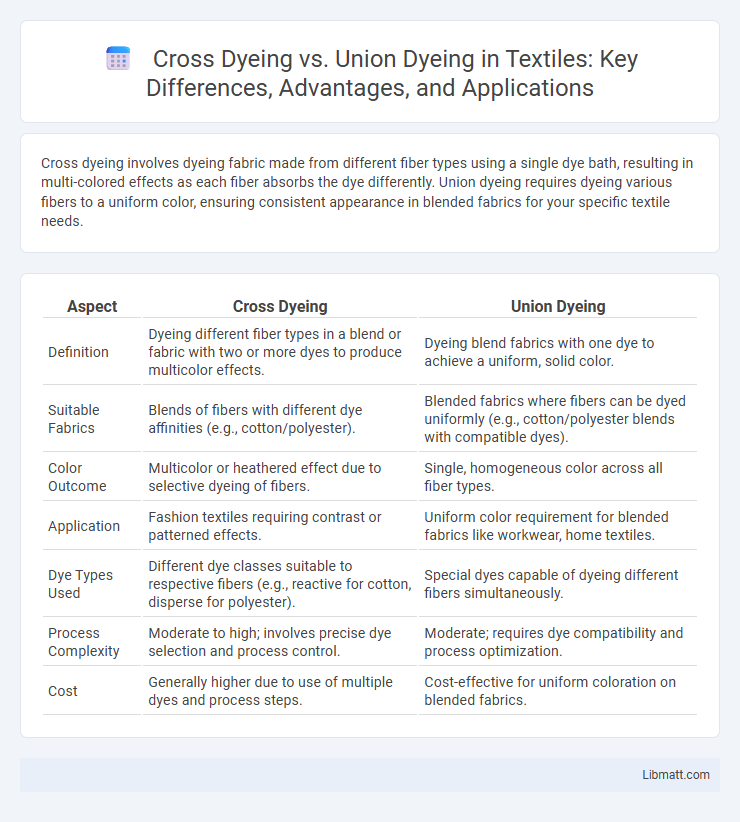
Cross dyeing involves dyeing fabric made from different fiber types using a single dye bath, resulting in multi-colored effects as each fiber absorbs the dye differently. Union dyeing requires dyeing various fibers to a uniform color, ensuring consistent appearance in blended fabrics for your specific textile needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cross Dyeing | Union Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing different fiber types in a blend or fabric with two or more dyes to produce multicolor effects. | Dyeing blend fabrics with one dye to achieve a uniform, solid color. |
| Suitable Fabrics | Blends of fibers with different dye affinities (e.g., cotton/polyester). | Blended fabrics where fibers can be dyed uniformly (e.g., cotton/polyester blends with compatible dyes). |
| Color Outcome | Multicolor or heathered effect due to selective dyeing of fibers. | Single, homogeneous color across all fiber types. |
| Application | Fashion textiles requiring contrast or patterned effects. | Uniform color requirement for blended fabrics like workwear, home textiles. |
| Dye Types Used | Different dye classes suitable to respective fibers (e.g., reactive for cotton, disperse for polyester). | Special dyes capable of dyeing different fibers simultaneously. |
| Process Complexity | Moderate to high; involves precise dye selection and process control. | Moderate; requires dye compatibility and process optimization. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to use of multiple dyes and process steps. | Cost-effective for uniform coloration on blended fabrics. |
Introduction to Cross Dyeing and Union Dyeing
Cross dyeing and union dyeing are textile coloring techniques used to achieve unique fabric appearances by dyeing different fiber types in a single piece. Cross dyeing involves applying different dyes that selectively bond to each fiber type, creating a multicolored effect, while union dyeing uses a single dyebath with a dye capable of coloring all fiber blends uniformly. Understanding these methods allows you to select the optimal dyeing process for mixed-fiber textiles, enhancing fabric aesthetics and performance.
Key Differences Between Cross Dyeing and Union Dyeing
Cross dyeing involves dyeing fabric made from two different fiber types with two different dyes, resulting in a multicolored effect, while union dyeing uses a single dye bath to color blended fibers uniformly. Cross dyeing emphasizes color contrast on mixed-fiber textiles by exploiting the varied dye affinities, whereas union dyeing aims for a consistent, uniform color across all fiber components. The key differences lie in fiber composition compatibility, dye selection, and the desired aesthetic outcome, with cross dyeing offering selective coloration and union dyeing providing color unity.
How Cross Dyeing Works
Cross dyeing works by dyeing a fabric made from two or more types of fibers with different dye classes, allowing selective coloration in one process. Each fiber type absorbs a different dye, resulting in a multicolored or patterned effect without additional printing steps. This method optimizes your textile production by delivering unique color contrasts using a single dye bath.
How Union Dyeing Works
Union dyeing works by using a special dye formulation that simultaneously colors different fibers in a fabric to achieve a uniform shade. It involves selecting compatible dyes that bond effectively with each fiber type, ensuring consistent color on blends such as cotton-polyester or wool-nylon. By optimizing dye uptake processes and chemical compatibility, union dyeing offers a seamless finish that enhances the overall appearance of your multi-fiber textiles.
Advantages of Cross Dyeing
Cross dyeing offers significant advantages by enabling different fiber types within a blended fabric to be dyed in multiple colors using a single dye bath, resulting in unique, multi-tonal effects and enhanced design versatility. It enhances production efficiency by reducing processing time and energy consumption compared to separate dyeing methods, while allowing cost-effective customization for complex fabric blends. The technique improves colorfastness and fabric quality by using compatible dyes that selectively adhere to specific fibers, ensuring vibrant and durable coloration.
Advantages of Union Dyeing
Union dyeing offers distinct advantages by enabling uniform coloration of blended fabrics made from different fiber types, such as cotton and polyester, in a single dyeing process. This method reduces production time and costs while delivering consistent, vibrant colors, improving fabric quality and customer satisfaction. Your textile products will benefit from enhanced color fastness and a more efficient manufacturing workflow with union dyeing.
Common Applications of Cross Dyeing
Cross dyeing is commonly applied in the textile industry to create multicolored fabrics using blended fibers, such as cotton-polyester or wool-silk blends. It is particularly favored for fashion apparel, home textiles, and upholstery where visually appealing patterns and color contrasts are desired without resorting to printing. This technique enhances fabric design versatility by selectively dyeing different fiber components in a single process.
Common Applications of Union Dyeing
Union dyeing is commonly applied in the textile industry for fabrics composed of blended fibers such as cotton-polyester or wool-nylon, where achieving a uniform color across different fiber types is essential. This method is extensively used in apparel manufacturing, including activewear, workwear, and fashion garments, to ensure consistent coloration and enhanced fabric aesthetics. Union dyeing also plays a critical role in home textiles like upholstery, curtains, and bed linens, where colorfastness and durability are prioritized.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Dyeing Methods
Selecting between cross dyeing and union dyeing depends on fabric composition, desired color effects, and production efficiency. Cross dyeing is ideal for blended fabrics with different fibers, allowing distinct colors on each fiber for complex patterns, while union dyeing offers uniform coloration across fiber blends. You should also consider cost implications, colorfastness requirements, and end-use applications to determine the best dyeing method for your textile project.
Future Trends in Textile Dyeing Techniques
Future trends in textile dyeing techniques emphasize sustainability and innovation, with cross dyeing and union dyeing evolving to meet eco-friendly demands. Cross dyeing enhances multi-fiber fabric coloration by using selective dyes, reducing water and chemical usage, while union dyeing achieves uniform coloration on blended fabrics, optimizing energy efficiency. Your textile production can benefit from these advanced dyeing methods through improved fabric aesthetics and lower environmental impact, aligning with industry shifts towards sustainable manufacturing.
Cross dyeing vs Union dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com