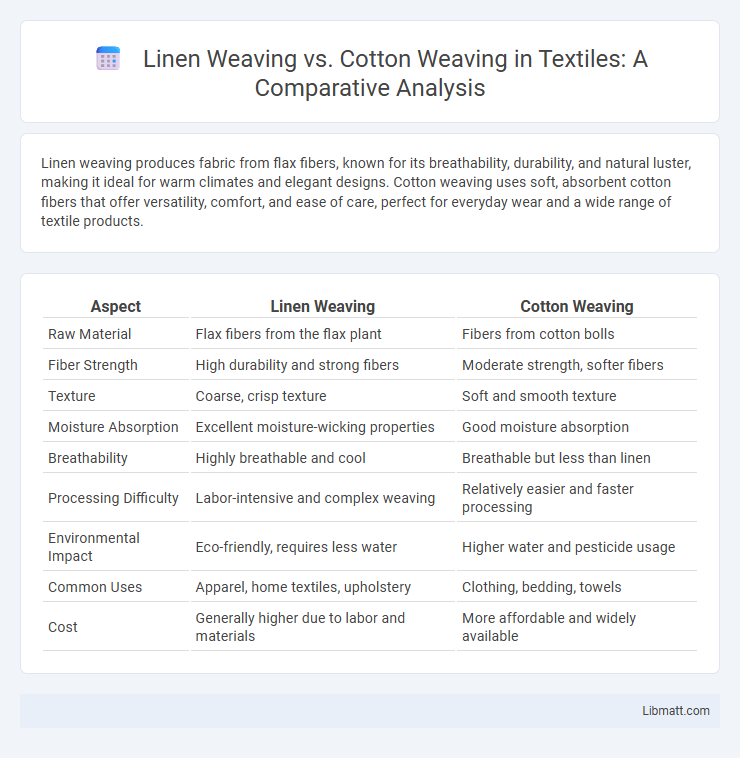
Linen weaving produces fabric from flax fibers, known for its breathability, durability, and natural luster, making it ideal for warm climates and elegant designs. Cotton weaving uses soft, absorbent cotton fibers that offer versatility, comfort, and ease of care, perfect for everyday wear and a wide range of textile products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Linen Weaving | Cotton Weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Flax fibers from the flax plant | Fibers from cotton bolls |
| Fiber Strength | High durability and strong fibers | Moderate strength, softer fibers |
| Texture | Coarse, crisp texture | Soft and smooth texture |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent moisture-wicking properties | Good moisture absorption |
| Breathability | Highly breathable and cool | Breathable but less than linen |
| Processing Difficulty | Labor-intensive and complex weaving | Relatively easier and faster processing |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, requires less water | Higher water and pesticide usage |
| Common Uses | Apparel, home textiles, upholstery | Clothing, bedding, towels |
| Cost | Generally higher due to labor and materials | More affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Linen and Cotton Weaving
Linen weaving involves the interlacing of fibers derived from the flax plant, known for producing strong, breathable, and moisture-wicking textiles ideal for warm climates and durable fabric applications. Cotton weaving utilizes natural fibers from the cotton plant, offering soft, flexible, and highly absorbent fabrics favored for everyday clothing and versatile household textiles. Your understanding of linen and cotton weaving highlights key differences in fiber origin, texture, and performance suitable for various uses.
Historical Background of Linen and Cotton Fabrics
Linen weaving dates back over 5,000 years, originating in ancient Egypt where flax plants were cultivated for durable, breathable fabric highly valued for its strength and natural luster. Cotton weaving has a similarly ancient history, with evidence of cotton use in the Indus Valley Civilization around 3,000 BCE, prized for its softness and versatility in textile production. Understanding the historical background of these fabrics helps you appreciate their distinct cultural significance and functional qualities in modern weaving practices.
Fiber Characteristics: Linen vs Cotton
Linen fibers, derived from the flax plant, are longer and stronger than cotton fibers, resulting in a fabric that is more durable and resistant to wear. Cotton fibers are shorter, softer, and more elastic, making cotton fabrics more breathable and flexible but less resistant to abrasion compared to linen. The natural moisture-wicking properties of linen fibers contribute to superior breathability and quick-drying characteristics, whereas cotton fibers absorb moisture more readily, affecting drying time and comfort.
Weaving Techniques: Linen vs Cotton
Linen weaving employs longer, finer fibers from flax plants, resulting in a fabric with a distinctively crisp texture and natural luster, while cotton weaving uses shorter, softer fibers that produce a smoother, more pliable textile. The weaving techniques for linen often involve tighter, plain weaves to enhance durability and showcase its strength, whereas cotton allows for more diverse weave patterns such as twill or sateen, optimizing comfort and breathability. Your choice between linen and cotton weaving will influence fabric performance, with linen providing greater longevity and cotton offering greater softness and flexibility.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Linen weaving exhibits superior durability and strength compared to cotton weaving due to flax fibers' longer and more robust structure, making linen fabrics highly resistant to wear and tear. Cotton fibers, being shorter and softer, result in fabrics that are comfortable but less durable, prone to pilling and abrasion over time. The tensile strength of linen is approximately 20%-25% higher than cotton, enhancing its longevity in heavy-use textiles.
Breathability and Comfort Factors
Linen weaving produces a fabric known for exceptional breathability due to its naturally large fibers, allowing air to flow freely and keep you cool in warm weather. Cotton weaving, while also breathable, typically offers a softer and more flexible texture, enhancing comfort for everyday wear and diverse climates. Your choice between linen and cotton should consider the intended use and climate, as linen excels in hot conditions with excellent moisture-wicking properties, whereas cotton provides a cozy, all-season feel.
Environmental Impact of Linen and Cotton Production
Linen weaving offers a lower environmental impact compared to cotton weaving due to flax cultivation requiring significantly less water and pesticides. Cotton production is resource-intensive, consuming about 2,700 liters of water per kilogram of fiber and involving heavy pesticide use that harms ecosystems. Linen fibers are biodegradable and promote sustainable agriculture, making linen weaving a more eco-friendly textile choice.
Common Applications in Textiles
Linen weaving is prized for producing durable, breathable fabrics often used in home textiles like tablecloths, curtains, and upholstery due to its strength and moisture-wicking properties. Cotton weaving dominates in apparel and everyday clothing because of its softness, flexibility, and ease of dyeing, making it ideal for t-shirts, underwear, and casual wear. Your choice between linen and cotton weaving directly impacts the texture, durability, and application suitability of the final textile product.
Care and Maintenance Differences
Linen weaving requires gentle care due to its natural fiber's sensitivity to high temperatures and frequent washing, making hand washing or cold machine cycles optimal for preserving fabric strength and texture. Cotton weaving offers greater durability and ease of maintenance, withstanding higher temperatures and more frequent washing without significant wear, making it suitable for everyday use and machine drying. Choosing the appropriate care method for each fabric preserves longevity: linen benefits from air drying and ironing while slightly damp, whereas cotton tolerates standard tumble drying and higher ironing temperatures.
Choosing Between Linen and Cotton Weaving
Linen weaving produces a fabric known for its strength, breathability, and natural luster, making it ideal for warm climates and durable textiles. Cotton weaving offers softness, versatility, and easier maintenance, perfect for everyday wear and a wide range of textile products. When choosing between linen and cotton weaving, consider your preference for texture, durability, and the environmental impact of fiber production to match your specific needs.
Linen weaving vs Cotton weaving Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com