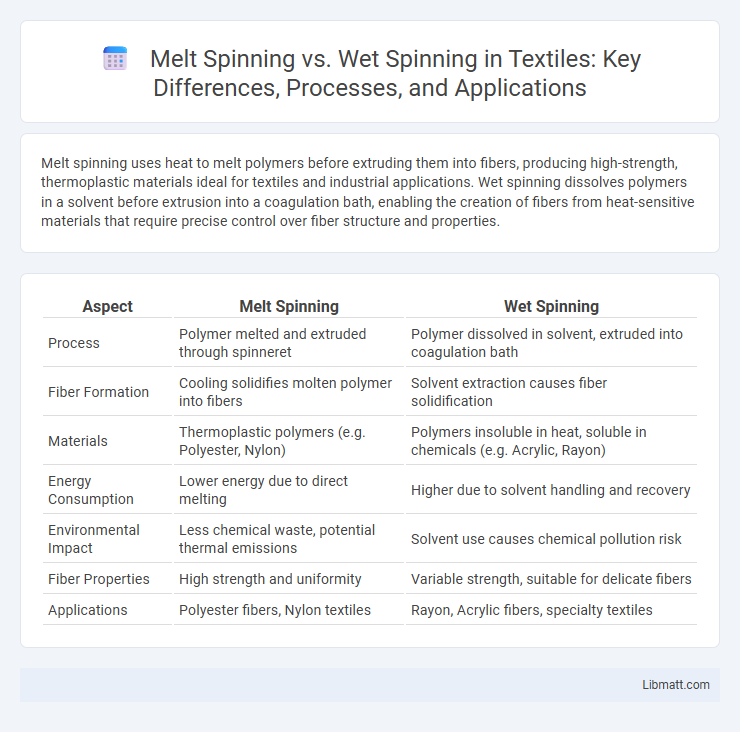
Melt spinning uses heat to melt polymers before extruding them into fibers, producing high-strength, thermoplastic materials ideal for textiles and industrial applications. Wet spinning dissolves polymers in a solvent before extrusion into a coagulation bath, enabling the creation of fibers from heat-sensitive materials that require precise control over fiber structure and properties.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Melt Spinning | Wet Spinning |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Polymer melted and extruded through spinneret | Polymer dissolved in solvent, extruded into coagulation bath |
| Fiber Formation | Cooling solidifies molten polymer into fibers | Solvent extraction causes fiber solidification |
| Materials | Thermoplastic polymers (e.g. Polyester, Nylon) | Polymers insoluble in heat, soluble in chemicals (e.g. Acrylic, Rayon) |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy due to direct melting | Higher due to solvent handling and recovery |
| Environmental Impact | Less chemical waste, potential thermal emissions | Solvent use causes chemical pollution risk |
| Fiber Properties | High strength and uniformity | Variable strength, suitable for delicate fibers |
| Applications | Polyester fibers, Nylon textiles | Rayon, Acrylic fibers, specialty textiles |
Introduction to Melt Spinning and Wet Spinning
Melt spinning involves melting a polymer and extruding it through a spinneret to form fibers that solidify upon cooling, commonly used for thermoplastic fibers like nylon and polyester. Wet spinning dissolves polymers in a solvent before extrusion into a coagulation bath, suitable for fibers sensitive to heat such as acrylic and rayon. Both methods are essential in textile manufacturing, with melt spinning offering faster production and wet spinning providing better control over fiber morphology.
Process Overview: Melt Spinning
Melt spinning involves melting a polymer resin and extruding it through fine spinnerets into cool air, where the fibers solidify rapidly. This process is highly efficient for thermoplastic polymers like nylon, polyester, and polypropylene, resulting in continuous filaments with controlled diameter and strength. The absence of solvents reduces environmental impact and simplifies fiber production compared to wet spinning.
Process Overview: Wet Spinning
Wet spinning involves dissolving a polymer in a solvent to create a viscous solution, which is then extruded through a spinneret into a coagulation bath where fibers solidify. This process is ideal for producing fibers from polymers that cannot be melted, such as rayon, acrylic, and spandex. Your choice of wet spinning impacts fiber strength, elasticity, and surface texture due to the controlled coagulation environment.
Key Differences Between Melt Spinning and Wet Spinning
Melt spinning involves extruding molten polymer through a spinneret and solidifying it by cooling, whereas wet spinning dissolves the polymer in a solvent before extrusion into a coagulation bath for fiber formation. Melt spinning is typically faster and used for thermoplastic polymers like nylon and polyester, while wet spinning suits polymers that degrade before melting, such as acrylic and rayon. The choice between melt spinning and wet spinning impacts fiber properties, production speed, and environmental considerations related to solvent recovery.
Fiber Types Produced by Melt and Wet Spinning
Melt spinning produces thermoplastic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and polypropylene, known for their strength and durability. Wet spinning is used to create fibers like acrylic, rayon, and spandex, which require solvent-based extrusion due to their chemical structure. Your choice depends on the desired fiber properties and processing conditions suitable for specific textile applications.
Advantages of Melt Spinning
Melt spinning offers faster production rates and lower energy consumption compared to wet spinning, as it eliminates the use of solvents and drying processes. This method produces strong, uniform fibers with excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon. Your manufacturing process can benefit from reduced environmental impact and cost-efficiency by choosing melt spinning over wet spinning.
Advantages of Wet Spinning
Wet spinning offers superior control over fiber morphology and molecular orientation, resulting in high-strength, uniform fibers ideal for delicate polymers that cannot withstand high temperatures. This method enables the production of fibers with enhanced moisture absorption and elasticity, making it suitable for applications in textiles and biomedical materials. Its ability to process a wide range of polymers, including those insoluble in common solvents, provides versatile options for specialized fiber manufacturing.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Methods
Melt spinning faces limitations such as a restricted range of polymers due to high processing temperatures and challenges in controlling fiber morphology. Wet spinning encounters difficulties with solvent recovery, environmental concerns, and slower production rates compared to melt spinning. Your choice between these methods should consider the trade-offs in fiber quality, scalability, and cost-effectiveness associated with each technique.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Melt spinning is predominantly used in the production of synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and polypropylene, which are essential for manufacturing durable textiles, sportswear, and industrial fabrics. Wet spinning serves applications involving fibers like acrylic, rayon, and spandex, offering fine control over fiber properties for high-quality apparel, upholstery, and medical textiles. Both methods are integral in producing diverse textile materials, with melt spinning favored for high-strength fibers and wet spinning preferred for fibers requiring solvent-based extrusion.
Future Trends in Fiber Spinning Technologies
Future trends in fiber spinning technologies emphasize sustainability and efficiency improvements in both melt spinning and wet spinning processes. Melt spinning advances focus on developing bio-based polymers and enhancing energy efficiency to reduce environmental impact. Wet spinning innovations prioritize eco-friendly solvents and recycling methods, providing Your textile production with greener and more versatile fiber options.
Melt spinning vs Wet spinning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com