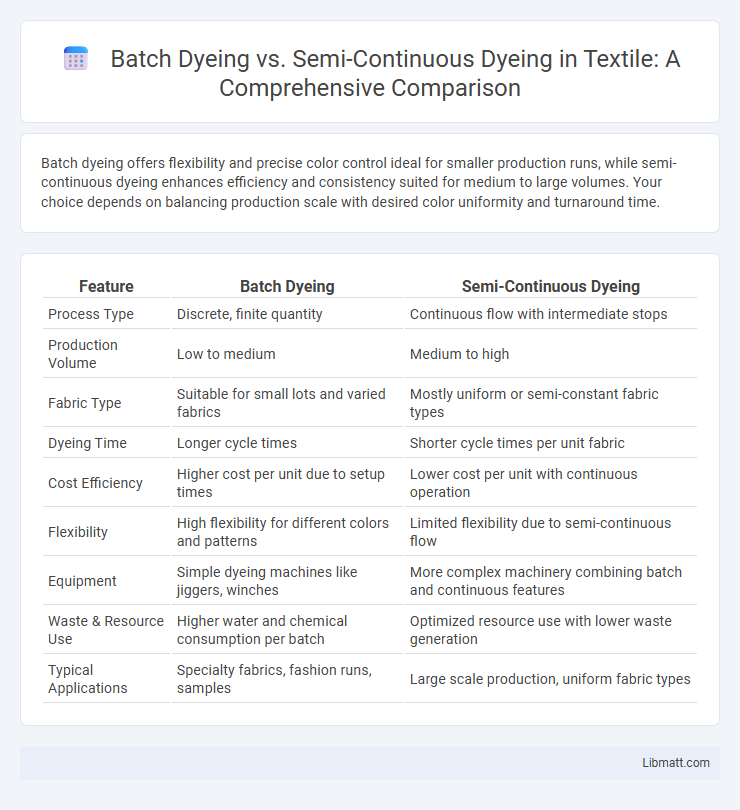
Batch dyeing offers flexibility and precise color control ideal for smaller production runs, while semi-continuous dyeing enhances efficiency and consistency suited for medium to large volumes. Your choice depends on balancing production scale with desired color uniformity and turnaround time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Batch Dyeing | Semi-Continuous Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Discrete, finite quantity | Continuous flow with intermediate stops |
| Production Volume | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Fabric Type | Suitable for small lots and varied fabrics | Mostly uniform or semi-constant fabric types |
| Dyeing Time | Longer cycle times | Shorter cycle times per unit fabric |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost per unit due to setup times | Lower cost per unit with continuous operation |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for different colors and patterns | Limited flexibility due to semi-continuous flow |
| Equipment | Simple dyeing machines like jiggers, winches | More complex machinery combining batch and continuous features |
| Waste & Resource Use | Higher water and chemical consumption per batch | Optimized resource use with lower waste generation |
| Typical Applications | Specialty fabrics, fashion runs, samples | Large scale production, uniform fabric types |
Introduction to Dyeing Methods
Batch dyeing involves processing fabric or yarn in fixed quantities within a single vessel, allowing precise control over color uniformity and depth, commonly used for small to medium production runs. Semi-continuous dyeing combines aspects of batch and continuous methods by treating materials in stages, enhancing efficiency and flexibility for medium to large-scale operations while maintaining consistent quality. Both methods optimize dye uptake and fabric performance but differ significantly in production speed, scalability, and operational costs.
Overview of Batch Dyeing
Batch dyeing involves processing textiles in discrete quantities, allowing precise control over dye uptake and color consistency. This method is especially suitable for small to medium production runs and diverse fabric types, offering flexibility in color changes and customized results. Your choice of batch dyeing can optimize quality for specialty textiles while balancing operational efficiency.
Overview of Semi-continuous Dyeing
Semi-continuous dyeing is a textile dyeing process that combines the advantages of batch and continuous methods by intermittently treating fabric in an automated system. This method allows for efficient dye penetration and color uniformity while minimizing water and energy consumption compared to traditional batch dyeing. Semi-continuous dyeing is particularly suited for medium to large production runs requiring consistent dye quality and resource optimization.
Process Workflow: Batch vs Semi-continuous
Batch dyeing involves processing textiles in discrete lots where fabric is immersed in dye liquor for a specific time, ensuring uniform color but requiring longer cycle times and downtime between batches. Semi-continuous dyeing employs a continuous flow of dye liquor through fabric wound on rollers, optimizing production efficiency by reducing fabric handling and enabling rapid color changes. Your choice between these methods depends on desired throughput, fabric type, and color consistency requirements.
Key Equipment Used in Each Method
Batch dyeing primarily employs equipment such as jet dyeing machines, jiggers, winches, and beam dyeing machines, designed to treat fabrics in discrete lots with controlled liquor ratio and temperature. Semi-continuous dyeing utilizes padding mangles or padding ranges combined with stenter frames, enabling fabric impregnation with dye solutions followed by fixation during continuous drying and curing processes. The choice of equipment directly influences factors such as dye uniformity, production speed, and fabric compatibility in each dyeing method.
Dyeing Efficiency and Production Speed
Batch dyeing offers high color uniformity and control, making it efficient for small to medium production volumes, but typically suffers from lower production speed due to its intermittent processing nature. Semi-continuous dyeing enhances production speed by combining batch and continuous processes, allowing for faster throughput while maintaining acceptable dyeing efficiency for larger scale operations. The choice between the two depends on balancing precision in color matching against the need for higher production capacity.
Color Consistency and Quality Control
Batch dyeing provides excellent color consistency due to controlled, uniform processing and thorough quality control at each stage, making it ideal for small to medium production runs requiring precise color matching. Semi-continuous dyeing offers faster throughput but may have slight color variations as fabric moves through intermittent dyeing and washing steps, requiring rigorous monitoring to maintain quality. Your choice between these methods impacts the uniformity and reliability of final fabric coloration, especially when stringent quality control is prioritized.
Resource and Energy Consumption
Batch dyeing consumes more water, energy, and chemicals per cycle due to the repeated heating and cooling processes required for each batch. Semi-continuous dyeing optimizes resource use by maintaining a steady flow and temperature, resulting in lower water and energy consumption per unit of fabric. This method reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and improving overall process efficiency.
Ideal Applications for Each Technique
Batch dyeing is ideal for small to medium production runs, customized color matching, and dyeing delicate or high-value textiles requiring precise control over dyeing parameters. Semi-continuous dyeing suits large-scale production of textiles with consistent color requirements, offering higher throughput and efficient use of water and energy. Industries focusing on fast fashion and mass production benefit from semi-continuous dyeing, while boutique manufacturers prefer batch dyeing for flexibility and quality.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Process
Batch dyeing offers flexibility and precision, ideal for small to medium production runs requiring frequent color changes or specialized effects. Semi-continuous dyeing suits large-scale, uniform fabric processing with faster throughput and better resource efficiency. Selecting the right dyeing process depends on factors like production volume, fabric type, color consistency demands, and cost efficiency.
Batch dyeing vs Semi-continuous dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com