Warp knit fabrics are created by interlocking loops vertically along the fabric length, resulting in a more stable and less stretchy material ideal for sportswear and lingerie. Weft knit fabrics, produced by horizontal loop interlocking, offer greater elasticity and comfort, making them perfect for t-shirts, sweaters, and casual wear.
Table of Comparison
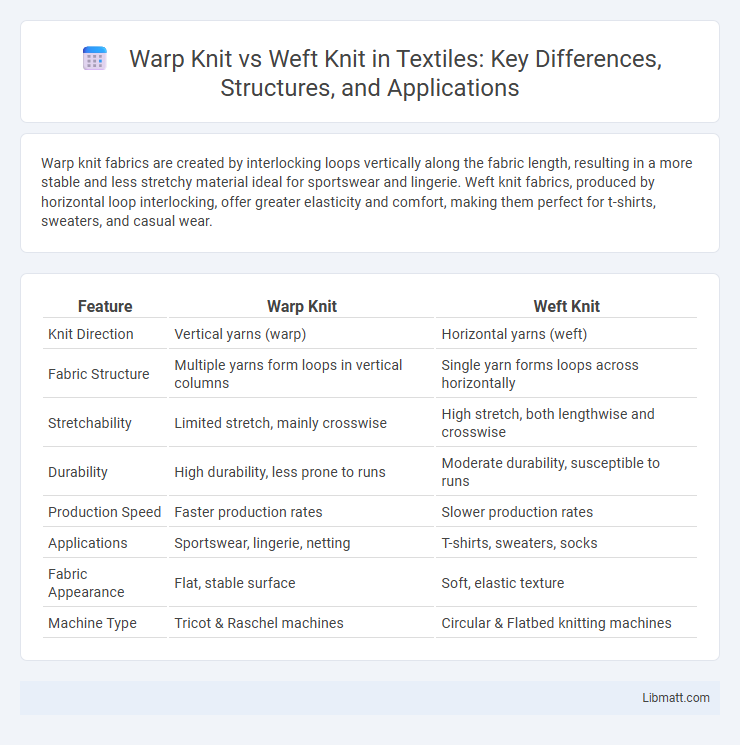
| Feature | Warp Knit | Weft Knit |
|---|---|---|
| Knit Direction | Vertical yarns (warp) | Horizontal yarns (weft) |
| Fabric Structure | Multiple yarns form loops in vertical columns | Single yarn forms loops across horizontally |
| Stretchability | Limited stretch, mainly crosswise | High stretch, both lengthwise and crosswise |
| Durability | High durability, less prone to runs | Moderate durability, susceptible to runs |
| Production Speed | Faster production rates | Slower production rates |
| Applications | Sportswear, lingerie, netting | T-shirts, sweaters, socks |
| Fabric Appearance | Flat, stable surface | Soft, elastic texture |
| Machine Type | Tricot & Raschel machines | Circular & Flatbed knitting machines |
Introduction to Warp Knit and Weft Knit
Warp knit fabrics are created by interlocking yarns vertically along the length of the fabric, offering superior stability and less stretch compared to weft knits. Weft knit fabrics, made by looping yarns horizontally across the width of the fabric, provide greater elasticity and a softer feel, making them ideal for stretchable garments. Understanding the differences between your warp and weft knit options helps in selecting the right fabric for durability, comfort, and specific application needs.
Understanding Warp Knitting
Warp knitting employs parallel yarns that move vertically, creating a stable and durable fabric ideal for sportswear and technical textiles. Unlike weft knitting, which loops yarns horizontally and offers more stretch, warp knitting provides less elasticity but superior resistance to runs and holes. Understanding warp knitting helps you choose fabrics with enhanced strength and shape retention for your projects.
Exploring Weft Knitting
Weft knitting involves creating fabric by interlocking horizontal loops, producing a stretchable and flexible textile ideal for garments requiring comfort and elasticity. The construction enables rapid production of shaped pieces with minimal waste, making it popular for t-shirts, sweaters, and hosiery. Compared to warp knitting, weft knits offer superior stretch and adaptability but tend to have lower dimensional stability and durability.
Key Differences Between Warp and Weft Knit
Warp knit fabric is created by interlocking loops vertically along the length of the fabric, offering high dimensional stability and minimal stretch, making it ideal for activewear and swimwear. Weft knit fabric consists of loops formed horizontally across the width, providing excellent elasticity and comfort, commonly used in t-shirts and sweaters. Your choice between warp knit and weft knit impacts fabric durability, stretchability, and application suitability based on these key structural differences.
Structural Characteristics of Warp and Weft Knits
Warp knits feature yarns that run vertically with loops interlocked in a zigzag pattern along the fabric length, providing high dimensional stability and resistance to runs and laddering. Weft knits have horizontal yarns looped across the fabric width, allowing greater stretch and pliability but less structural stability compared to warp knits. The interlooping direction in warp knits results in faster production and firmer texture, whereas weft knits offer softer, more flexible textiles ideal for apparel that requires elasticity.
Common Applications of Warp Knit Fabrics
Warp knit fabrics are commonly used in activewear, swimwear, and lingerie due to their excellent elasticity, durability, and resistance to runs. These fabrics provide a stable, lightweight structure ideal for sportswear, automotive upholstery, and netting applications. Your choice of warp knit material ensures breathability and quick drying, making it perfect for performance-focused garments.
Typical Uses of Weft Knit Fabrics
Weft knit fabrics are commonly used in garments requiring stretch and comfort, such as T-shirts, sweaters, and activewear, due to their ability to stretch both widthwise and lengthwise. These fabrics are favored for casual wear and underwear because they offer excellent breathability and flexibility, adapting well to body movements. Your choice of weft knit fabric ensures lightweight, soft, and breathable clothing suitable for everyday use and sportswear.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Warp Knitting
Warp knitting offers higher production speeds and superior dimensional stability compared to weft knitting, making it ideal for technical fabrics and lightweight materials. Its advantages include minimal fabric distortion and excellent resistance to runs and ladders, but it generally lacks the stretch and elasticity found in weft knit fabrics. You should consider warp knitting when durability and shape retention are priorities, despite its limited flexibility and comfort for close-fitting garments.
Pros and Cons of Weft Knitting
Weft knitting offers excellent stretch and flexibility, making it ideal for garments that require comfort and body contouring, such as T-shirts and sweaters. However, it tends to unravel easily when cut and may lack the dimensional stability of warp knit fabrics, which can affect durability and shape retention. Your choice depends on whether softness and elasticity are prioritized over strength and structural integrity.
Choosing Between Warp Knit and Weft Knit Fabrics
Choosing between warp knit and weft knit fabrics depends on your project's requirements for stretch, durability, and texture. Warp knit fabrics offer greater stability, less stretch, and superior resistance to runs, making them ideal for activewear and swimwear. Weft knit fabrics provide excellent elasticity and softness, suitable for casual clothing and garments requiring high flexibility.
Warp knit vs Weft knit Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com