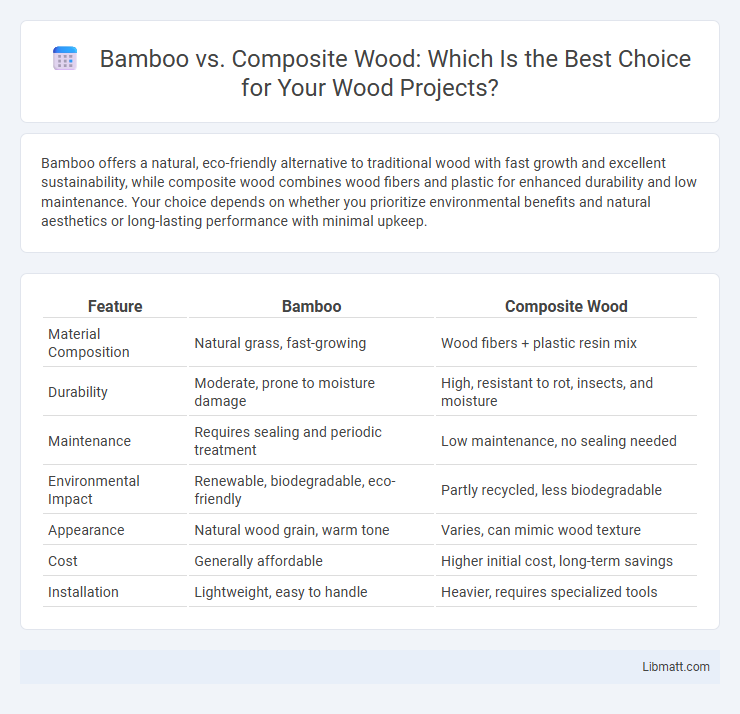
Bamboo offers a natural, eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood with fast growth and excellent sustainability, while composite wood combines wood fibers and plastic for enhanced durability and low maintenance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize environmental benefits and natural aesthetics or long-lasting performance with minimal upkeep.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo | Composite Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural grass, fast-growing | Wood fibers + plastic resin mix |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to moisture damage | High, resistant to rot, insects, and moisture |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing and periodic treatment | Low maintenance, no sealing needed |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, eco-friendly | Partly recycled, less biodegradable |
| Appearance | Natural wood grain, warm tone | Varies, can mimic wood texture |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Higher initial cost, long-term savings |
| Installation | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier, requires specialized tools |
Introduction: Understanding Bamboo and Composite Wood
Bamboo is a fast-growing, renewable grass known for its natural strength, flexibility, and sustainability, often used in flooring and furniture due to its eco-friendly properties. Composite wood is manufactured from a blend of wood fibers, plastics, and additives, designed for durability, low maintenance, and resistance to moisture and insects. Both materials offer distinct environmental benefits and performance characteristics, making them popular choices in construction and interior design.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Bamboo is a natural, fast-growing grass composed primarily of cellulose and lignin, harvested and processed through cutting, drying, and treatment to enhance durability. Composite wood combines wood fibers or sawdust with plastic resins, typically polyethylene or polypropylene, undergoing extrusion or molding to produce a uniform, weather-resistant material. The manufacturing process of composite wood involves blending recycled wood and plastic, resulting in a low-maintenance product with consistent performance properties compared to the organic, variable nature of bamboo.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact compared to composite wood due to its rapid growth rate, typically reaching maturity within 3-5 years, and its ability to sequester high levels of carbon dioxide. Composite wood, while often made from recycled materials, relies heavily on synthetic resins and adhesives, which can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and include non-renewable resources. The sustainability of bamboo is enhanced by its biodegradability and minimal need for pesticides or fertilizers, contrasting with the energy-intensive manufacturing process of composite wood that affects its overall carbon footprint.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Bamboo offers impressive durability with a natural resistance to moisture and insects, often lasting up to 20-25 years when properly maintained. Composite wood combines wood fibers and plastic, providing enhanced resistance to rot, decay, and warping, with an average lifespan of 25-30 years or more in outdoor applications. Your choice depends on balancing bamboo's eco-friendly appeal with composite wood's superior longevity and low maintenance benefits.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bamboo requires regular cleaning and periodic sealing to prevent moisture damage and maintain its natural appearance. Composite wood demands minimal maintenance, needing only occasional washing to remove dirt and debris, and is resistant to rot, insects, and fading. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the eco-friendly appeal of bamboo with more upkeep or the low-maintenance durability of composite wood.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Bamboo offers a natural, warm aesthetic with unique grain patterns that enhance eco-friendly designs, while composite wood delivers consistent colors and textures ideal for modern and customizable finishes. The durability and weather resistance of composite wood make it suitable for intricate outdoor projects, whereas bamboo's flexibility supports creative, organic shapes in interior applications. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize natural beauty or design adaptability in your space.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Bamboo decking typically has a lower upfront cost compared to composite wood, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Composite wood often carries higher initial expenses but offers enhanced durability and minimal maintenance, which reduces long-term costs. Over time, bamboo may require more frequent repairs or replacements due to its susceptibility to moisture and insect damage, impacting overall lifecycle expenses.
Indoor and Outdoor Applications
Bamboo offers superior sustainability and rapid growth, making it ideal for indoor flooring and furniture due to its natural aesthetic and durability. Composite wood, made from a blend of wood fibers and plastic, excels in outdoor applications like decking and fencing because of its resistance to moisture, rot, and insect damage. Both materials provide eco-friendly alternatives, but composite wood's enhanced weather resistance gives it a distinct advantage in exposed outdoor environments.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bamboo is a natural, non-toxic material that is often favored for its hypoallergenic properties and resistance to mold and mildew, promoting healthier indoor air quality. Composite wood contains resins and adhesives, such as formaldehyde, which can off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs), potentially affecting respiratory health if not properly sealed or ventilated. Your choice should prioritize materials with low VOC emissions and certifications like GREENGUARD to ensure safe indoor environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Bamboo offers exceptional sustainability and rapid renewability, making it ideal for environmentally conscious projects, while composite wood provides superior durability and low maintenance for long-lasting applications. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize eco-friendliness with natural aesthetics or require resistance to weather, insects, and decay. Evaluate your specific project needs, budget, and environmental goals to select the most suitable material for optimal performance and satisfaction.
Bamboo vs composite wood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com