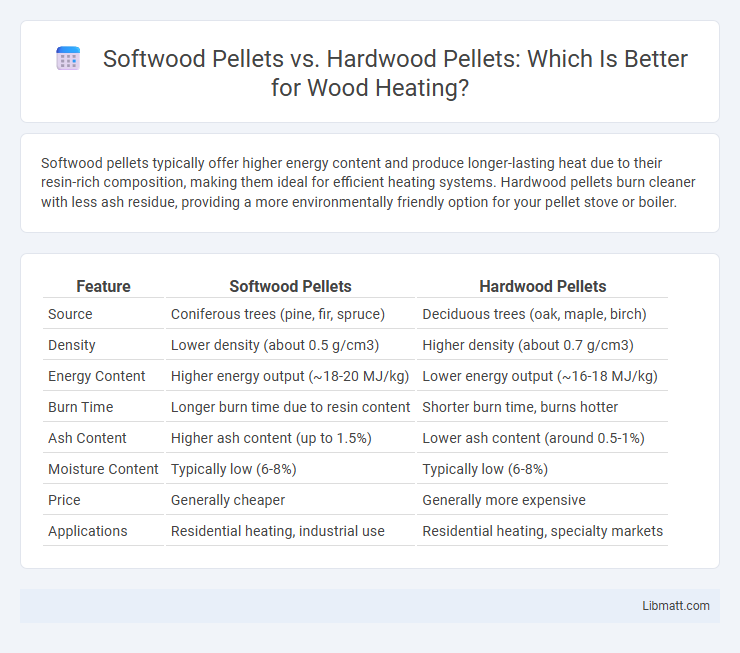
Softwood pellets typically offer higher energy content and produce longer-lasting heat due to their resin-rich composition, making them ideal for efficient heating systems. Hardwood pellets burn cleaner with less ash residue, providing a more environmentally friendly option for your pellet stove or boiler.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Softwood Pellets | Hardwood Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coniferous trees (pine, fir, spruce) | Deciduous trees (oak, maple, birch) |
| Density | Lower density (about 0.5 g/cm3) | Higher density (about 0.7 g/cm3) |
| Energy Content | Higher energy output (~18-20 MJ/kg) | Lower energy output (~16-18 MJ/kg) |
| Burn Time | Longer burn time due to resin content | Shorter burn time, burns hotter |
| Ash Content | Higher ash content (up to 1.5%) | Lower ash content (around 0.5-1%) |
| Moisture Content | Typically low (6-8%) | Typically low (6-8%) |
| Price | Generally cheaper | Generally more expensive |
| Applications | Residential heating, industrial use | Residential heating, specialty markets |
Introduction to Softwood and Hardwood Pellets
Softwood pellets, derived primarily from coniferous trees like pine and spruce, offer higher energy content and burn longer due to their dense resin composition. Hardwood pellets, sourced from deciduous trees such as oak and maple, contain less resin but produce less ash, making them ideal for cleaner combustion. Both types serve distinct purposes in heating and energy production, with softwood pellets favored for higher heat output and hardwood pellets preferred for emissions-sensitive applications.
What Are Softwood Pellets?
Softwood pellets are biomass fuel made from compressed softwood materials such as pine, fir, and spruce, known for their high resin content and lower density compared to hardwood pellets. These pellets typically burn hotter and faster, producing more heat energy but generating more ash and creosote, which may require more frequent maintenance of your heating system. Softwood pellets are often preferred for their availability and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for large-scale industrial use and residential heating where quick, intense heat output is desired.
What Are Hardwood Pellets?
Hardwood pellets are biofuel products made from compressed hardwood sawdust and wood chips, primarily sourced from deciduous trees like oak, maple, and birch. These pellets offer higher density and longer burn times compared to softwood pellets, making them ideal for heating with consistent, efficient energy output. Their lower resin content results in reduced creosote buildup, enhancing appliance longevity and safety in pellet stoves and boilers.
Key Differences Between Softwood and Hardwood Pellets
Softwood pellets have a lower density and higher resin content, resulting in longer burn times and more heat output compared to hardwood pellets, which are denser and produce less ash. Hardwood pellets typically generate more consistent heat with less creosote buildup, making them ideal for indoor heating applications. Your choice depends on priorities like burn duration, heat intensity, and appliance compatibility with pellet types.
Burning Efficiency: Softwood vs Hardwood Pellets
Softwood pellets generally offer higher burning efficiency due to their lower density and resin content, which allows for quicker ignition and more consistent heat output. Hardwood pellets, while denser and slower to ignite, provide longer burn times and produce more energy per pellet, ideal for sustained heating. Your choice between softwood and hardwood pellets should depend on whether you prioritize rapid heating or extended burn duration for optimal energy use.
Heat Output and BTU Comparison
Softwood pellets generally produce a higher heat output with an average of 8,000 to 8,500 BTU per pound compared to hardwood pellets, which range from 7,000 to 8,000 BTU per pound. The resin content in softwood contributes to this increased energy density, making them more efficient for heating. Hardwood pellets, while having slightly lower BTU values, burn longer and produce less ash, offering a cleaner fuel option.
Ash Production and Maintenance Needs
Softwood pellets typically produce lower ash content, around 0.3-0.5%, compared to hardwood pellets which can have ash content ranging from 0.8-2%. Reduced ash production in softwood pellets leads to less frequent cleaning and maintenance of stoves and boilers, extending the intervals between ash disposal. Hardwood pellets require more regular maintenance due to higher ash buildup, which can affect combustion efficiency and increase wear over time.
Cost Analysis: Softwood vs Hardwood Pellets
Softwood pellets typically cost less than hardwood pellets due to faster growth rates and higher availability of softwood species such as pine and fir. Hardwood pellets, made from denser woods like oak and maple, often have higher energy content but come at a premium price reflecting their slower growth and processing costs. You can optimize your budget by choosing softwood pellets for cost-effectiveness or hardwood pellets for longer burning times and higher heat output.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Softwood pellets generally have a lower environmental impact due to their rapid growth rates and higher carbon sequestration capacity, making them a more sustainable biomass energy source compared to hardwood pellets. Hardwood pellets, while denser and providing more energy per ton, often come from slower-growing trees, which can strain forest ecosystems if not managed responsibly. Choosing softwood pellets supports your commitment to sustainable energy by promoting faster forest regeneration and reducing carbon emissions.
Choosing the Right Pellet for Your Needs
Softwood pellets typically burn longer and produce more heat, making them ideal for heating larger spaces efficiently, while hardwood pellets offer a cleaner burn with less ash, suitable for users needing lower maintenance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize heat output or ease of cleaning, as hardwood pellets tend to be denser and create less residue in stoves. Understanding the differences helps you select the right pellet that aligns with your heating system's requirements and personal convenience.
Softwood pellets vs hardwood pellets Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com