Solution dyeing and dope dyeing both refer to the process of adding color pigments directly into the polymer solution before fiber extrusion, ensuring vibrant, long-lasting color with excellent colorfastness. You benefit from enhanced environmental sustainability and reduced water consumption through these methods, making them ideal for eco-conscious textile production.
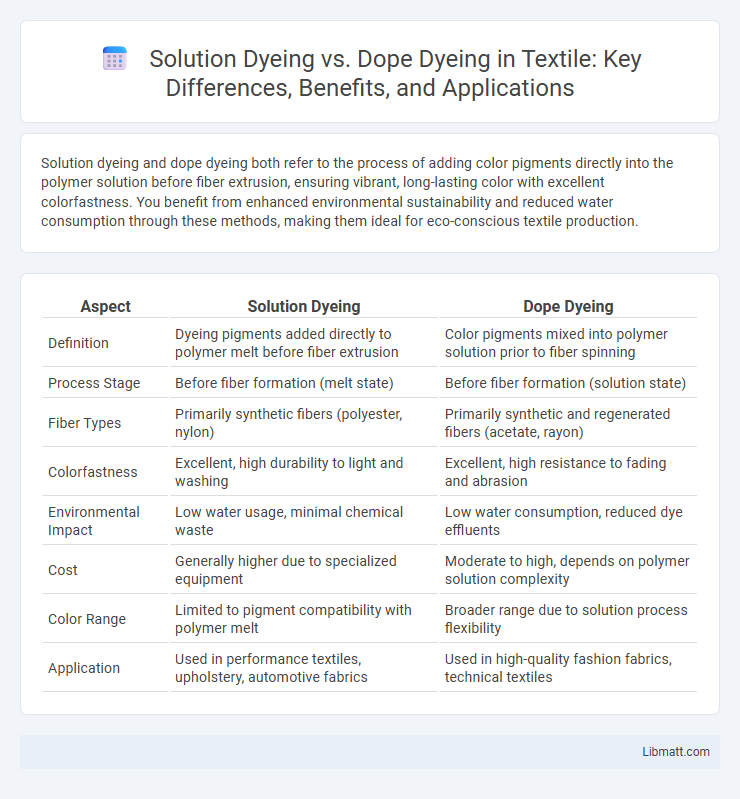
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solution Dyeing | Dope Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing pigments added directly to polymer melt before fiber extrusion | Color pigments mixed into polymer solution prior to fiber spinning |
| Process Stage | Before fiber formation (melt state) | Before fiber formation (solution state) |
| Fiber Types | Primarily synthetic fibers (polyester, nylon) | Primarily synthetic and regenerated fibers (acetate, rayon) |
| Colorfastness | Excellent, high durability to light and washing | Excellent, high resistance to fading and abrasion |
| Environmental Impact | Low water usage, minimal chemical waste | Low water consumption, reduced dye effluents |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized equipment | Moderate to high, depends on polymer solution complexity |
| Color Range | Limited to pigment compatibility with polymer melt | Broader range due to solution process flexibility |
| Application | Used in performance textiles, upholstery, automotive fabrics | Used in high-quality fashion fabrics, technical textiles |
Introduction to Solution Dyeing and Dope Dyeing
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing are innovative fabric coloring techniques that involve integrating color pigments directly into the polymer solution before fiber extrusion. Solution dyeing, often used in synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, ensures long-lasting colorfastness and superior resistance to fading from sunlight and washing. Dope dyeing, a form of solution dyeing, injects color at the fiber melt stage, producing vibrant hues with minimal environmental impact due to reduced water and chemical consumption, enhancing your fabric's sustainability and durability.
What is Solution Dyeing?
Solution dyeing is a textile coloring technique where pigments are added directly to the polymer solution before fiber extrusion, resulting in fibers with inherent color throughout their structure. This process enhances colorfastness, reduces water and energy consumption, and minimizes environmental impact compared to traditional dyeing methods. Your fabrics benefit from improved durability and consistent coloration, making solution dyeing ideal for sustainable textile production.
What is Dope Dyeing?
Dope dyeing, also known as solution dyeing, involves adding color pigments directly into the polymer solution before fiber extrusion, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors. This method enhances colorfastness, reduces water and chemical use, and minimizes environmental impact compared to traditional dyeing techniques. Dope dyeing is widely used in synthetic fiber production, including polyester and nylon, due to its efficiency and sustainability benefits.
Key Differences Between Solution Dyeing and Dope Dyeing
Solution dyeing involves adding colorants directly to the polymer melt before fiber extrusion, ensuring deep, uniform pigmentation and excellent colorfastness. Dope dyeing, a subset of solution dyeing, also incorporates pigments into the polymer solution but is specifically utilized for synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon, providing enhanced color stability and reduced water usage compared to traditional methods. Your choice between these processes will impact fabric durability, environmental footprint, and final product appearance.
Environmental Impact of Solution vs Dope Dyeing
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing both minimize water usage and chemical waste compared to traditional dyeing methods, significantly reducing environmental pollution. Solution dyeing integrates pigments directly into polymer chips before fiber extrusion, leading to less energy consumption during production and enhanced colorfastness. Dope dyeing, similarly embedding color into synthetic fibers, reduces toxic effluents but may have slightly higher energy demands due to fiber-processing variations.
Color Fastness and Quality Comparison
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing both enhance color fastness by integrating pigments directly into synthetic fibers during production, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting hues resistant to fading and washing. Solution dyeing often delivers superior uniformity and durability due to pigment dispersion at the polymer melt stage, while dope dyeing embeds color into fiber filaments, ensuring excellent color retention and minimal environmental impact. Your choice between these methods depends on desired fabric quality, with solution dyeing favored for consistent performance and dope dyeing for eco-friendly textile solutions.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing both involve adding color directly into synthetic fibers before they are spun into yarn, ensuring long-lasting, vibrant hues with superior colorfastness. Solution dyeing mixes pigments into the polymer melt during fiber production, while dope dyeing introduces colorants into the liquid polymer solution before fiber extrusion. These manufacturing processes minimize water usage and reduce environmental impact compared to traditional fabric dyeing methods.
Cost Implications: Solution Dyeing vs Dope Dyeing
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing are often used interchangeably but differ slightly in process and cost implications. Solution dyeing typically involves adding pigments directly to the polymer melt before fiber extrusion, leading to higher initial setup costs due to specialized equipment but lower long-term expenses through reduced water and energy usage. Dope dyeing, a subset of solution dyeing, integrates color during fiber production as well, offering significant cost savings by eliminating post-dyeing processes, minimizing waste, and enhancing colorfastness, which reduces expenses related to reprocessing and environmental compliance.
Applications in Textile Industry
Solution dyeing and dope dyeing are both integral to the textile industry, primarily used for producing color in synthetic fibers before they are spun into yarns. Solution dyeing is commonly applied in manufacturing polyester and nylon fibers for high-performance textiles, including outdoor gear and automotive interiors, due to its colorfastness and resistance to fading. Dope dyeing is preferred for bulk-colored fibers in applications such as carpets, upholstery, and technical textiles, offering excellent durability and environmental benefits by reducing water and chemical use during production.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right dyeing method between solution dyeing and dope dyeing depends on factors such as fabric type, colorfastness requirements, and environmental impact. Solution dyeing, ideal for synthetic fibers like polyester, integrates pigments during fiber extrusion, resulting in superior colorfastness and reduced water usage. Dope dyeing, a variant of solution dyeing, offers consistent coloration and lower energy consumption, making it suitable for large-scale production of high-performance textiles.
Solution dyeing vs Dope dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com