Stenter machines precisely stretch and dry fabrics to achieve consistent width and enhance fabric stability, improving the overall quality of textile products. Compacting machines reduce fabric shrinkage by compressing fibers, which preserves the fabric's dimensions and softness, ensuring your finished garments maintain their shape and feel after washing.
Table of Comparison
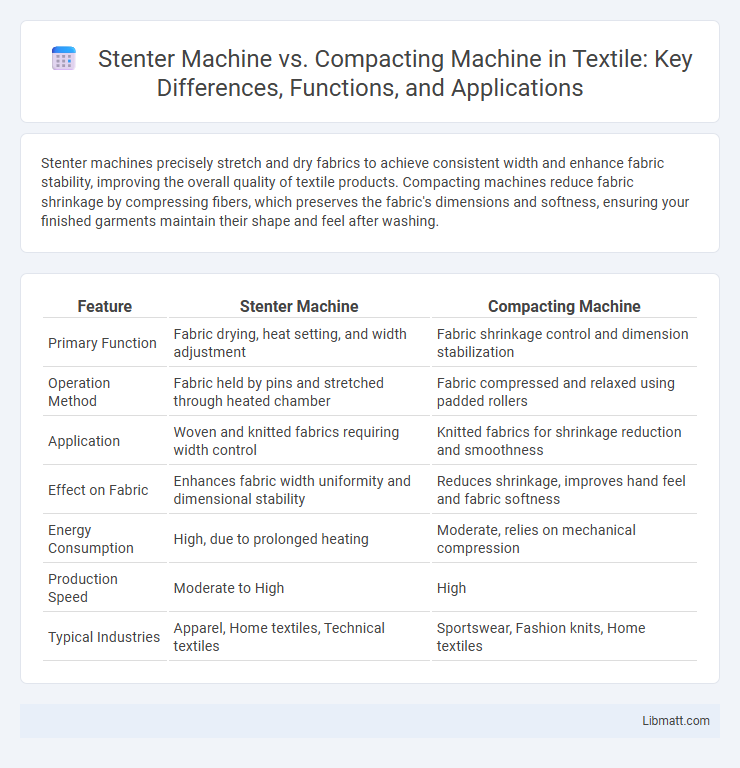
| Feature | Stenter Machine | Compacting Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fabric drying, heat setting, and width adjustment | Fabric shrinkage control and dimension stabilization |
| Operation Method | Fabric held by pins and stretched through heated chamber | Fabric compressed and relaxed using padded rollers |
| Application | Woven and knitted fabrics requiring width control | Knitted fabrics for shrinkage reduction and smoothness |
| Effect on Fabric | Enhances fabric width uniformity and dimensional stability | Reduces shrinkage, improves hand feel and fabric softness |
| Energy Consumption | High, due to prolonged heating | Moderate, relies on mechanical compression |
| Production Speed | Moderate to High | High |
| Typical Industries | Apparel, Home textiles, Technical textiles | Sportswear, Fashion knits, Home textiles |
Introduction to Stenter and Compacting Machines
Stenter machines are essential in textile finishing, used to stretch and dry fabrics to ensure uniform width and enhance texture. Compacting machines focus on reducing fabric shrinkage and improving dimensional stability through controlled compression processes. Understanding the roles of both machines helps optimize your textile production for quality and efficiency.
Basic Functions: Stenter vs Compacting Machine
Stenter machines primarily focus on drying, heat-setting, and finishing woven or knitted fabrics by stretching them to maintain dimensional stability and desired width. Compacting machines concentrate on preventing fabric shrinkage and improving fabric quality by compressing the fabric to control length and width dimensions. Both machines are essential in textile finishing but serve distinct roles: stenters control fabric shape and texture, while compactors enhance fabric density and dimensional stability.
Key Differences in Machinery Design
Stenter machines feature a continuous frame with adjustable pins or clips that hold the fabric as it passes through heated chambers for drying and heat-setting, whereas compacting machines use a compacting roller system to compress and shorten fabric lengthwise to prevent shrinkage. The design of stenter machines emphasizes precise fabric tension control and surface finishing, while compacting machines focus on fabric relaxation and dimensional stability through mechanical compression. Both machines integrate temperature and speed controls, but stenters prioritize uniform heat application, contrasting with the compacting machine's mechanical compaction mechanism.
Process Workflow Comparison
The Stenter machine primarily involves fabric drying, heat setting, and finishing through precise control of temperature and fabric tension, ensuring dimensional stability and color fixation. The Compacting machine focuses on reducing fabric shrinkage by mechanically compressing the fibers after washing, enhancing fabric smoothness and dimensional accuracy. While the Stenter process emphasizes thermal treatment and fabric stabilization, compacting centers on physical contraction and surface improvement for knitted and woven textiles.
Fabric Types Suitable for Each Machine
Stenter machines are ideal for woven and knitted fabrics requiring precise width control and heat setting, commonly used with cotton, polyester, and blended textiles. Compacting machines excel with knitted fabrics like jersey, interlock, and rib knits, enhancing fabric stability and reducing shrinkage. Your choice depends on whether dimensional stability or fabric finish is the priority for your specific textile type.
Impact on Fabric Quality and Shrinkage
Stenter machines enhance fabric quality by providing precise control over fabric width, tension, and drying temperature, resulting in improved fabric smoothness, dimensional stability, and consistent finish. Compacting machines focus on reducing fabric shrinkage by mechanically compressing the fabric after washing or dyeing, ensuring minimal distortion and maintaining the original dimensions during subsequent use. Both machines are critical in textile finishing, with stenters optimizing surface properties and compactors primarily controlling garment shrinkage and fabric stability.
Energy Consumption and Operational Costs
Stenter machines generally consume more energy due to their complex drying and heat-setting processes, leading to higher operational costs compared to compacting machines, which typically use less energy for fabric shrinkage control. The compacting machine's energy-efficient design contributes to reduced utility expenses and lower maintenance requirements. Optimizing production with compacting machines can significantly decrease overall manufacturing costs in textile finishing operations.
Maintenance and Durability
Stenter machines require regular calibration and thorough lubrication of chain guides and clips to ensure long-term functionality, while compacting machines demand more frequent inspection of rollers and belts to prevent fabric tension inconsistencies. Both machines benefit from routine cleaning to remove lint and debris that impact durability, but compacting machines may face higher wear due to constant mechanical pressure on fabric surfaces. High-quality components and adherence to manufacturer maintenance schedules significantly enhance the lifespan of stenter and compacting machines in textile production.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Stenter machines are essential in the textile industry for fabric drying, heat setting, and applying finishes to woven and knitted fabrics, enhancing dimensional stability and surface smoothness. Compacting machines are primarily used for knitted fabric processing, preventing shrinkage by compressing and relaxing fibers to improve fabric width and length stability. Both machines are critical in garment manufacturing, with stenters optimizing fabric quality and compactors ensuring consistent fabric size during production.
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Production Line
Selecting the right machine between a stenter and compacting machine depends on fabric type and production goals, where stenters excel in drying, heat setting, and stretching fabric to stabilize dimensions, while compacting machines specialize in fabric shrinkage control and improving fabric smoothness and hand feel. Production lines requiring precise dimensional stability in woven or knitted textiles benefit from stenter machines, particularly for polyester, nylon, and cotton blends, whereas compacting machines are ideal for knitted fabrics needing shrinkage control and enhanced surface appearance. Evaluating factors such as fabric composition, desired fabric finish, production speed, and quality requirements ensures optimal machine integration for efficient textile processing.
Stenter machine vs Compacting machine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com