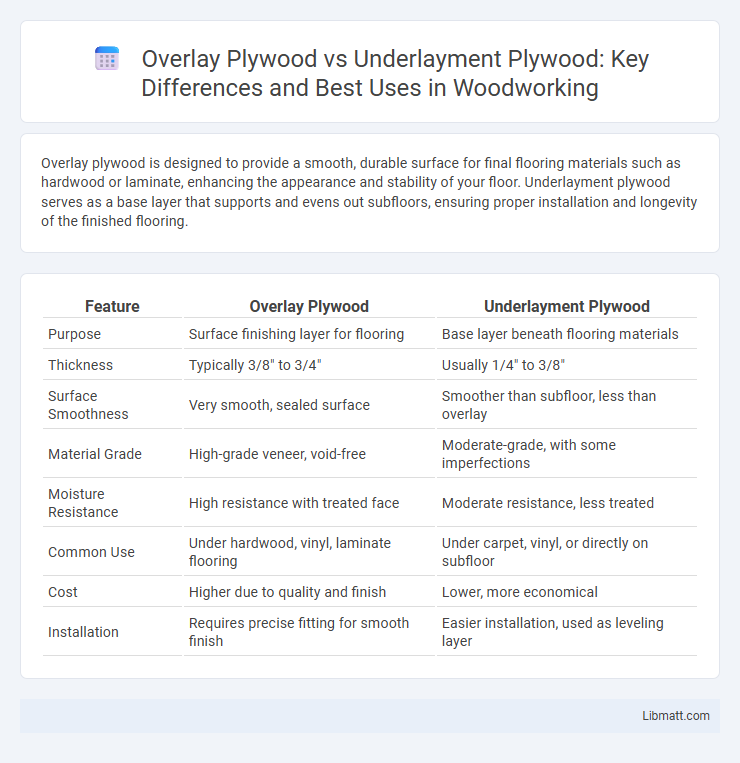
Overlay plywood is designed to provide a smooth, durable surface for final flooring materials such as hardwood or laminate, enhancing the appearance and stability of your floor. Underlayment plywood serves as a base layer that supports and evens out subfloors, ensuring proper installation and longevity of the finished flooring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Overlay Plywood | Underlayment Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface finishing layer for flooring | Base layer beneath flooring materials |
| Thickness | Typically 3/8" to 3/4" | Usually 1/4" to 3/8" |
| Surface Smoothness | Very smooth, sealed surface | Smoother than subfloor, less than overlay |
| Material Grade | High-grade veneer, void-free | Moderate-grade, with some imperfections |
| Moisture Resistance | High resistance with treated face | Moderate resistance, less treated |
| Common Use | Under hardwood, vinyl, laminate flooring | Under carpet, vinyl, or directly on subfloor |
| Cost | Higher due to quality and finish | Lower, more economical |
| Installation | Requires precise fitting for smooth finish | Easier installation, used as leveling layer |
Introduction to Overlay Plywood and Underlayment Plywood
Overlay plywood features a smooth surface designed for visible applications such as furniture or cabinetry, providing durability and a refined finish. Underlayment plywood serves as a supportive base beneath flooring materials, ensuring stability and preventing surface imperfections. Your choice depends on whether the plywood will be exposed or hidden beneath other layers.
Defining Overlay Plywood: Structure and Uses
Overlay plywood features a smooth, durable surface typically coated with phenolic resin or melamine, enhancing moisture resistance and wear durability. It consists of multiple veneer layers bonded with waterproof adhesive, making it ideal for outdoor applications like concrete formwork, cabinet panels, and exterior furniture. Its robust structure allows superior adhesion for laminates and paints, distinguishing it from underlayment plywood, which primarily serves as a preparatory layer beneath flooring materials.
Understanding Underlayment Plywood: Essential Features
Underlayment plywood is designed to provide a smooth, stable surface for finishing materials like vinyl or hardwood flooring, featuring a thinner construction compared to standard plywood. Its essential features include a sanded, smooth face to minimize imperfections and reduce telegraphing of underlying joints, along with resistance to moisture and warping. This type of plywood also typically has fewer voids and knots, ensuring durability and an even base for floor coverings.
Key Differences Between Overlay and Underlayment Plywood
Overlay plywood features a smooth, water-resistant surface designed for direct finishing applications like laminates and veneers, enhancing durability and aesthetics. Underlayment plywood typically has a thinner, uniform-grade surface meant to provide a stable, flat base for floor coverings such as vinyl or carpet, ensuring minimal telegraphing of subfloor imperfections. The key differences lie in surface quality, moisture resistance, and intended use, with overlay plywood optimized for visible finishing layers and underlayment plywood for subfloor support.
Material Composition and Surface Quality
Overlay plywood features a smooth, high-grade veneer surface that enhances paint adhesion and aesthetic appeal, typically made from hardwood species like birch or maple. Underlayment plywood, constructed from softwood cores with a thinner, sanded face, provides a smooth, defect-free surface ideal for laying floor coverings but has less durability in appearance compared to overlay plywood. The material composition differences impact both the surface quality and suitability for specific applications, with overlay plywood offering superior surface finish for visible areas.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Overlay plywood offers superior performance in high-moisture environments due to its waterproof adhesive and smooth surface, making it ideal for exterior applications and heavy-duty projects. Underlayment plywood, designed primarily as a substrate for flooring, provides a smooth, sanded finish that enhances laminate or vinyl installation but lacks the same moisture resistance and durability as overlay plywood. Your choice depends on the environment and exposure conditions, with overlay plywood excelling in durability and performance under stress, while underlayment plywood prioritizes surface smoothness for flooring applications.
Installation Guidelines for Overlay vs Underlayment Plywood
Overlay plywood requires precise alignment with the existing subfloor, fastening with screws or nails at recommended intervals to ensure a smooth surface for finished flooring. Underlayment plywood must be installed over a structurally sound subfloor, with staggered joints and proper fastening to prevent movement and squeaking underfoot. Your installation should follow manufacturer guidelines for thickness and fastening to optimize durability and floor performance.
Cost Considerations for Overlay and Underlayment Plywood
Overlay plywood generally costs more than underlayment plywood due to its higher-grade surface veneer designed for durability and smooth finishes. Underlayment plywood is more affordable, making it a cost-effective choice for subflooring or beneath finished surfaces where appearance is less critical. Your decision should weigh the upfront material costs against the long-term benefits of wear resistance and finish quality.
Best Applications: Where to Use Each Type
Overlay plywood is best suited for exterior applications and visible surfaces, such as roofing, siding, and concrete formwork, due to its smooth, durable surface and weather-resistant properties. Underlayment plywood is ideal for interior flooring underlayment where a smooth, stable base is required for finishes like vinyl, tile, or hardwood, ensuring even surface preparation and preventing imperfections. You should choose overlay plywood when durability and exposure resistance matter most, while underlayment plywood excels in providing a flawless substrate beneath your finished floor materials.
Choosing the Right Plywood: Overlay or Underlayment?
Selecting the right plywood depends on the specific application, with overlay plywood designed for enhanced surface durability and smoothness, ideal for exterior finishes, while underlayment plywood offers a thinner, smoother surface to provide a stable base for flooring materials such as vinyl, carpet, or hardwood. Overlay plywood features a resin-impregnated paper surface that resists moisture and wear, making it suitable for exposed areas, whereas underlayment plywood emphasizes uniformity and minimal voids for an even flooring foundation. Understanding the differences in thickness, surface treatment, and intended use ensures optimal performance and longevity in construction and renovation projects.
Overlay plywood vs Underlayment plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com