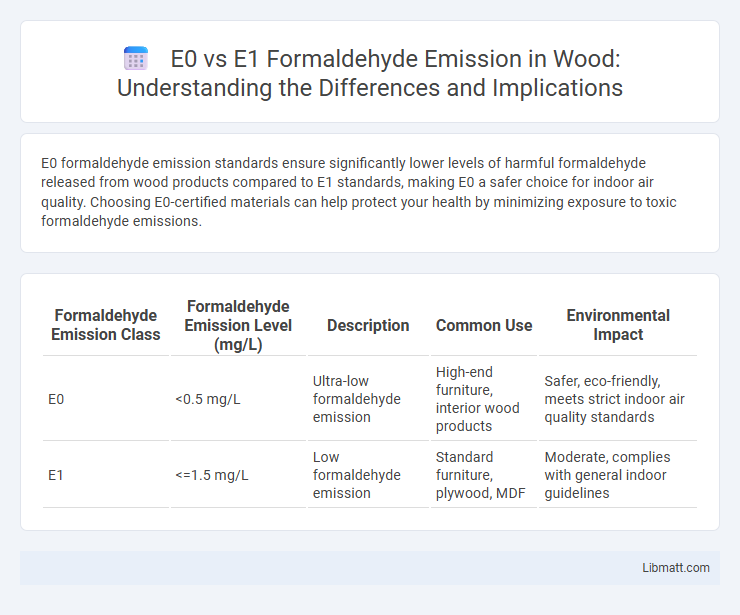
E0 formaldehyde emission standards ensure significantly lower levels of harmful formaldehyde released from wood products compared to E1 standards, making E0 a safer choice for indoor air quality. Choosing E0-certified materials can help protect your health by minimizing exposure to toxic formaldehyde emissions.
Table of Comparison
| Formaldehyde Emission Class | Formaldehyde Emission Level (mg/L) | Description | Common Use | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E0 | <0.5 mg/L | Ultra-low formaldehyde emission | High-end furniture, interior wood products | Safer, eco-friendly, meets strict indoor air quality standards |
| E1 | <=1.5 mg/L | Low formaldehyde emission | Standard furniture, plywood, MDF | Moderate, complies with general indoor guidelines |
Introduction to Formaldehyde Emission Standards
E0 and E1 formaldehyde emission standards regulate the permissible levels of formaldehyde released from wood-based products, ensuring indoor air quality safety. E0 represents ultra-low emissions with formaldehyde content less than 0.5 mg/L, making it suitable for sensitive environments, while E1 allows slightly higher emissions up to 1.5 mg/L, commonly used in residential and commercial settings. Understanding these standards helps you select materials that minimize health risks associated with formaldehyde exposure.
What is E0 Formaldehyde Emission?
E0 formaldehyde emission refers to the lowest formaldehyde emission class, typically defined as less than 0.5 mg/L of formaldehyde released from composite wood products. This standard signifies ultra-low formaldehyde emissions, ensuring superior indoor air quality and minimal health risks related to formaldehyde exposure. E0 is often preferred in environments demanding heightened safety, such as schools, hospitals, and residential areas.
Understanding E1 Formaldehyde Emission
E1 formaldehyde emission standards allow a maximum release of 0.1 parts per million (ppm), which is higher than the stricter E0 standard limiting emissions to 0.005 ppm. E1 boards are commonly used in furniture manufacturing, offering a balance between cost and indoor air quality by adhering to regulated formaldehyde limits. Understanding E1 formaldehyde emission is crucial for evaluating material safety in environments requiring low volatile organic compound (VOC) exposure.
Key Differences Between E0 and E1 Standards
E0 and E1 formaldehyde emission standards differ primarily in their maximum allowable formaldehyde release levels, with E0 limits set at <=0.5 mg/L and E1 allowing up to 1.5 mg/L. E0-certified products are considered ultra-low emission, ideal for sensitive environments such as homes with children or individuals with respiratory issues, whereas E1 is widely accepted for general indoor use. The stricter E0 standard ensures better indoor air quality by significantly reducing formaldehyde exposure compared to E1-certified materials.
Health Impacts of Formaldehyde Exposure
E0 formaldehyde emission levels are significantly lower than E1, reducing the risk of respiratory issues, eye irritation, and allergic reactions linked to formaldehyde exposure. Prolonged contact with E1-grade materials can increase your chances of developing asthma or other chronic health conditions due to higher formaldehyde release. Choosing E0-rated products helps minimize indoor air pollution and protects long-term health by maintaining safer formaldehyde concentrations.
Regulatory Guidelines for E0 and E1 Emissions
E0 and E1 formaldehyde emission standards are governed by strict regulatory guidelines set by organizations like CARB (California Air Resources Board) and the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). E0 emissions are classified as ultra-low, typically less than 0.5 parts per million (ppm), meeting the most stringent health and safety standards for indoor air quality. E1 emissions permit up to 0.5 ppm of formaldehyde, complying with industry regulations but representing a higher emission threshold compared to E0 standards.
E0 vs E1: Which is Safer for Indoor Environments?
E0 formaldehyde emission standards represent the lowest allowable limit, typically <=0.5 mg/L, compared to E1 standards, which allow up to 1.5 mg/L, making E0 significantly safer for indoor air quality. Your indoor environment benefits from using E0-certified materials as they emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing health risks such as respiratory irritation and allergic reactions. Choosing E0 over E1 ensures a healthier and more sustainable living space with minimal formaldehyde exposure.
Product Applications: E0 and E1 Certified Materials
E0 certified materials are primarily used in environments demanding ultra-low formaldehyde emissions, such as furniture for nurseries, children's rooms, and healthcare facilities, ensuring enhanced indoor air quality. E1 certified materials suit general applications including cabinetry, flooring, and office furniture where formaldehyde emissions must meet stringent, yet less restrictive, regulatory standards. Both E0 and E1 certifications are critical in sustainable building practices, supporting compliance with global green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM.
How to Identify E0 and E1 Certified Products
E0 and E1 formaldehyde emission standards are determined by measuring the release of formaldehyde gas from wood products, with E0 certified products emitting <=0.5 mg/L and E1 certified products emitting <=1.5 mg/L. Identification of E0 and E1 certified products is typically done through product labels or technical datasheets that specify compliance with formaldehyde emission limits set by regulatory bodies such as CARB (California Air Resources Board) or the European E.U. standards. Consumers and builders should look for certification marks or official documents that verify the product has been tested and meets the stringent E0 or E1 formaldehyde emission criteria, ensuring healthier indoor air quality.
Choosing the Right Formaldehyde Emission Standard for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate formaldehyde emission standard depends on your specific health and environmental safety requirements, with E0 representing the lowest emission level (<=0.5 mg/L) suitable for sensitive indoor environments and E1 allowing slightly higher emissions (<=1.5 mg/L) commonly used in general construction. Understanding the differences between E0 and E1 ensures compliance with regulations and minimizes indoor air pollution risks. Prioritizing E0-rated materials offers superior protection against formaldehyde exposure, essential for households with children or individuals with respiratory concerns.
E0 vs E1 formaldehyde emission Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com