Knitting creates fabric by interlocking loops of yarn, resulting in stretchy and flexible material ideal for garments like sweaters and socks. Weaving binds yarns at right angles, producing a stable and durable fabric commonly used for items such as denim and upholstery, allowing you to choose the best technique based on your project's needs.
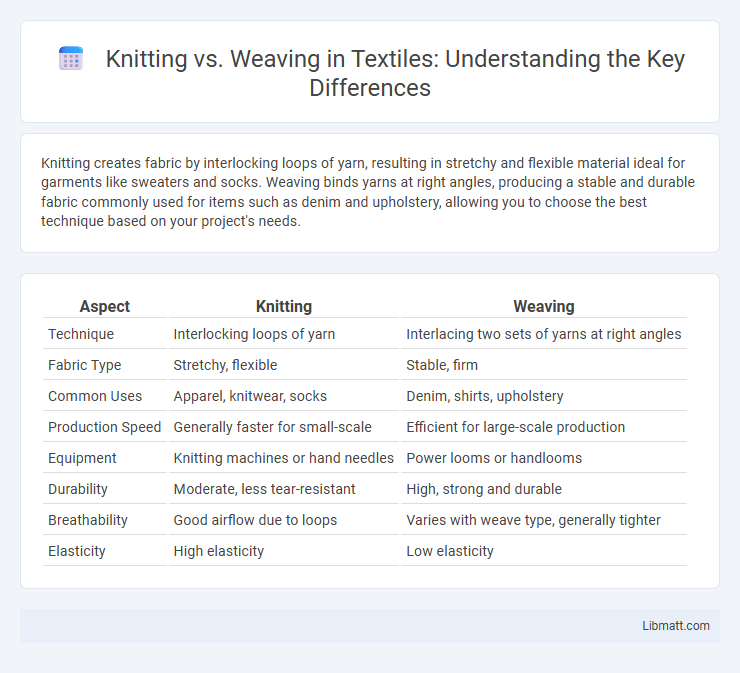
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Knitting | Weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Interlocking loops of yarn | Interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles |
| Fabric Type | Stretchy, flexible | Stable, firm |
| Common Uses | Apparel, knitwear, socks | Denim, shirts, upholstery |
| Production Speed | Generally faster for small-scale | Efficient for large-scale production |
| Equipment | Knitting machines or hand needles | Power looms or handlooms |
| Durability | Moderate, less tear-resistant | High, strong and durable |
| Breathability | Good airflow due to loops | Varies with weave type, generally tighter |
| Elasticity | High elasticity | Low elasticity |
Introduction to Knitting and Weaving
Knitting involves creating fabric by interlocking loops of yarn using needles, resulting in a stretchy and flexible material ideal for garments like sweaters and socks. Weaving produces fabric by interlacing two sets of yarn--warp and weft--at right angles on a loom, creating a stronger, more structured textile suitable for items such as upholstery and denim. Understanding the basic techniques behind knitting and weaving helps you choose the best fabric type for your specific textile needs.
Historical Background of Knitting and Weaving
Knitting originated in the Middle East around the 5th century and spread to Europe by the 14th century, initially serving as a practical craft for creating warm, flexible garments. Weaving dates back thousands of years earlier, with archaeological evidence from ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, where woven textiles became fundamental for clothing and trade. Understanding the historical background of knitting and weaving highlights how these textile techniques shaped your cultural heritage and the development of fabric production.
Basic Techniques: Knitting vs Weaving
Knitting involves interlocking loops of yarn using needles, creating flexible and stretchable fabric ideal for garments like sweaters and socks, while weaving interlaces two distinct sets of threads--the warp and the weft--at right angles on a loom, producing a more rigid and structured textile suitable for items like upholstery or denim. The fundamental knitting technique uses continuous looping, allowing for varied stitch patterns such as knit, purl, and cables, whereas weaving relies on tension and the crossing pattern of threads with basic weaves like plain, twill, and satin. Understanding these basic techniques highlights knitting's stretchability and design versatility versus weaving's durability and strong fabric construction.
Materials Used in Knitting and Weaving
Knitting primarily uses yarns made from wool, cotton, acrylic, or blends, chosen for their stretchability and flexibility to create loops. Weaving typically employs stronger fibers like cotton, linen, silk, or synthetic threads, which are interlaced tightly on a loom to form durable fabrics. Understanding the distinct materials for your knitting or weaving project influences texture, strength, and final product functionality.
Structural Differences Between Knitted and Woven Fabrics
Knitted fabrics are created by interlocking loops of yarn, resulting in a stretchy and flexible structure that adapts well to body movement. Woven fabrics consist of interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles, producing a stable and firm texture with less elasticity. Your choice between these methods influences the fabric's durability, breathability, and suitability for various textile applications.
Applications: Common Uses of Knitting and Weaving
Knitting is commonly used in apparel such as sweaters, socks, and hats due to its stretchability and comfort, making it ideal for garments requiring flexibility. Weaving is predominantly applied in home textiles like upholstery, curtains, and carpets, as well as in industrial fabrics where durability and strength are essential. Your choice between knitting and weaving depends on whether flexibility or structural integrity is the primary requirement for your project.
Pros and Cons of Knitting
Knitting creates stretchy, breathable fabrics ideal for clothing that requires flexibility and comfort, but it tends to be less durable and more prone to snagging than woven textiles. The process allows for intricate patterns and textures, providing versatility in design, while the production speed is generally slower compared to weaving techniques. Your choice between knitting and weaving depends on the need for elasticity and softness versus strength and structure in the final fabric.
Pros and Cons of Weaving
Weaving creates a strong and durable fabric by interlacing warp and weft threads at right angles, making it ideal for applications requiring structural stability such as upholstery and denim. The process tends to be less flexible and stretchable compared to knitting, which limits comfort and adaptability in garments. Weaving is also more time-consuming and requires specialized machinery, increasing production costs relative to the faster, more versatile knitting method.
Knitting vs Weaving: Which is Best for Your Project?
Knitting offers greater elasticity and flexibility, making it ideal for garments requiring stretch, such as sweaters and socks, while weaving produces a more stable, durable fabric suited for upholstery and home textiles. The choice depends on the desired texture, durability, and elasticity, with knitting providing softness and comfort, and weaving delivering strength and shape retention. Consider project requirements like fabric weight, stretch, and wear resistance to determine whether knitting or weaving best suits your needs.
Future Trends in Textile Arts: Knitting and Weaving
Future trends in textile arts highlight the integration of smart fibers and sustainable materials in both knitting and weaving techniques, transforming traditional crafts into innovative, eco-friendly practices. Advances in digital technology and 3D knitting software allow for intricate, customized fabric designs, while automated weaving looms enhance precision and production efficiency. Your engagement with these evolving methods can lead to unique, high-performance textiles that blend artistry with functionality.
Knitting vs Weaving Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com