Sizing enhances fabric strength and smoothness by applying a protective coating that reduces breakage during weaving, while finishing involves treatments that improve the fabric's appearance, texture, and performance, such as softening, waterproofing, or dyeing. Understanding the difference between sizing and finishing allows you to select textiles that best suit your production and end-use requirements.
Table of Comparison
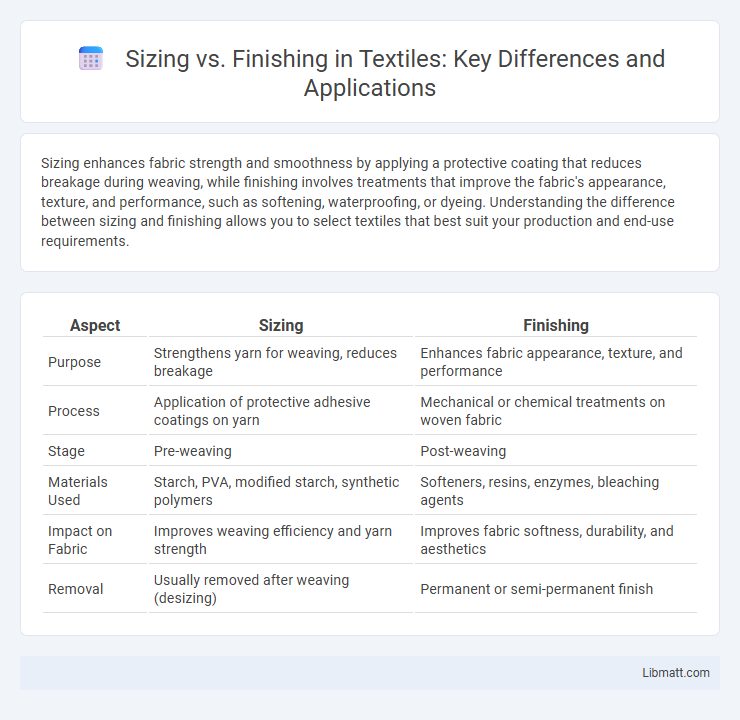
| Aspect | Sizing | Finishing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Strengthens yarn for weaving, reduces breakage | Enhances fabric appearance, texture, and performance |
| Process | Application of protective adhesive coatings on yarn | Mechanical or chemical treatments on woven fabric |
| Stage | Pre-weaving | Post-weaving |
| Materials Used | Starch, PVA, modified starch, synthetic polymers | Softeners, resins, enzymes, bleaching agents |
| Impact on Fabric | Improves weaving efficiency and yarn strength | Improves fabric softness, durability, and aesthetics |
| Removal | Usually removed after weaving (desizing) | Permanent or semi-permanent finish |
Introduction to Sizing and Finishing
Sizing involves applying a protective adhesive coating to yarns or fabrics to enhance strength, reduce breakage, and improve weaving efficiency, predominantly used in textile manufacturing. Finishing includes various chemical or mechanical processes such as bleaching, dyeing, printing, and softening, designed to enhance the fabric's appearance, texture, and performance. Both sizing and finishing are critical in preparing textiles for end-use, impacting durability, aesthetics, and functionality.
Definition of Sizing
Sizing is a crucial textile finishing process that involves applying a protective adhesive coating to yarns before weaving, enhancing their strength and reducing breakage. This treatment improves the yarn's abrasion resistance and weaving efficiency, ensuring smoother machine operation and higher quality fabric production. Your fabric's durability and overall finish significantly benefit from the precision and effectiveness of proper sizing.
Definition of Finishing
Finishing refers to the final processes applied to textiles or papers to enhance appearance, texture, and performance, such as coating, pressing, or chemical treatments. It improves characteristics like durability, colorfastness, and smoothness to meet specific product requirements. Unlike sizing, which primarily strengthens and protects fibers during manufacturing, finishing focuses on the end-use quality and aesthetics.
Key Differences Between Sizing and Finishing
Sizing involves applying a protective coating to fibers or yarns to enhance strength and reduce breakage during weaving, while finishing refers to post-weaving treatments that improve the fabric's texture, appearance, and performance. Sizing primarily focuses on preparing yarns for the weaving process, whereas finishing modifies the final fabric to achieve desired qualities like softness, durability, and wrinkle resistance. Your choice between sizing and finishing impacts the textile production stages and the overall quality of the final fabric product.
Importance of Sizing in Textile Processing
Sizing in textile processing plays a crucial role in strengthening yarns by coating them with a protective adhesive, which reduces breakage during weaving and improves fabric quality. Proper sizing enhances weaving efficiency, minimizes defects, and ensures consistent fabric appearance, directly impacting the durability of your textiles. Finishing complements this by refining texture and appearance, but without effective sizing, the foundational strength and uniformity of the fabric would be compromised.
Role of Finishing in Material Enhancement
Finishing plays a crucial role in material enhancement by improving the surface properties, durability, and appearance of fabrics beyond the foundational support provided by sizing. It involves processes such as coating, calendaring, and heat-setting, which enhance texture, strength, and resistance to wear and environmental factors. Your products benefit from finishing treatments that optimize performance and aesthetic appeal, ensuring higher quality and longer-lasting materials.
Types of Sizing Agents and Their Applications
Sizing agents such as starch, gelatin, and synthetic polymers are applied to textiles to enhance fabric strength, surface smoothness, and printability. Natural sizing agents like starch improve warp yarn strength in weaving, while synthetic alternatives such as polyvinyl alcohol offer superior film-forming properties for industrial fabrics. Specialized agents, including wax-based and resin-based sizings, provide water repellency and wrinkle resistance, catering to applications in apparel and technical textiles.
Common Finishing Techniques and Methods
Common finishing techniques include sanding, polishing, buffing, and coating to enhance surface smoothness, appearance, and durability. Methods such as heat treatment, anodizing, and plating improve material strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. These processes optimize product quality by addressing surface imperfections and functional requirements across various industries.
Impact of Sizing and Finishing on Product Quality
Sizing enhances fabric strength and smoothness by applying adhesives that reduce yarn hairiness, directly improving the durability and appearance of your textile products. Finishing processes, including calendaring, coating, and chemical treatments, further refine texture, color, and function to meet specific quality standards. Both sizing and finishing critically influence product performance, longevity, and market value by optimizing fabric integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Sizing vs Finishing: Which Is More Critical?
Sizing and finishing both play crucial roles in textile production, but sizing is more critical for enhancing fabric strength and reducing warp breakage during weaving. Finishing, while important for improving texture, appearance, and performance, typically occurs after the fabric has been woven and sized. Your choice should depend on whether you prioritize durability during production (sizing) or the final look and feel of the fabric (finishing).
Sizing vs Finishing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com