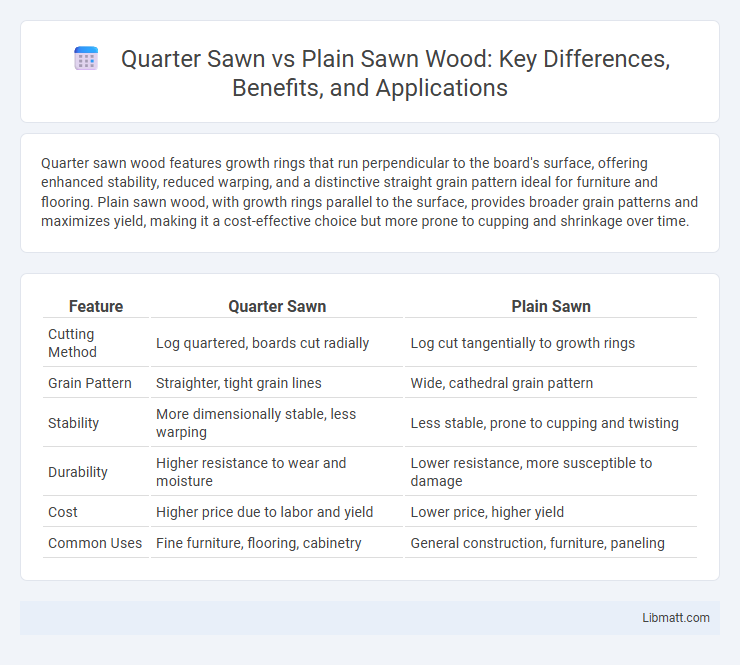
Quarter sawn wood features growth rings that run perpendicular to the board's surface, offering enhanced stability, reduced warping, and a distinctive straight grain pattern ideal for furniture and flooring. Plain sawn wood, with growth rings parallel to the surface, provides broader grain patterns and maximizes yield, making it a cost-effective choice but more prone to cupping and shrinkage over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Quarter Sawn | Plain Sawn |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | Log quartered, boards cut radially | Log cut tangentially to growth rings |
| Grain Pattern | Straighter, tight grain lines | Wide, cathedral grain pattern |
| Stability | More dimensionally stable, less warping | Less stable, prone to cupping and twisting |
| Durability | Higher resistance to wear and moisture | Lower resistance, more susceptible to damage |
| Cost | Higher price due to labor and yield | Lower price, higher yield |
| Common Uses | Fine furniture, flooring, cabinetry | General construction, furniture, paneling |
Understanding Wood Sawn Methods
Quarter sawn wood features growth rings cut at a 60 to 90-degree angle, resulting in superior stability, reduced warping, and enhanced grain patterns like ray flecks, making it ideal for fine woodworking and flooring. Plain sawn, or flat sawn, wood is cut tangentially to the growth rings, producing wider grain patterns and maximizing yield but with greater susceptibility to cupping and shrinkage. Choosing between quarter sawn and plain sawn methods depends on balancing aesthetic preferences, dimensional stability, and cost considerations in woodworking projects.
What Is Quarter Sawn Lumber?
Quarter sawn lumber is wood that has been cut at a 90-degree angle to the tree's growth rings, resulting in a distinctive grain pattern known for its stability and resistance to warping. Unlike plain sawn lumber, which features a more varied and prominent grain pattern, quarter sawn lumber offers enhanced durability and a straighter grain that is highly prized in fine woodworking and furniture making. Your choice of quarter sawn lumber ensures greater dimensional stability and aesthetic appeal, especially for projects requiring uniformity and long-lasting quality.
What Is Plain Sawn Lumber?
Plain sawn lumber, also known as flat sawn, is the most common and economical method of cutting logs into boards. This technique involves slicing the log tangentially to the growth rings, producing boards with a distinct cathedral grain pattern on the face. Plain sawn lumber typically exhibits wider grain patterns and is more prone to cupping and warping compared to quarter sawn lumber but offers maximum yield and a traditional aesthetic.
Visual Differences: Grain and Appearance
Quarter sawn lumber features straight, closely spaced grain patterns with ray flecks that create a distinctive, uniform appearance prized in fine woodworking and furniture making. Plain sawn lumber displays wider, more varied grain patterns with cathedral or flame-shaped markings, offering a more rustic and natural look. These visual differences impact not only aesthetics but also the wood's stability and durability in finished products.
Stability and Durability Comparison
Quarter sawn wood exhibits superior stability and durability compared to plain sawn lumber due to its grain orientation, which reduces warping, cupping, and shrinking. Its tight, straight grain pattern enhances resistance to moisture changes, making it ideal for furniture and flooring subjected to heavy use. Choosing quarter sawn wood for your project ensures long-lasting performance and structural integrity in varying environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability Factors
Quarter sawn lumber generally costs more than plain sawn due to its labor-intensive milling process and lower yield from each log. Availability of quarter sawn wood is more limited, especially for certain species, because it requires selecting specific logs and precise cutting angles, making it less common in standard inventory. Your choice depends on budget and access, with plain sawn being more affordable and widely available for most woodworking projects.
Best Uses for Quarter Sawn Wood
Quarter sawn wood offers superior stability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for fine cabinetry, flooring, and musical instruments where precision and durability are essential. Its pronounced ray flecks and tighter grain patterns enhance the aesthetic appeal, perfect for decorative woodwork and furniture that benefit from a unique, elegant look. If Your project demands both structural integrity and visual sophistication, quarter sawn wood provides unmatched performance compared to plain sawn alternatives.
Ideal Applications for Plain Sawn Wood
Plain sawn wood is ideal for applications requiring wide, flat boards such as flooring, paneling, and general construction due to its cost-effectiveness and efficient use of the log. Its distinct grain pattern adds aesthetic appeal to furniture and cabinetry while providing a good balance of strength and stability for everyday use. Choosing plain sawn boards can optimize your project budget without sacrificing durability or visual impact.
Pros and Cons: Quarter Sawn vs. Plain Sawn
Quarter sawn wood offers superior stability and reduced warping compared to plain sawn lumber, making it ideal for flooring and fine woodworking projects, though it is more expensive due to lower yield and increased labor. Plain sawn wood provides a wider grain pattern and is more cost-effective, with faster production and less waste, but it is more prone to cupping and uneven expansion in humid conditions. Choosing between quarter sawn and plain sawn depends on balancing budget constraints, aesthetic preferences, and the wood's intended use and exposure to environmental changes.
How to Choose the Right Sawn Lumber for Your Project
Choosing between quarter sawn and plain sawn lumber depends on your project's needs for stability and aesthetics. Quarter sawn wood offers enhanced dimensional stability and a unique grain pattern ideal for fine furniture or flooring exposed to moisture. Plain sawn lumber provides a more cost-effective option with a varied grain appearance, suitable for general construction or projects where budget is a priority.
Quarter sawn vs plain sawn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com