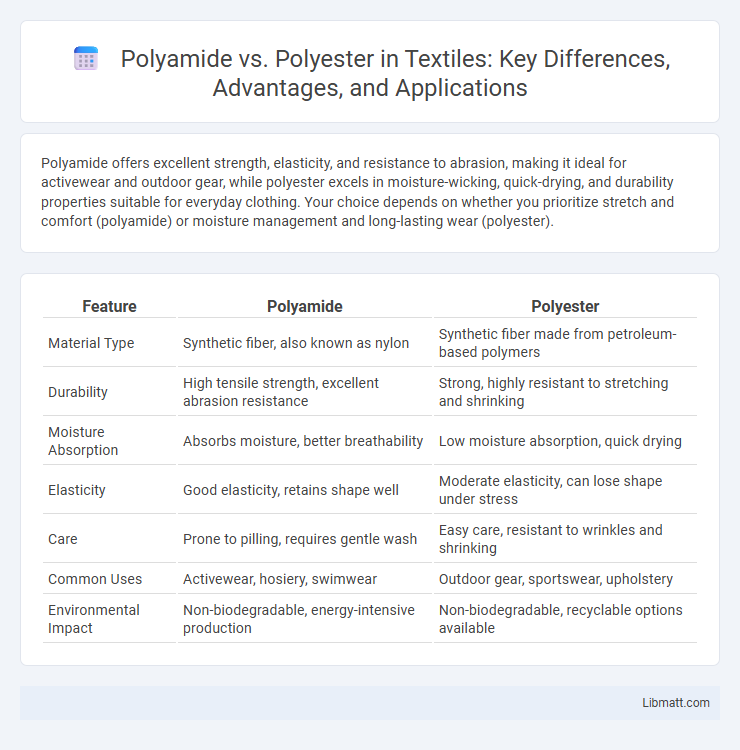
Polyamide offers excellent strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for activewear and outdoor gear, while polyester excels in moisture-wicking, quick-drying, and durability properties suitable for everyday clothing. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stretch and comfort (polyamide) or moisture management and long-lasting wear (polyester).
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyamide | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic fiber, also known as nylon | Synthetic fiber made from petroleum-based polymers |
| Durability | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance | Strong, highly resistant to stretching and shrinking |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs moisture, better breathability | Low moisture absorption, quick drying |
| Elasticity | Good elasticity, retains shape well | Moderate elasticity, can lose shape under stress |
| Care | Prone to pilling, requires gentle wash | Easy care, resistant to wrinkles and shrinking |
| Common Uses | Activewear, hosiery, swimwear | Outdoor gear, sportswear, upholstery |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production | Non-biodegradable, recyclable options available |
Introduction to Polyamide and Polyester
Polyamide and polyester are two widely used synthetic fibers in textiles known for their durability and versatility. Polyamide, commonly referred to as nylon, offers excellent strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for activewear and industrial fabrics. Polyester is prized for its moisture-wicking properties, quick-drying ability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching, which enhances the performance and longevity of your clothing and home textiles.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a synthetic polymer made of repeating units linked by amide bonds, which provide high tensile strength and elasticity due to its crystalline and semi-crystalline molecular structure. Polyester consists primarily of ester functional groups in its polymer chain, offering excellent durability, resistance to stretching, and quick drying because of its hydrophobic, linear molecular arrangement. Understanding the distinct chemical composition and structure of polyamide versus polyester helps you select fabrics based on performance requirements like moisture management and mechanical resilience.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, exhibits higher elasticity and abrasion resistance compared to polyester, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and stretch. Polyester offers superior moisture-wicking and UV resistance, contributing to enhanced longevity and comfort in outdoor wear. Both fibers differ in melting points, with polyamide melting around 215degC and polyester around 260degC, influencing their suitability for various thermal processing methods.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polyamide fibers exhibit superior durability and tensile strength compared to polyester, making them highly resistant to abrasion and wear over time. Polyester offers excellent resistance to stretching and shrinking, while polyamide maintains structural integrity under heavy stress and repetitive use. Your choice between polyamide and polyester should consider the specific demands of durability and strength required for your application.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Polyamide fibers exhibit higher moisture absorption compared to polyester, allowing them to absorb up to 4-5% of their weight in water, which enhances comfort during physical activities. Polyester has lower moisture absorption, around 0.4%, making it more water-resistant but less breathable than polyamide. The superior breathability of polyamide fibers contributes to better moisture management and faster drying times, ideal for activewear and outdoor clothing.
Applications in Textiles and Industry
Polyamide fibers, known for their excellent strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, are widely used in technical textiles such as automotive components, industrial ropes, and activewear. Polyester, prized for its durability, quick-drying properties, and resistance to chemicals, dominates in applications including upholstery, outdoor gear, and packaging materials. Your choice between polyamide and polyester depends on the specific performance requirements of the textile or industrial product being manufactured.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyamide production typically involves higher energy consumption and emits more greenhouse gases compared to polyester, making its environmental impact more significant. Polyester, often derived from recycled PET bottles, offers better sustainability credentials by reducing plastic waste and lowering resource use. Both fibers pose challenges in biodegradability, but advancements in recycling technologies aim to improve their ecological footprint over time.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity
Polyamide offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability, making it ideal for sensitive skin and active wear without causing irritation. Polyester, while durable and moisture-resistant, can trap heat and may lead to discomfort or redness for those with sensitive skin. Choosing polyamide enhances your comfort by maintaining dryness and reducing the risk of skin irritation during prolonged wear.
Care, Maintenance, and Longevity
Polyamide fabrics require gentle washing with mild detergents and air drying to maintain their elasticity and prevent damage, while polyester is more resistant to shrinking and stretching, tolerating machine washing and high-temperature drying. Polyamide's durability under abrasion is moderate but can degrade with prolonged exposure to sunlight and heat, whereas polyester offers superior resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and moisture, enhancing its longevity in various conditions. Proper care extends the lifespan of both fibers, but polyester generally lasts longer with less maintenance compared to polyamide.
Choosing Between Polyamide and Polyester
Choosing between polyamide and polyester depends on specific fabric requirements such as durability, moisture-wicking, and comfort. Polyamide offers superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for activewear and outdoor gear. Polyester excels in moisture management, quick-drying capabilities, and color retention, suitable for athletic clothing and fashion textiles.
Polyamide vs Polyester Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com