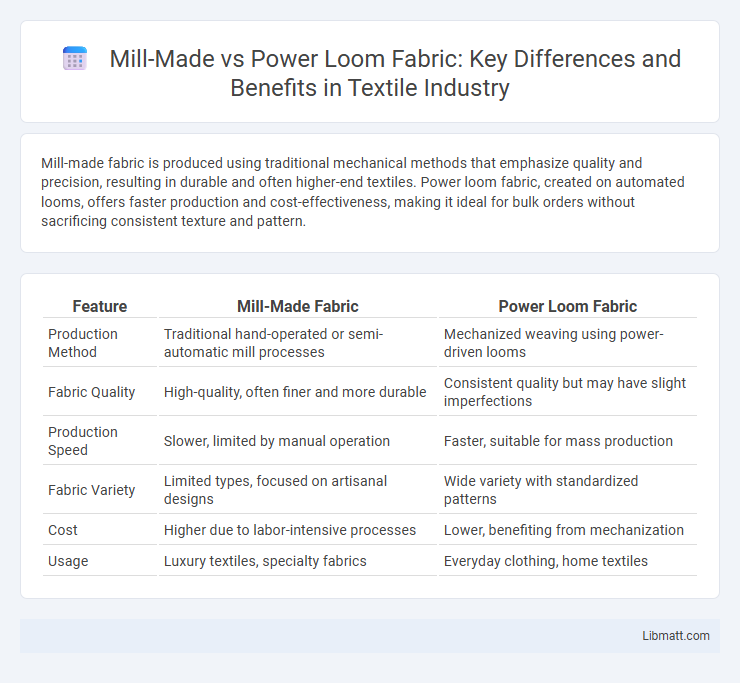
Mill-made fabric is produced using traditional mechanical methods that emphasize quality and precision, resulting in durable and often higher-end textiles. Power loom fabric, created on automated looms, offers faster production and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for bulk orders without sacrificing consistent texture and pattern.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mill-Made Fabric | Power Loom Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Traditional hand-operated or semi-automatic mill processes | Mechanized weaving using power-driven looms |
| Fabric Quality | High-quality, often finer and more durable | Consistent quality but may have slight imperfections |
| Production Speed | Slower, limited by manual operation | Faster, suitable for mass production |
| Fabric Variety | Limited types, focused on artisanal designs | Wide variety with standardized patterns |
| Cost | Higher due to labor-intensive processes | Lower, benefiting from mechanization |
| Usage | Luxury textiles, specialty fabrics | Everyday clothing, home textiles |
Introduction to Mill-made and Power Loom Fabrics
Mill-made fabrics are traditionally woven on mechanized looms situated within textile mills, producing high-quality, consistent textiles with precise control over thread tension and weave patterns. Power loom fabrics are created using electrically powered looms that significantly increase production speed and efficiency, commonly used in large-scale manufacturing to produce various fabric types such as cotton, polyester, and blends. The distinction between mill-made and power loom fabrics lies in the weaving technology, influencing fabric texture, durability, and cost-efficiency in textile production.
Defining Mill-made Fabric
Mill-made fabric refers to textiles produced directly within textile mills, where fibers undergo processes like spinning, weaving, or knitting under controlled conditions to ensure consistent quality and strength. Unlike power loom fabric, which primarily emphasizes mechanical weaving speed, mill-made fabric involves integrated production stages from raw fiber to finished cloth, enhancing durability and uniformity. Choosing mill-made fabric ensures your garments benefit from precise manufacturing standards and material integrity.
What Is Power Loom Fabric?
Power loom fabric is textile produced using mechanized looms that automate the weaving process, enabling higher production speed and consistency compared to traditional handloom methods. This fabric often exhibits uniform texture and strength due to precise machine control, making it widely used in mass-produced garments and home textiles. The efficiency of power looms supports large-scale fabric manufacturing, reducing labor costs and increasing output quality.
Key Differences Between Mill-made and Power Loom Fabrics
Mill-made fabrics are traditionally woven using hand-operated or semi-automatic looms, resulting in higher craftsmanship and often superior texture compared to power loom fabrics, which are produced using fully automated machines designed for large-scale, rapid production. Power loom fabrics typically offer more uniformity, consistency, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for mass-market apparel and home textiles, whereas mill-made fabrics are valued for their unique patterns and artisanal quality. Your choice between mill-made and power loom fabric depends on whether you prioritize traditional craftsmanship and exclusivity or efficiency and affordability.
Production Processes: Mill-made vs Power Loom
Mill-made fabric undergoes traditional production processes involving manual skill and time-intensive weaving on handlooms, which often results in intricate designs and unique textures. Power loom fabric is produced using automated machinery, enabling faster, large-scale manufacturing with consistent patterns and uniform quality. Your choice between these fabrics depends on the desired texture, production speed, and cost-effectiveness.
Fabric Quality: A Comparative Analysis
Mill-made fabric typically exhibits superior quality due to controlled production processes ensuring consistent yarn strength, uniform texture, and minimal defects. Power loom fabric, while produced faster and at a lower cost, may show variability in weave tightness and durability, potentially affecting the fabric's longevity. Understanding these differences helps you choose the most suitable fabric based on quality requirements and end-use applications.
Cost Implications and Market Pricing
Mill-made fabrics generally have higher production costs due to traditional weaving techniques and skilled labor, which often results in premium market pricing. Power loom fabrics benefit from automation, reducing manufacturing expenses and enabling more competitive pricing in mass markets. Your choice between these fabrics depends on balancing budget constraints with desired quality and craftsmanship.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Perspectives
Mill-made fabrics generally exhibit lower environmental impact due to controlled production processes that optimize energy use and reduce waste, while power loom fabric production often consumes more electricity and generates higher emissions, contributing to environmental degradation. Sustainable textile mills implement eco-friendly technologies, such as water recycling and organic dyeing agents, which significantly minimize carbon footprints compared to conventional power loom operations. Emphasizing renewable energy sources and efficient resource management in mill-made fabric manufacturing aligns with growing sustainability trends and regulatory standards.
Applications in Fashion and Home Textiles
Mill-made fabrics offer superior quality and consistency, making them ideal for high-end fashion garments and luxury home textiles such as designer upholstery and premium curtains. Power loom fabric, with its efficient mass production capabilities, is widely used in affordable fashion collections and practical home textiles like bed linens and casual drapes. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize exclusivity and durability or cost-effectiveness and volume in fashion and interior design applications.
Choosing Between Mill-made and Power Loom Fabrics
Choosing between mill-made and power loom fabrics involves evaluating quality, production speed, and cost efficiency. Mill-made fabrics generally offer superior consistency and intricate designs due to controlled manufacturing processes, making them ideal for high-end applications. Power loom fabrics, produced faster and more affordably, suit large-scale, cost-sensitive projects without sacrificing basic durability.
Mill-made vs Power loom fabric Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com