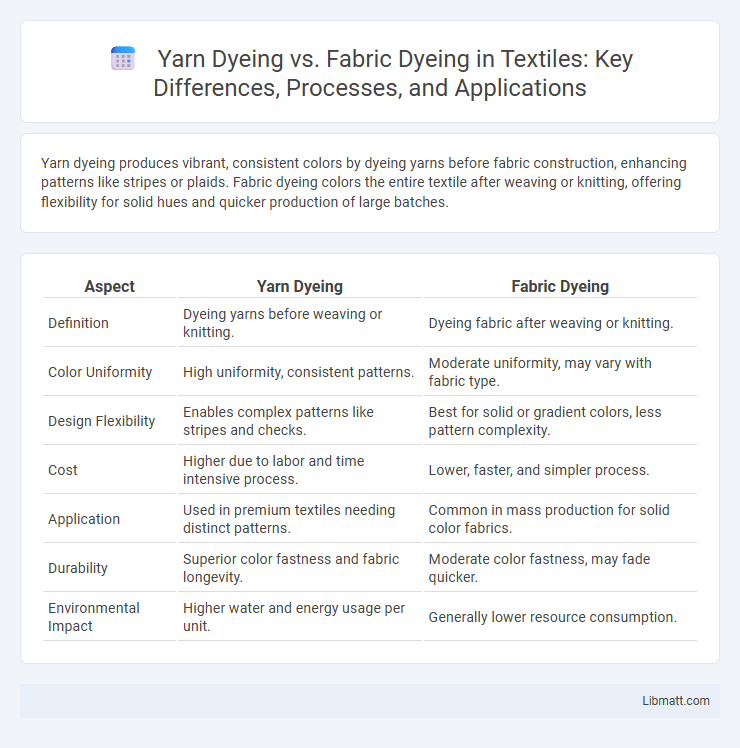
Yarn dyeing produces vibrant, consistent colors by dyeing yarns before fabric construction, enhancing patterns like stripes or plaids. Fabric dyeing colors the entire textile after weaving or knitting, offering flexibility for solid hues and quicker production of large batches.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Yarn Dyeing | Fabric Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing yarns before weaving or knitting. | Dyeing fabric after weaving or knitting. |
| Color Uniformity | High uniformity, consistent patterns. | Moderate uniformity, may vary with fabric type. |
| Design Flexibility | Enables complex patterns like stripes and checks. | Best for solid or gradient colors, less pattern complexity. |
| Cost | Higher due to labor and time intensive process. | Lower, faster, and simpler process. |
| Application | Used in premium textiles needing distinct patterns. | Common in mass production for solid color fabrics. |
| Durability | Superior color fastness and fabric longevity. | Moderate color fastness, may fade quicker. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water and energy usage per unit. | Generally lower resource consumption. |
Introduction to Dyeing Techniques
Yarn dyeing involves coloring fibers before they are woven or knitted into fabric, creating vibrant patterns and colors with enhanced durability and colorfastness. Fabric dyeing, on the other hand, colors entire pieces of textile after they have been formed, allowing for uniform shades but potentially less resistance to fading. Understanding these dyeing techniques helps you choose the best method based on your design needs and fabric performance requirements.
What is Yarn Dyeing?
Yarn dyeing is a textile process where yarns are dyed before being woven or knitted into fabric, allowing for precise color placement and patterns like stripes or checks. This method enhances colorfastness and consistency compared to fabric dyeing, which colors the finished fabric as a whole. Yarn dyeing is commonly used in high-quality garments and upholstery where design accuracy and vibrant hues are essential.
What is Fabric Dyeing?
Fabric dyeing involves coloring entire pieces of woven or knitted textiles after they have been constructed, ensuring uniform hue across the material. Unlike yarn dyeing, which colors individual threads before weaving, fabric dyeing allows for large-scale production and diverse color effects such as gradients or prints. Your choice between fabric dyeing and yarn dyeing depends on the desired pattern complexity, color fastness, and production scalability.
Key Differences Between Yarn and Fabric Dyeing
Yarn dyeing involves coloring individual yarns before weaving or knitting, resulting in vibrant patterns and consistent color penetration throughout the fabric. Fabric dyeing colors the finished textile, allowing for quicker production but potentially less colorfastness and uniformity. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right process based on design complexity, durability, and fabric type.
Advantages of Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing offers superior colorfastness and uniformity, ensuring vibrant and consistent hues throughout the fabric. This process allows for intricate patterns and designs, such as stripes and checks, to be created with precise control over color placement. Your textiles benefit from enhanced durability and a richer, more dimensional appearance compared to fabric dyeing methods.
Advantages of Fabric Dyeing
Fabric dyeing offers precise color control and uniformity, making it ideal for achieving consistent hues on finished textiles. It allows for complex patterns and designs through methods like piece dyeing, enhancing aesthetic versatility. This process also reduces inventory requirements by enabling just-in-time coloring, lowering storage costs and minimizing waste.
Disadvantages of Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing often involves higher production costs and longer lead times compared to fabric dyeing, impacting overall efficiency. It limits color variations within a single fabric piece, restricting design flexibility for your projects. Additionally, uneven dye absorption can result in inconsistent shades, affecting the uniformity of the final product.
Disadvantages of Fabric Dyeing
Fabric dyeing often results in uneven color distribution and fading over time, impacting the garment's overall quality and appearance. It typically consumes more water and energy compared to yarn dyeing, contributing to higher environmental costs. Additionally, fabric dyeing limits design flexibility since patterns must be applied after the fabric is woven, reducing precision in color placement.
Applications and End Uses
Yarn dyeing is primarily used for producing textiles with intricate patterns such as plaids, checks, and stripes, making it ideal for garments, upholstery, and knits that require color fastness and design precision. Fabric dyeing suits large-scale, solid-color applications such as curtains, bed linens, and casual wear where uniform color and cost efficiency are prioritized. Both methods are widely applied in fashion, home textiles, and industrial fabrics, with yarn dyeing favored for texture-rich products and fabric dyeing chosen for versatile, high-volume uses.
Which Dyeing Method is Better?
Yarn dyeing offers superior colorfastness and design precision by dyeing fibers before fabric construction, making it ideal for patterns like plaids and stripes. Fabric dyeing is more versatile and cost-effective for solid colors or bulk production, allowing quicker turnaround times. Your choice depends on the desired pattern complexity, color durability, and production scale.
Yarn Dyeing vs Fabric Dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com