Disperse printing uses disperse dyes primarily on polyester fabrics to produce vibrant, durable colors through heat transfer, while pigment printing applies pigment particles that sit on the fabric's surface, suitable for a wider range of materials but often offering less colorfastness. Understanding the differences helps you choose the best printing method for your fabric type and desired durability.
Table of Comparison
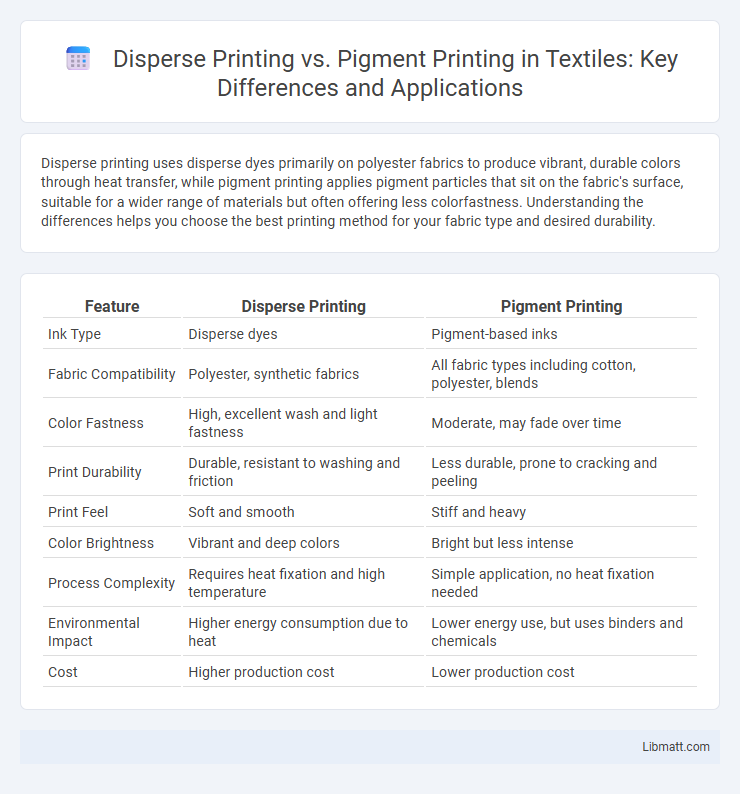
| Feature | Disperse Printing | Pigment Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Type | Disperse dyes | Pigment-based inks |
| Fabric Compatibility | Polyester, synthetic fabrics | All fabric types including cotton, polyester, blends |
| Color Fastness | High, excellent wash and light fastness | Moderate, may fade over time |
| Print Durability | Durable, resistant to washing and friction | Less durable, prone to cracking and peeling |
| Print Feel | Soft and smooth | Stiff and heavy |
| Color Brightness | Vibrant and deep colors | Bright but less intense |
| Process Complexity | Requires heat fixation and high temperature | Simple application, no heat fixation needed |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy consumption due to heat | Lower energy use, but uses binders and chemicals |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Disperse and Pigment Printing
Disperse printing uses disperse dyes that bond with synthetic fibers like polyester through high-temperature sublimation, delivering vibrant, long-lasting colors ideal for activewear and polyester fabrics. Pigment printing applies insoluble pigment particles fixed on fabric surfaces via binders, suitable for various textiles including cotton and polyester blends, offering sharp patterns and excellent colorfastness. Both methods cater to different fabric types and design requirements, influencing the choice of printing technique based on material compatibility and durability needs.
Definition and Principles of Disperse Printing
Disperse printing involves transferring dye in a finely ground, water-insoluble form onto synthetic fibers such as polyester through heat and pressure, where the dye sublimates and fixes into the fabric, ensuring vibrant and durable coloration. This method relies on disperse dyes that penetrate the fiber structure, creating a strong bond between the dye and the polymer molecules, which results in high wash and light fastness. Unlike pigment printing, which uses insoluble pigments sitting on the fabric surface, disperse printing achieves deeper color penetration and enhanced print sharpness on synthetic textiles.
Definition and Principles of Pigment Printing
Pigment printing involves applying color pigments directly onto the fabric's surface, using a binding agent to hold the pigments in place without penetrating the fibers. Unlike disperse printing, which relies on dye diffusion into synthetic fibers, pigment printing offers excellent colorfastness and is suitable for a wide range of textiles, including cotton and polyester blends. Your choice of pigment printing ensures vibrant, durable designs that resist fading and maintain sharpness after repeated washes.
Key Differences Between Disperse and Pigment Printing
Disperse printing uses water-based dyes that bond with synthetic fibers like polyester through heat transfer, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors with excellent wash fastness. Pigment printing applies color pigments that sit on the fabric surface and require binders, suitable for a wide range of fibers but often less colorfast and more prone to fading. Key differences include the bonding method, fiber compatibility, color vibrancy, and durability of the print on various textile materials.
Fabric Compatibility: Disperse vs Pigment Printing
Disperse printing is primarily compatible with synthetic fabrics such as polyester and nylon, where the disperse dyes penetrate the fibers for vibrant, long-lasting color. Pigment printing is versatile across a wider range of fabrics, including cotton, silk, and blends, as pigments sit on the fabric surface and bind through a binder. Fabric compatibility directly influences the print durability and wash fastness in both disperse and pigment printing techniques.
Color Vibrancy and Fastness Comparison
Disperse printing excels in color vibrancy on synthetic fibers like polyester, producing bright, vivid hues due to its dye sublimation process. Pigment printing offers superior fastness on a variety of fabrics, with pigments sitting on the surface and resisting washing, light, and abrasion better than disperse dyes. While disperse prints may fade faster over time, pigment prints provide more durable, long-lasting color retention in everyday use.
Process Workflow and Environmental Impact
Disperse printing uses sublimation inks that transfer dye into synthetic fibers through heat, offering vibrant colors and soft hand feel, while pigment printing applies pigment particles on fabric surfaces and requires a binding agent for adhesion. The disperse printing process generates less wastewater since dyes bond directly with fibers, reducing environmental contaminants, whereas pigment printing often involves additional water-intensive cleaning steps and chemical binders that can increase eco-toxicity. Choosing your printing method affects both production efficiency and environmental footprint, with disperse printing generally being more sustainable for polyester materials.
Cost Analysis: Disperse vs Pigment Printing
Disperse printing generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized sublimation dyes and heat transfer equipment, but offers lower ongoing expenses for polyester fabrics through efficient dye usage and vibrant color retention. Pigment printing demands less expensive inks and simpler machinery but may involve higher maintenance and fabric pretreatment costs, particularly on cotton and mixed textiles. Evaluating long-term profitability shows disperse printing as more cost-effective for polyester, while pigment printing suits diverse fabrics with moderate initial investment.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Disperse printing excels in dyeing synthetic fibers like polyester due to its ability to produce vibrant, long-lasting colors with excellent wash fastness, making it ideal for sportswear and fashion textiles. Pigment printing offers versatility across various fabric types, including cotton and blends, with advantages in surface color application and rapid production cycles favored for home textiles and casual wear. Understanding your textile's fiber composition helps determine the best printing method to achieve desired durability and color intensity in your applications.
Choosing the Right Printing Method
Choosing the right printing method depends on the fabric type and desired print durability. Disperse printing excels on synthetic fibers like polyester, offering vibrant colors and excellent wash fastness, while pigment printing works well on natural fabrics such as cotton, providing soft hand feel and versatility. Understanding your material and end-use ensures you select the most effective technique for your project's longevity and visual appeal.
Disperse Printing vs Pigment Printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com