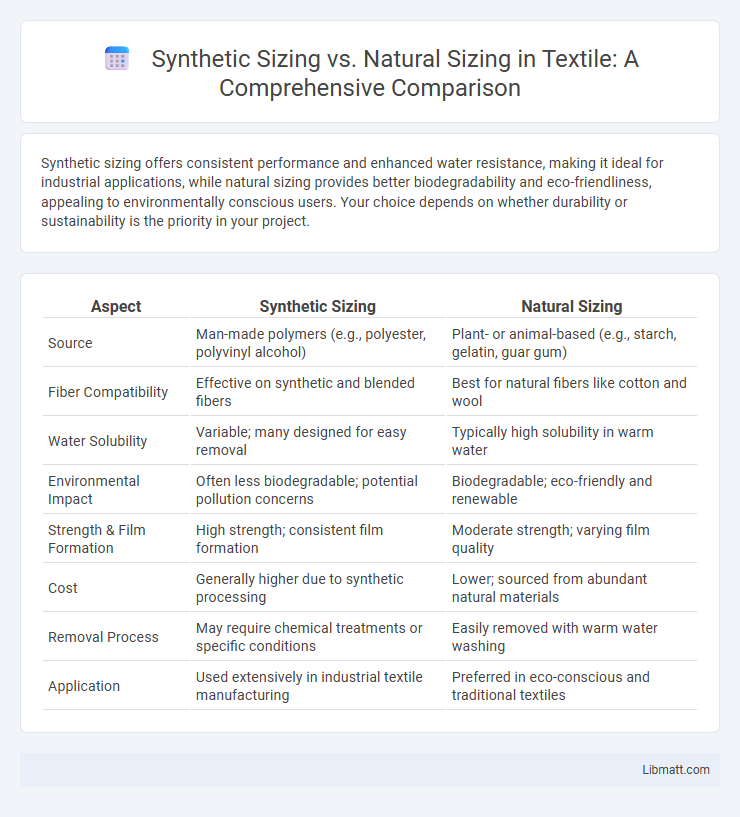
Synthetic sizing offers consistent performance and enhanced water resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications, while natural sizing provides better biodegradability and eco-friendliness, appealing to environmentally conscious users. Your choice depends on whether durability or sustainability is the priority in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synthetic Sizing | Natural Sizing |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Man-made polymers (e.g., polyester, polyvinyl alcohol) | Plant- or animal-based (e.g., starch, gelatin, guar gum) |
| Fiber Compatibility | Effective on synthetic and blended fibers | Best for natural fibers like cotton and wool |
| Water Solubility | Variable; many designed for easy removal | Typically high solubility in warm water |
| Environmental Impact | Often less biodegradable; potential pollution concerns | Biodegradable; eco-friendly and renewable |
| Strength & Film Formation | High strength; consistent film formation | Moderate strength; varying film quality |
| Cost | Generally higher due to synthetic processing | Lower; sourced from abundant natural materials |
| Removal Process | May require chemical treatments or specific conditions | Easily removed with warm water washing |
| Application | Used extensively in industrial textile manufacturing | Preferred in eco-conscious and traditional textiles |
Introduction to Paper Sizing: Synthetic vs Natural
Paper sizing enhances surface strength and printability by controlling absorbency through two main methods: synthetic sizing uses chemical additives like alkyl ketene dimer (AKD) or rosin to create a hydrophobic barrier, while natural sizing relies on agents such as starch or gelatin derived from organic sources. Synthetic sizing provides faster processing, greater water resistance, and improved durability ideal for high-speed printing, whereas natural sizing offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties suited for traditional and archival applications. Your choice between synthetic and natural sizing impacts the paper's performance in ink absorption, durability, and environmental footprint.
Defining Synthetic Sizing Agents
Synthetic sizing agents are chemical compounds engineered to improve the surface properties of paper and textiles by enhancing strength, smoothness, and resistance to water or oil. Unlike natural sizing agents derived from starches, gums, or resins, synthetic sizing agents offer greater consistency, durability, and customization for specific industrial applications. Understanding the distinction helps you select the appropriate sizing type for optimal product performance and longevity.
Understanding Natural Sizing Agents
Natural sizing agents, derived from renewable resources such as starch, cellulose, and proteins, enhance fabric strength and smoothness during weaving by forming a protective film over yarn fibers. These biodegradable materials improve weavability and reduce warp breakage, offering an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic sizing agents, which are typically petroleum-based and less environmentally sustainable. Understanding the chemical composition and performance characteristics of natural sizing agents is crucial for optimizing textile processing and meeting growing demands for sustainable production.
Key Differences Between Synthetic and Natural Sizing
Synthetic sizing is made from chemically engineered polymers designed to provide consistent film strength and improved resistance to moisture and abrasion, whereas natural sizing typically uses animal or plant-based starches offering biodegradable and eco-friendly properties. The uniform molecular structure of synthetic sizing ensures enhanced performance in high-speed papermaking machines, while natural sizing contributes to the paper's surface smoothness and printability. Your choice depends on balancing environmental impact with production efficiency and end-use requirements.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Efficiency
Synthetic sizing offers superior durability compared to natural sizing due to its resistance to moisture, heat, and mechanical wear, making it ideal for industrial textile applications. It enhances efficiency by providing consistent film formation and better adhesion, resulting in smoother weaving and reduced yarn breakage. Natural sizing, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, typically demonstrates lower durability and less uniform application, leading to shorter lifespan and increased maintenance in textile processing.
Environmental Impact: Synthetic vs Natural Sizing
Synthetic sizing often relies on petrochemical-based polymers, contributing to resource depletion and generating non-biodegradable waste that harms ecosystems. Natural sizing uses biodegradable starches or proteins derived from renewable plants, resulting in a lower environmental footprint and improved soil health. Choosing your sizing type can significantly influence the sustainability profile of textile production and reduce ecological impact.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Availability
Synthetic sizing materials often present a more cost-effective option due to lower production expenses and higher scalability, making them widely affordable and readily available in bulk quantities. Natural sizing, derived from organic sources like starch or gelatin, tends to incur higher costs because of limited raw material supply and more complex processing methods, impacting overall affordability. Availability of synthetic sizing is generally more consistent, while natural sizing can fluctuate seasonally or regionally, affecting pricing stability in industrial applications.
Applications in Industry and Art
Synthetic sizing materials, such as polyvinyl acetate and acrylic-based agents, offer enhanced durability and water resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications like textile manufacturing and paper production where long-lasting adhesion and protection are required. Natural sizing agents, including starch and gelatin, are preferred in traditional art restorations and handmade paper due to their eco-friendly properties and compatibility with historical materials. Your choice between synthetic and natural sizing should consider the specific requirements of the application, balancing longevity, environmental impact, and material compatibility.
Recent Innovations in Sizing Technologies
Recent innovations in sizing technologies have transformed both synthetic sizing and natural sizing processes by integrating bio-based polymers and enzyme-enabled formulations that enhance fiber adhesion and fabric performance. Advanced synthetic sizing now incorporates nanotechnology to improve film uniformity and reduce chemical usage, while natural sizing benefits from genetically modified starches that deliver superior stability and biodegradability. These breakthroughs optimize Your textile production by increasing efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring higher-quality fabric finishes.
Choosing the Right Sizing for Your Needs
Choosing the right sizing between synthetic and natural options depends on your specific application requirements and desired fabric performance. Synthetic sizing often offers greater durability, water resistance, and control over shrinkage, making it ideal for industrial or high-performance textiles. Natural sizing, derived from starch or plant-based materials, is biodegradable and generally preferred for eco-friendly products, though it may lack the strength and moisture resistance of synthetic alternatives.
Synthetic sizing vs Natural sizing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com