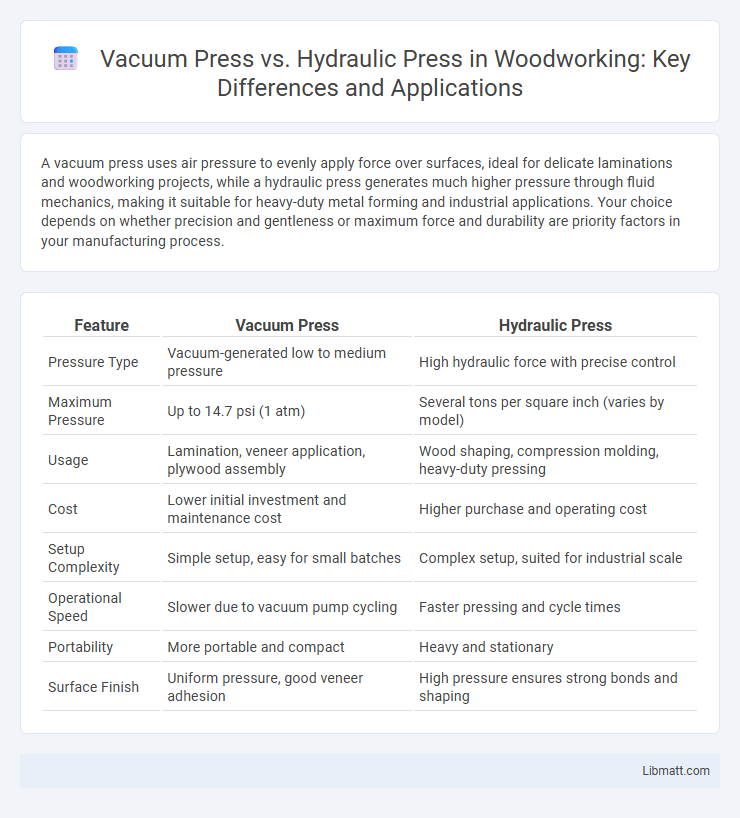
A vacuum press uses air pressure to evenly apply force over surfaces, ideal for delicate laminations and woodworking projects, while a hydraulic press generates much higher pressure through fluid mechanics, making it suitable for heavy-duty metal forming and industrial applications. Your choice depends on whether precision and gentleness or maximum force and durability are priority factors in your manufacturing process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Type | Vacuum-generated low to medium pressure | High hydraulic force with precise control |
| Maximum Pressure | Up to 14.7 psi (1 atm) | Several tons per square inch (varies by model) |
| Usage | Lamination, veneer application, plywood assembly | Wood shaping, compression molding, heavy-duty pressing |
| Cost | Lower initial investment and maintenance cost | Higher purchase and operating cost |
| Setup Complexity | Simple setup, easy for small batches | Complex setup, suited for industrial scale |
| Operational Speed | Slower due to vacuum pump cycling | Faster pressing and cycle times |
| Portability | More portable and compact | Heavy and stationary |
| Surface Finish | Uniform pressure, good veneer adhesion | High pressure ensures strong bonds and shaping |
Introduction to Vacuum Press and Hydraulic Press
Vacuum presses use atmospheric pressure to evenly bond materials by removing air between layers, making them ideal for woodworking, laminating, and composite fabrication. Hydraulic presses generate high mechanical force through fluid power, suitable for metal forming, molding, and heavy-duty industrial applications. Understanding the operational differences between your vacuum press and hydraulic press helps optimize efficiency and material compatibility in manufacturing processes.
How Vacuum Presses Work
Vacuum presses operate by creating a vacuum that removes air between the pressing surfaces, causing atmospheric pressure to evenly press materials together without the need for heavy mechanical force. This process allows for gentle, uniform pressure ideal for tasks like veneering, laminating, and woodworking. Your projects benefit from precise control and reduced risk of damaging delicate materials compared to hydraulic presses.
How Hydraulic Presses Operate
Hydraulic presses operate by using a hydraulic cylinder filled with fluid to generate a compressive force, leveraging Pascal's principle to amplify pressure onto the workpiece. This mechanism allows precise control over force and speed, making hydraulic presses ideal for heavy-duty applications such as metal forming, molding, and assembly. Unlike vacuum presses that rely on atmospheric pressure differential, hydraulic presses provide consistent, high-pressure output capable of deforming tougher materials.
Key Differences Between Vacuum and Hydraulic Presses
Vacuum presses use suction to apply even pressure over a surface, ideal for delicate materials and lamination tasks, while hydraulic presses rely on fluid power to generate high force, suitable for heavy-duty shaping and molding. You'll find vacuum presses offer gentler pressure with precise control, whereas hydraulic presses provide greater force versatility and durability for industrial applications. Understanding these differences helps optimize your choice for specific manufacturing needs, balancing pressure type, force capacity, and material sensitivity.
Applications of Vacuum Presses
Vacuum presses are widely used in woodworking, laminating, and composite material applications where delicate materials require uniform pressure distribution without damaging the substrate. Their versatility allows them to handle complex shapes and thin veneers, making them ideal for veneer pressing, plywood manufacturing, and art restoration tasks. Industries such as automotive and aerospace utilize vacuum presses to produce lightweight composite panels with precise bonding and minimal voids.
Applications of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses are widely utilized in automotive manufacturing, metal forming, and industrial forging due to their ability to exert controlled, high-pressure force for shaping and assembling materials. Your production process can benefit from hydraulic presses when precise pressure control and heavy-duty operations such as stamping, molding, and deep drawing are required. These presses are integral in applications demanding consistent force over large surfaces, making them ideal for fabricating metal panels, composite materials, and large-scale industrial components.
Advantages of Using a Vacuum Press
Vacuum presses offer precise and even pressure distribution, making them ideal for delicate materials and detailed laminations. They use air pressure to apply force uniformly, reducing the risk of damaging your workpieces compared to the intense force of hydraulic presses. This method enhances material consistency and improves overall product quality in woodworking, composites, and crafts.
Benefits of Choosing a Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press offers significantly higher force and precision compared to a vacuum press, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as metal forming, molding, and forging. Its ability to generate consistent pressure throughout the entire pressing area ensures superior product quality and uniformity in manufacturing processes. Hydraulic presses also provide better control over speed and force, resulting in enhanced safety and efficiency in production environments.
Cost Considerations: Vacuum vs Hydraulic Press
Vacuum presses generally have a lower initial cost and reduced maintenance expenses compared to hydraulic presses, making them ideal for small to medium-scale applications where budget is limited. Hydraulic presses require higher upfront investment and ongoing costs due to complex components and hydraulic fluid maintenance, but they offer superior force and precision for heavy-duty industrial tasks. Your choice should balance project scale and budget constraints while considering long-term operational expenses for optimal cost efficiency.
Which Press is Best for Your Project?
Choosing between a vacuum press and a hydraulic press depends on project requirements such as material type, pressure needs, and precision. Vacuum presses are ideal for delicate laminations, thin veneers, and composite materials due to their even pressure distribution and low cost. Hydraulic presses provide higher pressure capacity suitable for heavy-duty tasks like metal forming, deep embossing, and thick laminations, offering greater force and durability.
Vacuum press vs Hydraulic press Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com