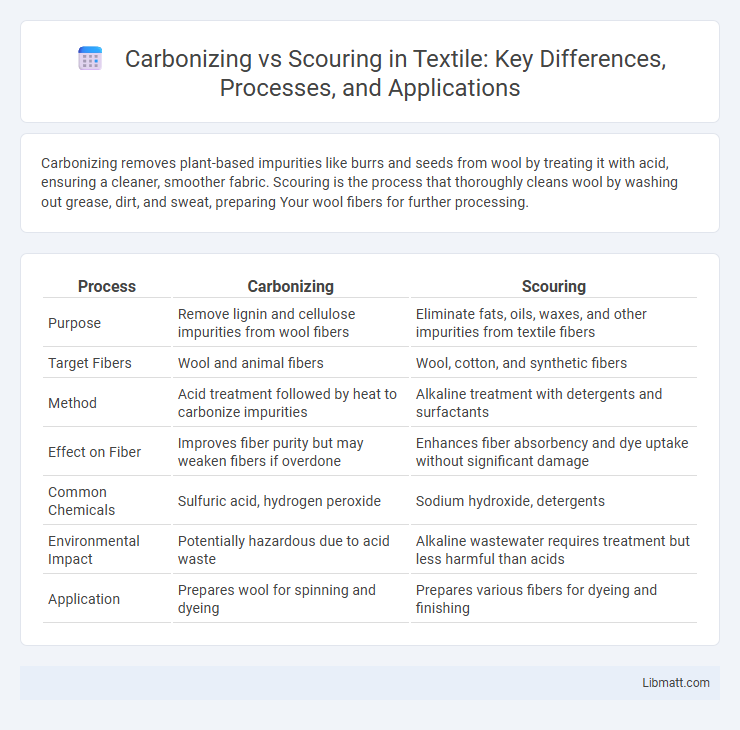
Carbonizing removes plant-based impurities like burrs and seeds from wool by treating it with acid, ensuring a cleaner, smoother fabric. Scouring is the process that thoroughly cleans wool by washing out grease, dirt, and sweat, preparing Your wool fibers for further processing.
Table of Comparison
| Process | Carbonizing | Scouring |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remove lignin and cellulose impurities from wool fibers | Eliminate fats, oils, waxes, and other impurities from textile fibers |
| Target Fibers | Wool and animal fibers | Wool, cotton, and synthetic fibers |
| Method | Acid treatment followed by heat to carbonize impurities | Alkaline treatment with detergents and surfactants |
| Effect on Fiber | Improves fiber purity but may weaken fibers if overdone | Enhances fiber absorbency and dye uptake without significant damage |
| Common Chemicals | Sulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide | Sodium hydroxide, detergents |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially hazardous due to acid waste | Alkaline wastewater requires treatment but less harmful than acids |
| Application | Prepares wool for spinning and dyeing | Prepares various fibers for dyeing and finishing |
Introduction to Carbonizing and Scouring
Carbonizing removes plant-based impurities such as seeds and leaves from wool by treating fibers with acid, enhancing fabric quality and smoothness. Scouring cleans wool by eliminating grease, dirt, and suint through detergent and water washing, ensuring fiber purity for further processing. Your textile production benefits from choosing the appropriate method to optimize fiber cleanliness and durability.
Understanding Carbonizing: Definition and Purpose
Carbonizing is a textile processing technique that removes plant matter from wool fibers by treating them with mild acids, primarily sulfuric acid. This process enhances the quality and appearance of wool by eliminating impurities like vegetable fibers that scouring alone cannot remove. Carbonizing improves fiber cleanliness, preparing wool for subsequent dyeing and finishing stages.
What is Scouring in Textile Processing?
Scouring in textile processing is a crucial wet treatment that removes natural impurities like wax, pectin, and oils from fibers, enhancing fabric absorbency and dye affinity. Unlike carbonizing, which targets and destroys vegetable matter in wool through acid treatment, scouring is primarily aimed at cleaning and preparing cotton, linen, or synthetic fibers for subsequent processing stages. Effective scouring improves fabric quality by ensuring uniform dyeing and finishing, directly impacting the textile's final appearance and performance.
Key Differences Between Carbonizing and Scouring
Carbonizing involves the removal of plant matter, such as leaves and seeds, from wool fibers using acid treatment, enhancing fiber purity and softness. Scouring, on the other hand, is a washing process that eliminates grease, dirt, and impurities from raw wool, ensuring cleanliness before further processing. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right method to improve fiber quality in textile production.
Step-by-Step Carbonizing Process
The step-by-step carbonizing process begins with treating the textile fibers using a strong acid, typically sulfuric acid, which targets and dissolves plant-based impurities like seeds and leaves embedded in raw fibers such as cotton or wool. After soaking, the fibers undergo thorough washing to eliminate residual acid and debris, ensuring the fabric is clean and free from organic contaminants. This process enhances fiber purity and quality, setting the stage for subsequent textile treatments like scouring to achieve the desired softness and absorbency in Your fabric.
Scouring Process Explained
Scouring is a vital textile preparation process that removes impurities such as oils, waxes, and natural fats from fibers to enhance fabric absorbency and dye uptake. This chemical treatment often involves alkaline solutions, typically sodium hydroxide, which breaks down non-cellulosic substances without damaging the fibers. Your fabrics become cleaner and more receptive to subsequent treatments, ensuring higher quality and durability in the finished textile.
Materials Suitable for Carbonizing and Scouring
Carbonizing is most effective for removing coarse vegetable matter like seed hairs and plant debris from wool and other animal fibers, making it suitable for materials with high levels of plant contamination. Scouring, on the other hand, is ideal for cleaning fine animal fibers such as wool, alpaca, and cashmere by removing grease, dirt, and sweat without harsh chemical treatment. Your choice depends on the fiber type and level of impurities; carbonizing targets fibrous contaminants, while scouring ensures a gentle, thorough cleanse of delicate fibers.
Environmental Impact: Carbonizing vs Scouring
Carbonizing and scouring are two textile processing methods with distinct environmental impacts. Carbonizing uses acidic chemicals to remove plant matter from wool, generating hazardous waste that requires careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination. Scouring involves emulsifying oils and impurities with detergents and alkalis, producing wastewater that demands effective treatment to minimize water pollution and reduce chemical load on ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between carbonizing and scouring depends on the fiber type, contaminant nature, and desired fabric quality. Carbonizing is effective for removing lignin and plant-based impurities from wool, enhancing softness and dye uptake, while scouring uses alkaline solutions to eliminate grease, oils, and dirt from various fibers. Your decision should weigh fabric sensitivity, environmental impact, and end-use requirements to select the best cleaning method.
Future Trends in Textile Cleaning Technologies
Future trends in textile cleaning technologies emphasize eco-friendly carbonizing processes that selectively remove impurities like plant matter without harmful chemicals, contrasting with traditional scouring methods relying on alkaline solutions. Advancements in enzymatic and bio-based carbonizing techniques enhance fabric quality while significantly reducing water and energy consumption. Integration of smart sensors and AI-driven automation in textile cleaning systems promises precise contaminant detection and optimized cleaning cycles, aligning with sustainability goals.
Carbonizing vs Scouring Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com