WBP plywood, known as Weather and Boil Proof, offers superior water resistance and durability compared to MR plywood, which is Moisture Resistant but not fully waterproof. Your choice should depend on exposure conditions, with WBP ideal for outdoor or high-moisture environments and MR suited for indoor use.
Table of Comparison
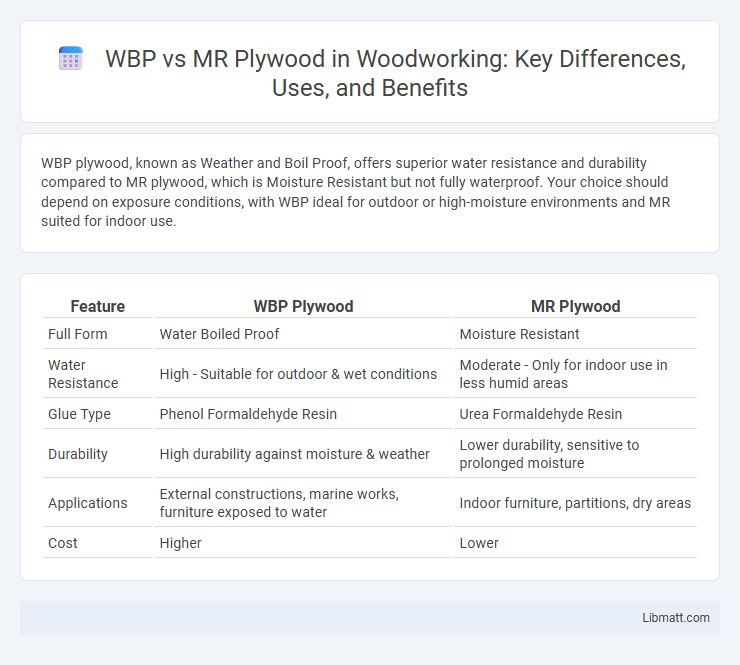
| Feature | WBP Plywood | MR Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Water Boiled Proof | Moisture Resistant |
| Water Resistance | High - Suitable for outdoor & wet conditions | Moderate - Only for indoor use in less humid areas |
| Glue Type | Phenol Formaldehyde Resin | Urea Formaldehyde Resin |
| Durability | High durability against moisture & weather | Lower durability, sensitive to prolonged moisture |
| Applications | External constructions, marine works, furniture exposed to water | Indoor furniture, partitions, dry areas |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to WBP and MR Plywood
WBP (Water Boiled Proof) plywood is designed for high moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications. MR (Moisture Resistant) plywood offers moderate resistance to damp environments and is commonly used for interior purposes like furniture and cabinets. Understanding the differences between WBP and MR plywood helps you choose the right material based on durability and exposure conditions.
What is WBP Plywood?
WBP plywood, or Water Boiled Proof plywood, is a type of high-quality plywood known for its exceptional water resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. It uses phenolic resin glue, which ensures the plywood withstands prolonged exposure to moisture and harsh weather conditions without delaminating. WBP plywood is commonly used in construction, furniture, and flooring projects where longevity and strength under wet conditions are critical.
What is MR Plywood?
MR plywood, or Moisture Resistant plywood, is engineered with phenolic resin adhesives to withstand moderate humidity and moisture, making it ideal for indoor applications like furniture and interior paneling. Unlike WBP plywood, which offers higher water resistance suitable for exterior use, MR plywood provides sufficient durability for environments where occasional moisture exposure occurs. Understanding the differences helps you select the right plywood type based on your project's moisture tolerance requirements.
Key Differences Between WBP and MR Plywood
WBP plywood features waterproof glue making it ideal for outdoor use and high-moisture environments, while MR plywood is moisture-resistant but not fully waterproof, suited for indoor applications. The adhesive quality in WBP plywood complies with IS 710 standards, ensuring durability under wet conditions, whereas MR plywood is bonded with synthetic resin for resistance to humidity but degrades if exposed to water continuously. Your choice depends on whether water exposure is a critical factor, with WBP plywood offering superior protection compared to MR plywood.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
WBP (Water Boiled Proof) plywood undergoes a high-pressure hot press process where waterproof phenolic glue is applied, ensuring superior moisture resistance and durability suitable for exterior use. MR (Moisture Resistant) plywood is produced using urea-formaldehyde adhesive with a conventional cold press method, making it ideal for indoor applications with moderate humidity. The key manufacturing distinction lies in the adhesive type and pressing conditions, directly impacting the plywood's water resistance and structural integrity.
Moisture and Water Resistance Level
WBP plywood, or Water Boiled Proof plywood, offers superior moisture and water resistance due to its phenolic resin adhesive, making it ideal for outdoor and high-humidity applications. MR plywood, or Moisture Resistant plywood, withstands limited moisture exposure but is not suitable for prolonged water contact or wet conditions. Your choice depends on the level of water exposure, with WBP plywood providing enhanced durability in wet environments compared to MR plywood.
Strength and Durability Factors
WBP plywood, made with weather and boil-proof adhesive, offers superior water resistance and enhanced bonding strength compared to MR plywood, which uses moisture-resistant adhesive but is less effective in wet conditions. The cross-laminated wood veneers in WBP plywood provide higher structural stability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications. MR plywood, while durable for indoor use, lacks the robust waterproof qualities and long-term durability exhibited by WBP plywood under harsh environmental stress.
Ideal Applications for WBP Plywood
WBP plywood is ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications due to its waterproof bonding and resistance to moisture and weather conditions, making it perfect for construction, furniture exposed to humidity, and marine environments. Your projects benefit from its durability in roofing, flooring, and exterior cladding where strength and water resistance are critical. It outperforms MR plywood in settings that demand prolonged exposure to water or humidity.
Ideal Uses for MR Plywood
MR plywood, also known as Moisture Resistant plywood, is ideal for interior applications where exposure to humidity is common but not direct water contact, such as in kitchen cabinets, furniture, and partition walls. Its ability to withstand moisture without swelling or warping makes it suitable for use in bathrooms and areas with moderate dampness. Choosing MR plywood ensures your projects maintain structural integrity in moist environments while offering a cost-effective alternative to Water Boiled Proof (WBP) plywood.
Which Plywood Should You Choose?
WBP (Water Boiled Proof) plywood offers superior waterproofing and durability, making it ideal for outdoor or moisture-prone environments, while MR (Moisture Resistant) plywood suits indoor settings with minimal water exposure. Your choice depends on the application: select WBP plywood for exterior projects or damp conditions and MR plywood for general interior use to balance cost and performance. Understanding the specific needs of your project ensures you invest in the right plywood type for long-lasting results.
WBP vs MR plywood Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com