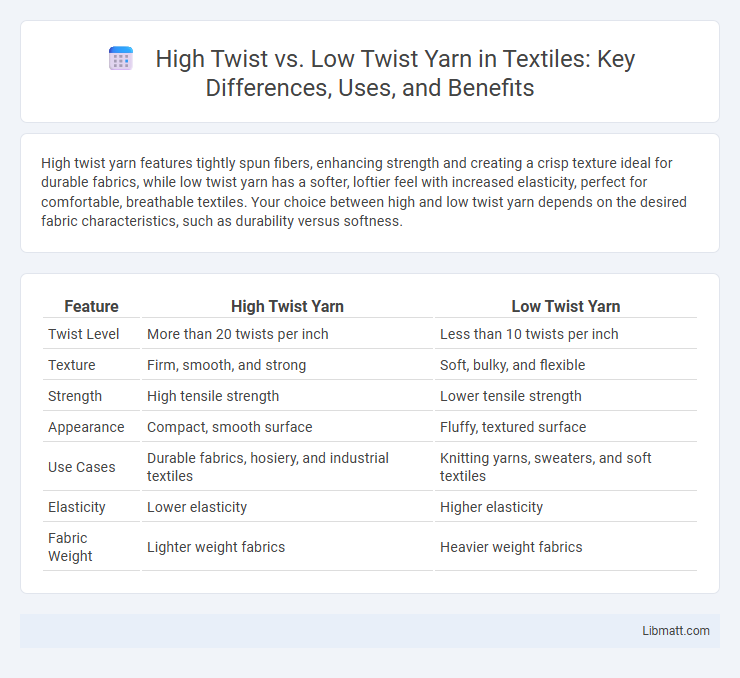
High twist yarn features tightly spun fibers, enhancing strength and creating a crisp texture ideal for durable fabrics, while low twist yarn has a softer, loftier feel with increased elasticity, perfect for comfortable, breathable textiles. Your choice between high and low twist yarn depends on the desired fabric characteristics, such as durability versus softness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High Twist Yarn | Low Twist Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| Twist Level | More than 20 twists per inch | Less than 10 twists per inch |
| Texture | Firm, smooth, and strong | Soft, bulky, and flexible |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Appearance | Compact, smooth surface | Fluffy, textured surface |
| Use Cases | Durable fabrics, hosiery, and industrial textiles | Knitting yarns, sweaters, and soft textiles |
| Elasticity | Lower elasticity | Higher elasticity |
| Fabric Weight | Lighter weight fabrics | Heavier weight fabrics |
Introduction to Yarn Twist
Yarn twist refers to the number of turns per unit length applied to fibers to hold them together, directly impacting strength, elasticity, and texture. High twist yarns feature more twists per inch, resulting in increased durability and a smoother, more compact surface ideal for fabrics requiring high strength and resistance to abrasion. Low twist yarns have fewer twists, creating softer, bulkier, and more flexible textiles commonly used in cozy garments and home textiles.
Defining High Twist and Low Twist Yarn
High twist yarn features tightly spun fibers that create strong, smooth, and durable threads often used in textiles requiring high strength and elasticity. Low twist yarn consists of loosely spun fibers resulting in soft, fluffy, and breathable fabric ideal for comfort and insulation purposes. Your choice between high twist and low twist yarn depends on the desired texture, durability, and application of the finished textile product.
Manufacturing Process Differences
High twist yarn undergoes a spinning process with a greater number of twists per inch, resulting in a stronger, more durable fiber suitable for applications demanding resilience. In contrast, low twist yarn incorporates fewer twists, producing a softer, more flexible texture ideal for lightweight, comfortable fabrics. Your choice between high twist and low twist yarn depends on the desired fabric characteristics and end-use performance.
Physical Characteristics of High vs Low Twist
High twist yarn exhibits increased strength, firmness, and elasticity due to the tightly spun fibers, resulting in a smoother texture and higher durability. Low twist yarn maintains a softer, bulkier feel with greater loft and flexibility but sacrifices tensile strength and tends to pill more easily. The physical differences impact fabric hand, abrasion resistance, and overall performance, making high twist ideal for durability and low twist preferred for softness.
Applications in Textile Industry
High twist yarns provide enhanced strength, durability, and elasticity, making them ideal for applications in denim production, sewing threads, and technical textiles requiring abrasion resistance. Low twist yarns offer softness and better drape, commonly used in knitted fabrics, apparel, and home textiles such as upholstery and curtains. Selecting between high twist and low twist yarns directly impacts fabric performance attributes like tensile strength, texture, and elasticity in various textile applications.
Impact on Fabric Texture and Appearance
High twist yarn produces fabric with a crisp, firm texture and enhanced durability, resulting in a smoother, more lustrous appearance ideal for shirting and suiting fabrics. Low twist yarn creates a softer, fluffier fabric with a matte finish and increased warmth, commonly used in knitwear and casual apparel for a relaxed, cozy look. The twist level directly influences the fabric's hand feel, drape, and visual texture, making it a critical factor in textile design and end-use performance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
High twist yarn exhibits superior durability and strength due to the increased tensile force applied during spinning, resulting in tightly bound fibers that resist abrasion and breakage more effectively than low twist yarn. Low twist yarn tends to be softer and more flexible but sacrifices some structural integrity, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications where high tensile strength is essential. Industries requiring robust textiles, such as upholstery and industrial fabrics, often prefer high twist yarn for its enhanced endurance and resilience.
Moisture Absorption and Comfort
High twist yarns exhibit tighter fiber structures, resulting in lower moisture absorption and reduced breathability, which may impact overall comfort in warm or humid conditions. Low twist yarns retain more natural fiber gaps, enhancing moisture wicking and air circulation, thereby improving comfort by keeping the skin dry and cool. These differences in twist level directly influence the fabric's performance in moisture management and wearer comfort.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
High twist yarn generally incurs higher production costs due to increased processing time and machinery wear, leading to more expensive finished products. Low twist yarns tend to be more widely available and economical, making them preferred for mass-market textiles and budget-conscious manufacturers. Market availability of high twist yarn is limited to niche applications requiring enhanced strength and durability, while low twist yarn dominates the mainstream textile industry.
Choosing the Right Yarn Twist for Your Project
High twist yarn offers increased strength, durability, and a firmer texture ideal for projects requiring resilience and defined stitch patterns, such as socks or activewear. Low twist yarn provides a softer, fluffier feel with enhanced loft and drape, perfect for cozy blankets or delicate garments where softness is essential. Assess your project's needs for durability versus softness to choose the right yarn twist that best supports your crafting goals.
High twist vs Low twist yarn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com