A punch press uses a movable punch to shear or shape metal by pressing it into a die, ideal for creating simple holes and shapes with precision. A stamping press performs a wider range of metal forming operations, including bending, embossing, and flanging, making it suitable for complex parts and high-volume production.
Table of Comparison
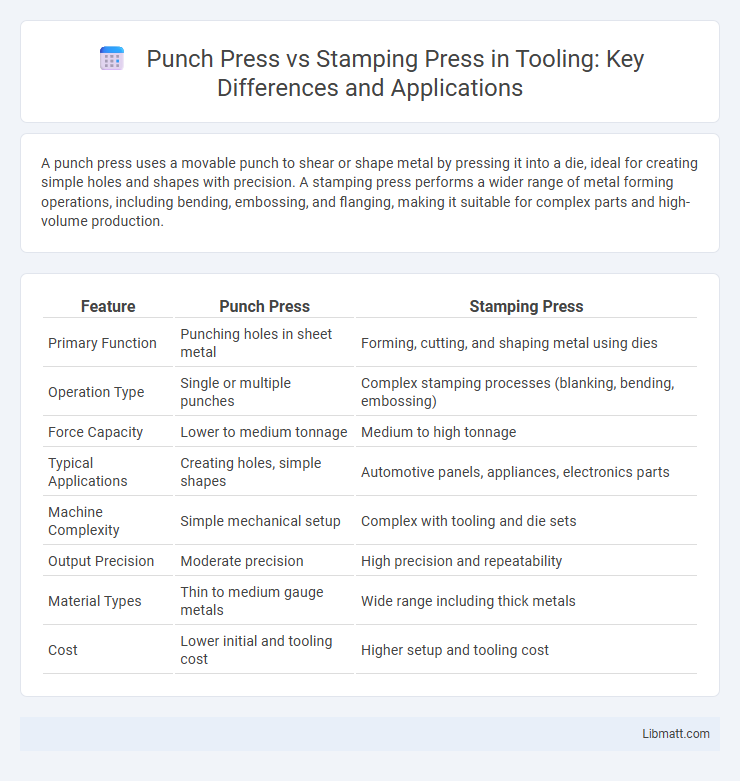
| Feature | Punch Press | Stamping Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Punching holes in sheet metal | Forming, cutting, and shaping metal using dies |
| Operation Type | Single or multiple punches | Complex stamping processes (blanking, bending, embossing) |
| Force Capacity | Lower to medium tonnage | Medium to high tonnage |
| Typical Applications | Creating holes, simple shapes | Automotive panels, appliances, electronics parts |
| Machine Complexity | Simple mechanical setup | Complex with tooling and die sets |
| Output Precision | Moderate precision | High precision and repeatability |
| Material Types | Thin to medium gauge metals | Wide range including thick metals |
| Cost | Lower initial and tooling cost | Higher setup and tooling cost |
Overview: Punch Press vs Stamping Press
Punch press machines primarily perform shearing operations by applying linear force to cut or shape metal sheets using a punch and die set, ideal for producing precise holes and shapes. Stamping presses encompass a broader range of metal forming processes including punching, bending, embossing, and coining, making them versatile for complex part manufacturing in automotive and appliance industries. Both machines vary in operation speed, force capacity, and tooling complexity, with stamping presses generally designed for high-volume production requiring intricate design details.
Key Differences Between Punch and Stamping Presses
Punch presses primarily perform shearing operations by driving a punch through material to create holes or shapes, while stamping presses apply a broader range of forming processes, including bending, embossing, and coining. The key difference lies in their tooling and versatility; punch presses use simple single tools for cutting, whereas stamping presses employ complex dies for multiple simultaneous operations. Your choice depends on the complexity of the metalworking task, with punch presses suited for straightforward cutting and stamping presses ideal for intricate forming and shaping.
How Punch Presses Work
Punch presses operate by driving a ram downward to force a tool through a workpiece, cutting or shaping metal with precision. The machine uses mechanical or hydraulic power to deliver controlled force, enabling repetitive punching, blanking, or forming operations on sheet metal. Your manufacturing efficiency improves with punch presses due to their ability to produce consistent, high-quality parts quickly.
How Stamping Presses Operate
Stamping presses operate by applying high force using a ram, which drives a die into the material to create precise shapes through cutting, bending, or forming. These presses typically utilize mechanical, hydraulic, or servo-driven mechanisms to control speed and pressure for consistent, high-volume production. Your understanding of stamping press operation can enhance efficiency in manufacturing processes requiring detailed metalworking.
Applications of Punch Presses
Punch presses excel in applications involving precise metal cutting, bending, and shaping, ideal for manufacturing components like brackets, clips, and enclosures. These machines are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics for producing detailed parts with consistent accuracy. Your choice of a punch press ensures efficient, high-volume output where dimensional precision and repeatability are critical.
Applications of Stamping Presses
Stamping presses are widely used in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and appliance industries for shaping and cutting metal sheets into precise components. Their ability to perform complex operations such as blanking, embossing, and coining makes them essential for high-volume production of parts like car body panels and electronic enclosures. You can rely on stamping presses to deliver consistent accuracy and efficiency in forming metal parts for diverse industrial applications.
Material Compatibility: Punch vs Stamping Press
Punch presses excel in working with softer materials such as aluminum, brass, and mild steel, offering precise hole punching and shaping capabilities. Stamping presses are designed to handle a broader range of materials, including high-strength steel and stainless steel, making them suitable for forming, embossing, and complex shaping tasks. Material compatibility in punch vs stamping presses depends largely on thickness, hardness, and the required precision of the final product.
Cost Comparison and Efficiency
Punch presses generally have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance requirements compared to stamping presses, making them more cost-effective for small to medium production runs. Stamping presses offer higher efficiency in large-scale manufacturing due to faster cycle times and the ability to perform complex, multi-step operations in one press. Selecting between the two depends on production volume and component complexity, with punch presses excelling in lower-cost prototyping and stamping presses optimizing high-volume batch processing.
Pros and Cons: Punch Presses vs Stamping Presses
Punch presses offer precise, cost-effective solutions for simple cutting and forming tasks, making them ideal for low to medium production volumes, but they may struggle with complex shapes and thicker materials. Stamping presses excel in high-volume manufacturing with superior speed and the ability to handle intricate designs and heavier gauge metals, although they require higher upfront investment and maintenance costs. Your choice depends on balancing production demands, part complexity, and budget considerations between the punch press's versatility and the stamping press's efficiency.
Choosing the Right Press for Your Manufacturing Needs
Selecting between a punch press and a stamping press depends on your specific manufacturing requirements, such as material thickness, production volume, and desired precision. Punch presses are ideal for creating holes or simple shapes in sheet metal with high accuracy, while stamping presses offer greater versatility for complex forms and embossing. Your decision should align with the type of operation, tooling investment, and cycle time considerations to optimize production efficiency.
Punch press vs stamping press Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com