Singeing removes surface fibers from fabric to create a smooth, clean appearance, while desizing eliminates sizing agents applied during weaving to improve fabric absorbency and cleanliness. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right finishing process for enhanced textile quality and performance.
Table of Comparison
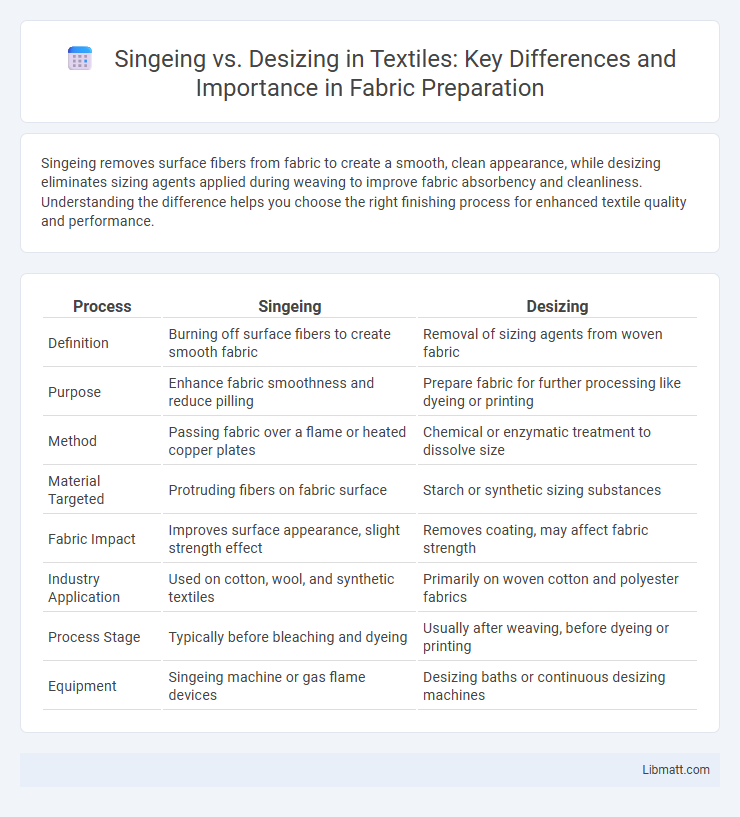
| Process | Singeing | Desizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Burning off surface fibers to create smooth fabric | Removal of sizing agents from woven fabric |
| Purpose | Enhance fabric smoothness and reduce pilling | Prepare fabric for further processing like dyeing or printing |
| Method | Passing fabric over a flame or heated copper plates | Chemical or enzymatic treatment to dissolve size |
| Material Targeted | Protruding fibers on fabric surface | Starch or synthetic sizing substances |
| Fabric Impact | Improves surface appearance, slight strength effect | Removes coating, may affect fabric strength |
| Industry Application | Used on cotton, wool, and synthetic textiles | Primarily on woven cotton and polyester fabrics |
| Process Stage | Typically before bleaching and dyeing | Usually after weaving, before dyeing or printing |
| Equipment | Singeing machine or gas flame devices | Desizing baths or continuous desizing machines |
Introduction to Singeing and Desizing
Singeing removes surface fibers from fabric to create a smoother and cleaner appearance, improving fabric quality and printability. Desizing eliminates starch or sizing agents applied during weaving, ensuring better dye absorption and fabric softness. Understanding the functions of singeing and desizing helps optimize your textile finishing process for enhanced fabric performance.
Definition of Singeing
Singeing is a textile finishing process that involves burning off surface fibers to create a smooth fabric surface, enhancing fabric appearance and reducing pilling. It uses controlled flame or heated plates to eliminate protruding fibers on cotton, polyester, wool, or blended fabrics. This technique improves fabric quality by providing a cleaner and more lustrous finish before further processing like dyeing or printing.
Definition of Desizing
Desizing is a textile finishing process that removes the size material applied to yarns during weaving to strengthen them. This step is essential to prepare fabric for subsequent treatments like dyeing or printing by ensuring proper absorption of dyes and chemicals. You can optimize fabric quality by choosing the appropriate desizing technique, such as enzymatic or chemical methods, depending on the material type.
Purpose of Singeing in Textile Processing
Singeing in textile processing aims to remove surface fibers and fuzz from fabrics to create a smooth and clean finish, improving the fabric's appearance and quality. This process reduces pilling and enhances subsequent treatments like printing and dyeing by providing an even surface. Singeing is essential for achieving precise and vibrant textile patterns while increasing fabric durability.
Purpose of Desizing in Textile Processing
Desizing in textile processing primarily removes sizing agents applied to yarns before weaving, ensuring fabric surfaces are clean and ready for subsequent treatments like dyeing or printing. This step enhances fabric absorbency and uniformity by eliminating starches or synthetic adhesives, which can interfere with color uptake and finishing quality. Your fabric's texture and appearance significantly improve after desizing, promoting better processing efficiency and end-product performance.
Key Differences Between Singeing and Desizing
Singeing removes fiber protrusions from fabric surfaces by burning them off, enhancing smoothness and preparing materials for printing or finishing. Desizing involves eliminating sizing agents like starch or synthetic starches applied during weaving to strengthen yarns, ensuring better dye absorption and fabric softness. While singeing affects the fabric's surface texture for aesthetic improvement, desizing targets chemical components for improved dyeing and finishing performance.
Methods Used in Singeing
Singeing methods primarily involve passing fabric over open flames or heated plates to burn off protruding fibers, enhancing surface smoothness and improving print quality. Common techniques include gas flame singeing, which uses natural gas burners, and plate singeing, where heated copper plates gently sear the fabric surface. These methods effectively reduce fuzziness and prevent pilling, ensuring a clean and polished textile appearance.
Methods Used in Desizing
Desizing commonly employs enzymatic, acid, or oxidative methods to remove starch-based sizing agents from textiles, ensuring fabric readiness for subsequent processing like dyeing or printing. Enzymatic desizing uses amylase enzymes to hydrolyze starch, providing an eco-friendly and precise removal process favored in cotton fabrics. Acid and oxidative methods involve chemical reactions to break down sizing, but they require careful handling due to potential fabric damage or environmental concerns.
Impact on Fabric Quality: Singeing vs Desizing
Singeing improves fabric quality by removing surface fibers, resulting in a smoother texture and enhanced printability, while desizing focuses on eliminating size materials to restore the fabric's absorbency and softness. Singeing reduces pilling and fuzz, leading to a cleaner finish, whereas desizing ensures proper dye uptake and prevents fabric stiffness caused by residual sizing agents. Understanding the impact of singeing versus desizing on fabric quality helps you select the appropriate process for achieving desired textile properties.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Singeing and Desizing
Singeing and desizing serve distinct purposes in textile processing, with singeing removing surface fibers for a smoother fabric finish, while desizing eliminates starch-based sizing agents to enhance fabric absorbency and print quality. Selecting between these processes depends on the fabric type and desired end-use performance, where singeing is preferred for creating a clean, lustrous appearance and desizing is essential for preparing fabrics for dyeing or printing. Optimal textile finishing strategies often combine both processes to achieve superior fabric aesthetics and functionality.
Singeing vs Desizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com