A pantograph is a mechanical device designed for manual tracing and copying of patterns, ideal for simple, low-volume engraving tasks, while a CNC router uses computer numerical control to automate complex cutting, shaping, and carving with high precision and speed. Your choice depends on whether you need traditional hands-on craftsmanship or advanced digital manufacturing for detailed projects.
Table of Comparison
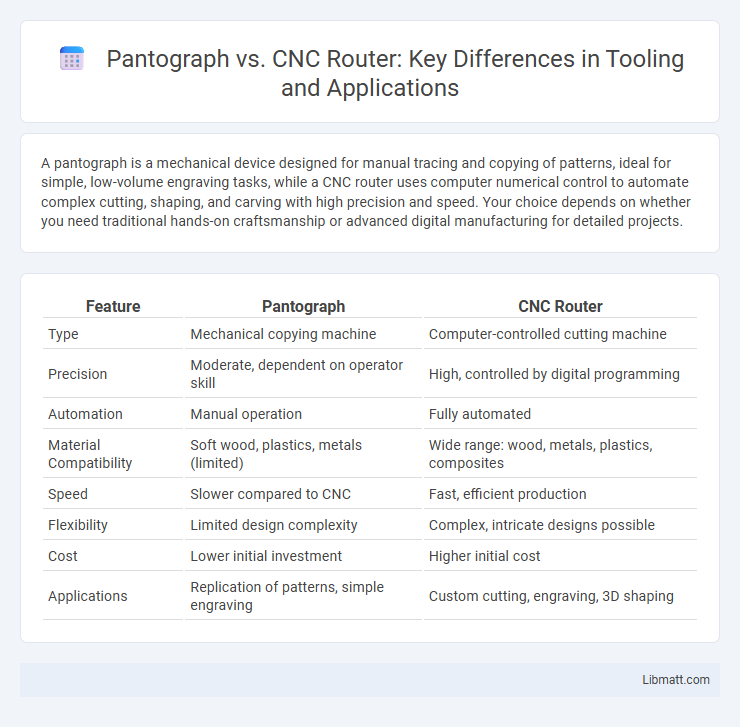
| Feature | Pantograph | CNC Router |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Mechanical copying machine | Computer-controlled cutting machine |
| Precision | Moderate, dependent on operator skill | High, controlled by digital programming |
| Automation | Manual operation | Fully automated |
| Material Compatibility | Soft wood, plastics, metals (limited) | Wide range: wood, metals, plastics, composites |
| Speed | Slower compared to CNC | Fast, efficient production |
| Flexibility | Limited design complexity | Complex, intricate designs possible |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial cost |
| Applications | Replication of patterns, simple engraving | Custom cutting, engraving, 3D shaping |
Introduction to Pantograph and CNC Router
Pantographs are mechanical devices used for scaling and replicating shapes, commonly employed in manual engraving and woodworking for precise pattern duplication. CNC routers, on the other hand, utilize computer numerical control to automate cutting, carving, and milling operations on various materials with high precision and repeatability. The key distinction lies in the pantograph's manual operation versus the CNC router's digital automation, influencing efficiency and complexity of tasks performed.
Understanding Pantograph Mechanisms
Pantograph mechanisms use a system of linked bars to scale and replicate movements, allowing for precise manual control in engraving and copying tasks. Unlike CNC routers, which operate via computer-controlled motors and software for automated cutting, pantographs rely on mechanical leverage to translate input movements to a working surface. This fundamental difference impacts accuracy, flexibility, and the range of materials each machine can effectively handle.
How CNC Routers Work
CNC routers operate using computer numerical control to precisely cut, carve, and shape materials such as wood, plastic, and metal by following programmed instructions. Unlike pantographs that require manual tracing, CNC routers use motors and computerized designs to automate complex patterns with high accuracy and repeatability. Your projects benefit from faster production times and greater detail due to the digital control system embedded in CNC routers.
Key Differences Between Pantograph and CNC Router
Pantographs operate through manual control and mechanical linkage systems, allowing for direct physical tracing to replicate designs, while CNC routers use computer numerical control to automate cutting and shaping with high precision. CNC routers offer greater flexibility with programmable tool paths for complex patterns and faster production speeds, contrasted with the pantograph's limited speed and reliance on operator skill. The CNC router's digital interface enables repeatability and scalability in manufacturing, whereas the pantograph is more suitable for simpler, small-scale engravings and routing tasks.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Pantographs offer moderate precision suitable for engraving and basic shaping tasks, often limited by manual operation and mechanical complexity. CNC routers deliver superior accuracy through computer-controlled movements, achieving tolerances within thousandths of an inch, making them ideal for intricate designs and repeatable production. Your choice depends on the required precision level, with CNC routers excelling in high-accuracy applications.
Applications in Woodworking and Metalworking
Pantographs excel in woodworking for precise engraving and duplicating intricate designs on furniture and decorative panels, offering manual control ideal for artisanal craftsmanship. CNC routers dominate metalworking applications by providing high-speed, automated cutting, milling, and shaping of complex metal parts with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the traditional, hands-on approach of pantographs or the advanced, programmable capabilities of CNC routers for detailed woodworking or robust metal fabrication.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Pantographs generally require a lower initial investment compared to CNC routers, making them more cost-effective for small-scale or hobbyist projects. CNC routers demand a higher upfront cost due to advanced computer-controlled technology but offer greater precision and automation, which can increase productivity and reduce long-term operational expenses. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with desired accuracy and production volume.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Pantographs offer straightforward operation with manual controls, making them accessible for beginners and hobbyists with minimal training. CNC routers require understanding of computer-aided design (CAD) software and G-code programming, which involves a steeper learning curve but provides greater precision and automation. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity and hands-on use or advanced control and efficiency.
Maintenance and Longevity
Pantographs require regular manual calibration and mechanical upkeep to maintain precision, while CNC routers benefit from automated calibration and software diagnostics that streamline maintenance. The longevity of a pantograph depends heavily on the quality of its mechanical parts and consistent servicing, whereas CNC routers typically have longer lifespans due to advanced hardware durability and easier component replacement. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between maintenance effort and equipment lifespan to optimize productivity.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Pantographs provide a cost-effective solution for simple, small-scale engraving and duplicating tasks, ideal for hobbyists or businesses with limited budgets and basic design requirements. CNC routers offer superior precision, automation, and versatility, making them suitable for complex projects and higher production volumes, especially in professional manufacturing environments. Evaluating your project complexity, material types, and production scale will help determine whether a pantograph or CNC router aligns best with your specific needs.
Pantograph vs CNC router Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com