Differential dyeing involves coloring different fibers or yarns in a fabric separately to create patterns or color contrasts, while union dyeing dye blends all fibers evenly in a fabric to produce a uniform color. Your choice depends on whether you want distinct color effects or a consistent, single-tone finish.
Table of Comparison
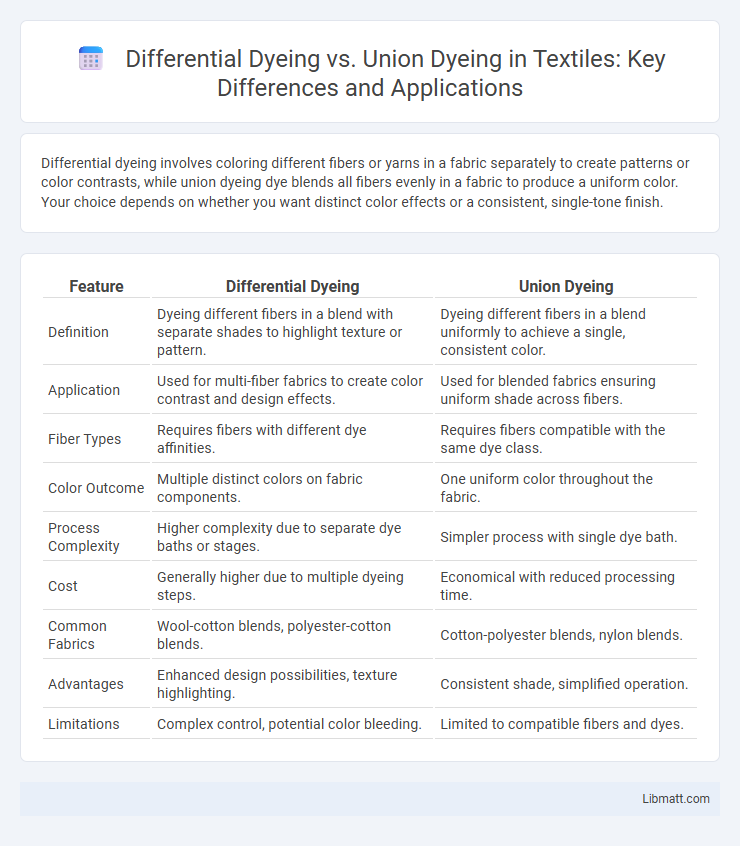
| Feature | Differential Dyeing | Union Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing different fibers in a blend with separate shades to highlight texture or pattern. | Dyeing different fibers in a blend uniformly to achieve a single, consistent color. |
| Application | Used for multi-fiber fabrics to create color contrast and design effects. | Used for blended fabrics ensuring uniform shade across fibers. |
| Fiber Types | Requires fibers with different dye affinities. | Requires fibers compatible with the same dye class. |
| Color Outcome | Multiple distinct colors on fabric components. | One uniform color throughout the fabric. |
| Process Complexity | Higher complexity due to separate dye baths or stages. | Simpler process with single dye bath. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to multiple dyeing steps. | Economical with reduced processing time. |
| Common Fabrics | Wool-cotton blends, polyester-cotton blends. | Cotton-polyester blends, nylon blends. |
| Advantages | Enhanced design possibilities, texture highlighting. | Consistent shade, simplified operation. |
| Limitations | Complex control, potential color bleeding. | Limited to compatible fibers and dyes. |
Introduction to Dyeing Methods
Differential dyeing targets individual fibers or yarns within a fabric, creating patterns or textures by exploiting the varying dye affinity of different fibers, while union dyeing achieves a uniform color across blended fibers by using a specific dye or combination of dyes that adheres equally to all fiber types. Differential dyeing is ideal for multi-fiber textiles where creative effects and contrast are desired, whereas union dyeing is essential for producing solid, consistent hues in fabric blends like polyester-cotton. Both methods rely on controlled chemical processes to ensure colorfastness, but their applications vary significantly based on the desired aesthetic and fiber composition.
What is Differential Dyeing?
Differential dyeing is a textile process where multiple fibers or fabric components are dyed in different colors within the same material, allowing for unique color effects and patterns. This method involves treating each fiber type or yarn separately before combining them, resulting in a fabric with varied hues and textures. Understanding differential dyeing can help you achieve complex, customized designs that enhance the visual and functional appeal of your textiles.
What is Union Dyeing?
Union dyeing is a textile dyeing process that allows multiple fiber types within a blended fabric to be dyed a uniform color in a single operation. This technique uses compatible dyes that can bond with different fibers simultaneously, ensuring consistent coloration across diverse materials such as cotton and polyester blends. Union dyeing enhances production efficiency by eliminating the need for separate dyeing processes for each fiber type.
Key Differences Between Differential and Union Dyeing
Differential dyeing involves coloring fiber blends separately before yarn formation, resulting in varied shades within the fabric, while union dyeing processes the fiber blend as a single entity to produce a uniform color. This distinction is crucial for achieving specific aesthetic effects, with differential dyeing offering multi-tone appearances and union dyeing ensuring color consistency across mixed fibers. The choice between these methods depends on the desired visual complexity and the fiber composition in textile manufacturing.
Types of Fibers Used in Each Dyeing Method
Differential dyeing primarily involves fabrics composed of multiple fiber types, such as polyester-cotton blends or nylon-wool mixtures, where each fiber absorbs dye differently to create distinct patterns or shades. Union dyeing is used for fabrics made from two or more fibers, like cotton-polyester blends, aiming to achieve a uniform color by selecting dyes that are compatible with all fiber types. Both methods require precise fiber identification to apply appropriate dyes, ensuring optimal color fastness and appearance.
Process Steps: Differential vs Union Dyeing
Differential dyeing involves dyeing individual fibers or yarns separately before fabric formation, allowing for multi-colored patterns and precise control over color placement. Union dyeing combines different fiber types in a single dye bath, using compatible dyes to achieve a uniform color across all fibers simultaneously. The differential dyeing process requires multiple dyeing stages, whereas union dyeing streamlines production by dyeing blended fibers together in one step.
Colorfastness in Differential and Union Dyeing
Differential dyeing involves using different dye classes for fibers in a blended fabric, which can lead to varied colorfastness due to the distinct dye-fiber interactions. Union dyeing employs a single dye class that bonds uniformly to all fiber types in the blend, resulting in more consistent colorfastness and improved resistance to washing, light, and rubbing. Your choice between differential and union dyeing directly impacts the durability and longevity of the fabric's color performance.
Applications and End Uses
Differential dyeing is predominantly used in producing multicolored textiles, such as patterns on denim, stripes on shirts, and blended fabrics, allowing individual fibers or yarns to exhibit distinct colors and enhancing aesthetic appeal. Union dyeing finds its primary application in uniform and solid-colored fabrics, especially in the production of polyester-cotton blends and garments requiring a uniform color outcome, like corporate uniforms and fashion apparel. The end uses of differential dyeing emphasize visual texture and color contrast for decorative textiles, while union dyeing targets consistent coloration for mass-produced clothing and technical textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Differential dyeing involves coloring individual fabric components separately, leading to higher water consumption and chemical use, which can increase environmental impact compared to Union dyeing. Union dyeing blends different fibers into a single bath, optimizing resource efficiency by reducing water, energy, and chemical inputs, thus promoting sustainability. You can significantly reduce your textile production's ecological footprint by choosing Union dyeing for mixed-fiber materials.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Your Needs
Differential dyeing targets fibers or components within a fabric separately, creating contrast and texture, while union dyeing produces a uniform color across blended fibers by dyeing them simultaneously. Your choice depends on whether you want distinct multi-tone effects or a consistent, homogenous appearance in your textile products. Evaluating fabric composition, desired aesthetics, and cost efficiency helps determine the ideal dyeing method for your specific needs.
Differential dyeing vs Union dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com