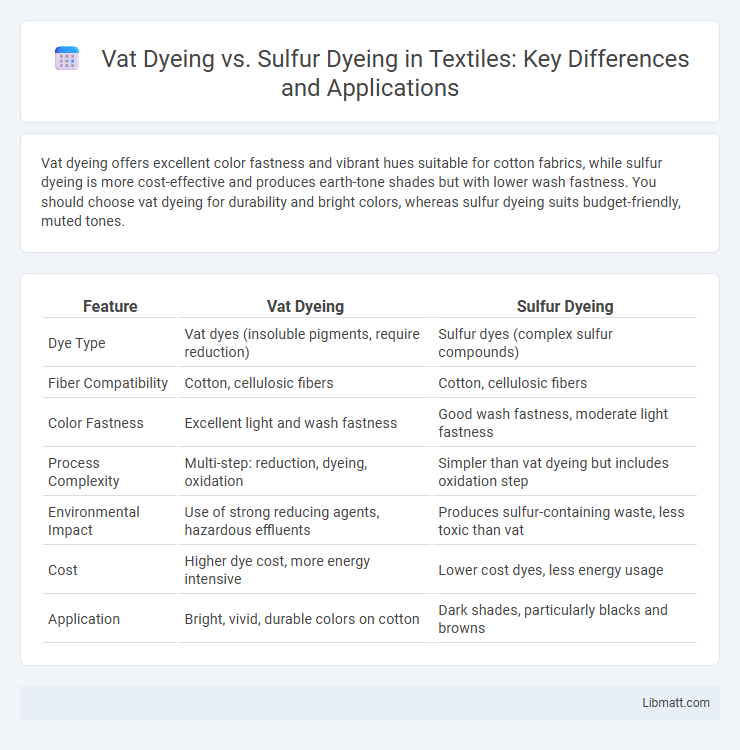
Vat dyeing offers excellent color fastness and vibrant hues suitable for cotton fabrics, while sulfur dyeing is more cost-effective and produces earth-tone shades but with lower wash fastness. You should choose vat dyeing for durability and bright colors, whereas sulfur dyeing suits budget-friendly, muted tones.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vat Dyeing | Sulfur Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Dye Type | Vat dyes (insoluble pigments, require reduction) | Sulfur dyes (complex sulfur compounds) |
| Fiber Compatibility | Cotton, cellulosic fibers | Cotton, cellulosic fibers |
| Color Fastness | Excellent light and wash fastness | Good wash fastness, moderate light fastness |
| Process Complexity | Multi-step: reduction, dyeing, oxidation | Simpler than vat dyeing but includes oxidation step |
| Environmental Impact | Use of strong reducing agents, hazardous effluents | Produces sulfur-containing waste, less toxic than vat |
| Cost | Higher dye cost, more energy intensive | Lower cost dyes, less energy usage |
| Application | Bright, vivid, durable colors on cotton | Dark shades, particularly blacks and browns |
Introduction to Vat Dyeing and Sulfur Dyeing
Vat dyeing involves the use of water-insoluble dyes that are chemically reduced to a soluble form, allowing deep penetration into fibers before oxidizing back to their insoluble state for excellent colorfastness. Sulfur dyeing utilizes sulfur-based dyes that form insoluble compounds within fibers, offering cost-effective and dark-colored results but with moderate wash fastness compared to vat dyes. Your choice between vat and sulfur dyeing depends on factors like fabric type, desired color durability, and production cost considerations.
Chemical Properties and Structures
Vat dyes possess a complex polycyclic structure featuring carbonyl groups that enable reduction into a soluble leuco form, facilitating strong fiber affinity and excellent colorfastness through oxidative regeneration. Sulfur dyes consist of sulfur-containing heterocyclic compounds with sulfide linkages that form insoluble, high-molecular-weight polymers upon oxidation, offering deep, durable shades predominantly on cotton. The contrasting chemical mechanisms--redox reactions in vat dyes versus sulfur polymerization in sulfur dyes--determine their distinct application processes and durability characteristics.
Dyeing Process Overview
Vat dyeing involves a reduction process where the dye is rendered water-soluble in an alkaline solution, allowing it to penetrate the fabric before oxygen exposure restores the dye to its insoluble form. Sulfur dyeing uses a simpler, cost-effective process that involves boiling the fabric with sulfur dyes in an alkaline medium, producing deep, rich colors primarily on cotton fibers. Both methods are valued for their colorfastness, but vat dyeing requires more complex chemical handling compared to the straightforward procedure of sulfur dyeing.
Application Techniques
Vat dyeing involves immersing fabric in a reducing agent solution to make the dye soluble, followed by oxidation to develop color, which works best for cotton and cellulosic fibers. Sulfur dyeing uses a heating process with sulfur compounds to bond the dye to the fabric, offering cost-effective, deep black and olive shades mainly for cotton textiles. Your choice depends on the desired colorfastness, fabric type, and cost considerations during the application process.
Color Fastness Comparison
Vat dyeing offers superior color fastness compared to sulfur dyeing, with excellent resistance to washing, light, and perspiration, making it ideal for durability in textiles. Sulfur dyeing provides moderate fastness, especially against light and washing, but tends to fade more quickly under prolonged exposure. Your choice between these dyeing methods should consider the desired longevity and intensity of color in the fabric.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vat dyeing uses water-intensive processes and strong reducing agents, resulting in significant wastewater with high pollutant loads, making it less sustainable despite producing vibrant, long-lasting colors. Sulfur dyeing, while also involving chemical treatments, generally produces lower toxicity effluents but can generate sulfur compounds that contribute to environmental pollution if not properly managed. You can reduce your environmental footprint by choosing dyeing methods with advanced effluent treatment and sustainable chemical management to minimize water contamination and hazardous waste.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Vat dyeing offers higher colorfastness and durability but involves more complex processing, resulting in higher initial costs compared to sulfur dyeing. Sulfur dyeing is more cost-efficient for large-scale production due to lower material and processing expenses, making it economically suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Your choice depends on balancing long-term fabric quality requirements with immediate cost savings.
Suitability for Different Fibers
Vat dyeing is highly suitable for cellulose fibers such as cotton and linen due to its strong affinity and excellent wash fastness, offering vibrant, long-lasting colors. Sulfur dyeing, on the other hand, is primarily used for cotton and cellulosic fibers as well but is more cost-effective for producing darker shades with moderate wash fastness. Both methods are less effective on synthetic fibers, with vat dyes occasionally adapted for polyester blends, while sulfur dyes generally perform poorly outside natural fibers.
Industrial Usage and Market Trends
Vat dyeing dominates industrial usage for cotton textiles due to its superior colorfastness and ability to produce vibrant, long-lasting shades, especially in denim manufacturing. Sulfur dyeing remains popular in markets demanding economical, earthy tones on cellulosic fibers, prominently in workwear and home textiles where cost efficiency is crucial. Current market trends indicate a gradual shift toward vat dyes in premium and fashion segments driven by sustainability regulations, while sulfur dyes maintain strong presence in bulk, cost-sensitive production.
Challenges and Future Developments
Vat dyeing faces challenges such as high water usage, lengthy processing times, and the need for complex chemical handling, while sulfur dyeing struggles with inconsistent color fastness and environmental pollution caused by sulfur compounds. Future developments aim to enhance eco-friendly processes through enzyme-assisted vat dyeing and improved sulfur dye formulations to reduce toxic byproducts. Innovations also focus on integrating digital monitoring systems to optimize dyeing efficiency and minimize resource consumption in both methods.
Vat dyeing vs Sulfur dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com