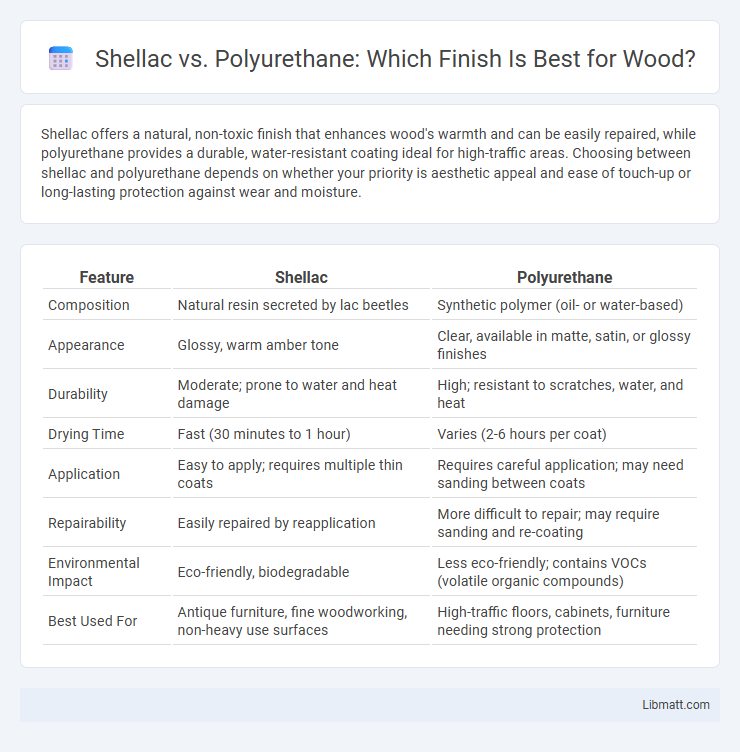
Shellac offers a natural, non-toxic finish that enhances wood's warmth and can be easily repaired, while polyurethane provides a durable, water-resistant coating ideal for high-traffic areas. Choosing between shellac and polyurethane depends on whether your priority is aesthetic appeal and ease of touch-up or long-lasting protection against wear and moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shellac | Polyurethane |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural resin secreted by lac beetles | Synthetic polymer (oil- or water-based) |
| Appearance | Glossy, warm amber tone | Clear, available in matte, satin, or glossy finishes |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to water and heat damage | High; resistant to scratches, water, and heat |
| Drying Time | Fast (30 minutes to 1 hour) | Varies (2-6 hours per coat) |
| Application | Easy to apply; requires multiple thin coats | Requires careful application; may need sanding between coats |
| Repairability | Easily repaired by reapplication | More difficult to repair; may require sanding and re-coating |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Less eco-friendly; contains VOCs (volatile organic compounds) |
| Best Used For | Antique furniture, fine woodworking, non-heavy use surfaces | High-traffic floors, cabinets, furniture needing strong protection |
Introduction to Shellac and Polyurethane
Shellac is a natural resin secreted by the lac bug, prized for its quick-drying, non-toxic properties and rich, warm finish often used on antique furniture. Polyurethane, a synthetic polymer, offers superior durability and resistance to scratches, heat, and chemicals, making it ideal for high-traffic surfaces and modern applications. Understanding the core differences between shellac and polyurethane can help you choose the best finish for your woodworking or refinishing projects.
Key Differences Between Shellac and Polyurethane
Shellac is a natural resin-based finish derived from lac bugs, offering a warm, amber tone and excellent drying speed, while polyurethane is a synthetic polymer providing superior durability and water resistance. Shellac is best suited for indoor furniture and antiques due to its susceptibility to heat and alcohol damage, whereas polyurethane excels in high-traffic areas and surfaces exposed to moisture. The application process differs as shellac requires multiple thin coats with sanding, whereas polyurethane can be applied more thickly and is available in oil- and water-based formulas for varied drying times and finishes.
Pros and Cons of Shellac
Shellac offers a natural, non-toxic finish that dries quickly and enhances wood grain with a warm, amber tone, making it ideal for fine furniture and antiques. Its main drawbacks include poor water and heat resistance, limited durability, and sensitivity to alcohol and chemicals, which can damage the surface. When considering your wood finishing options, shellac works best in low-traffic areas or as a sealing base under other finishes for enhanced protection.
Pros and Cons of Polyurethane
Polyurethane offers exceptional durability and water resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic surfaces like floors and furniture. Its fast-drying formula supports multiple coats in a short time, enhancing protection against scratches and chemicals. However, polyurethane can yellow over time and emits stronger fumes compared to shellac, requiring proper ventilation during application.
Application Methods Compared
Shellac is typically applied using a brush or cloth in thin, quick-drying coats that allow for easy build-up and quick re-coating, making it ideal for delicate wood surfaces and detailed woodworking. Polyurethane, on the other hand, requires careful brush or applicator use to minimize bubbles and is often applied in thicker layers, offering durable, water-resistant protection suitable for high-traffic areas. Both finishes require sanding between coats for optimal adhesion, but polyurethane usually demands more extensive surface preparation due to its stronger chemical composition.
Durability and Protection Levels
Shellac offers moderate durability and water resistance, making it suitable for interior wood surfaces but less effective against heat and chemical exposure. Polyurethane provides superior protection with excellent resistance to scratches, heat, and moisture, ideal for high-traffic areas and surfaces prone to wear. The chemical composition of polyurethane forms a tougher, more resilient film compared to the natural resin in shellac.
Aesthetic Effects: Finish and Appearance
Shellac provides a warm, natural glow that enhances wood grain with a slightly amber tint, perfect for traditional or antique furniture restoration. Polyurethane offers a durable, clear finish available in gloss, semi-gloss, and satin sheens, maintaining the wood's true color while resisting scratches and moisture. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize rich, classic aesthetics or long-lasting, high-gloss protection.
Suitability for Different Wood Projects
Shellac excels in fine woodworking and restoration projects due to its natural finish and quick drying time, making it ideal for furniture and antiques. Polyurethane offers superior durability and water resistance, making it suitable for high-traffic surfaces like floors and kitchen cabinets. Choosing the right finish depends on your project's need for aesthetic appeal versus long-term protection.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Shellac requires more frequent maintenance due to its lower durability and sensitivity to water and heat, often needing touch-ups or reapplication to maintain its finish. Polyurethane offers superior resistance to scratches, chemicals, and moisture, significantly reducing the need for repairs and providing long-lasting protection. For your furniture or flooring, choosing polyurethane can save time and effort on upkeep while shellac suits projects needing easy spot repairs or historical authenticity.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Shellac, derived from natural resin secreted by the lac bug, offers a biodegradable and non-toxic finish, making it safer for indoor use and posing minimal environmental hazards. Polyurethane, a petroleum-based product, releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application and curing, contributing to air pollution and potential health risks. Your eco-conscious choice should lean toward shellac for lower environmental impact and enhanced safety, especially in enclosed spaces.
Shellac vs polyurethane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com