High bypass ratio engines offer greater fuel efficiency and quieter operation by directing more air around the core, making them ideal for commercial airliners. Low bypass ratio engines provide higher thrust and faster acceleration, which suits military jets and supersonic aircraft where performance outweighs fuel economy.
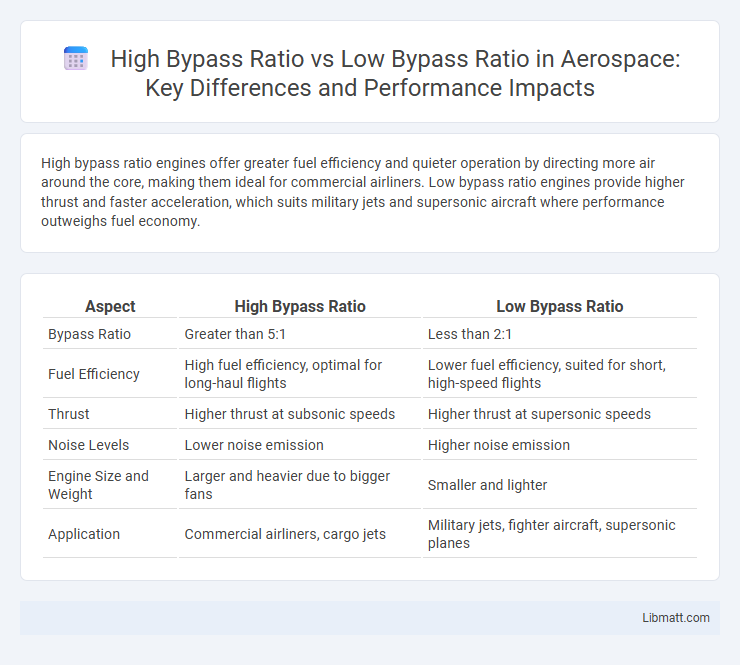
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | High Bypass Ratio | Low Bypass Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Bypass Ratio | Greater than 5:1 | Less than 2:1 |
| Fuel Efficiency | High fuel efficiency, optimal for long-haul flights | Lower fuel efficiency, suited for short, high-speed flights |
| Thrust | Higher thrust at subsonic speeds | Higher thrust at supersonic speeds |
| Noise Levels | Lower noise emission | Higher noise emission |
| Engine Size and Weight | Larger and heavier due to bigger fans | Smaller and lighter |
| Application | Commercial airliners, cargo jets | Military jets, fighter aircraft, supersonic planes |
Introduction to Bypass Ratios in Jet Engines
Bypass ratio in jet engines refers to the ratio of the mass flow of air that bypasses the engine core to the mass flow passing through the core. High bypass ratio engines channel a larger volume of air around the core, resulting in greater fuel efficiency, reduced noise, and improved thrust for commercial airliners. Your choice of engine bypass ratio influences performance characteristics like fuel consumption, noise levels, and suitability for different flight speeds.
Defining High Bypass Ratio and Low Bypass Ratio
High bypass ratio (HBR) engines feature a large fan that moves significantly more air around the core engine than through it, resulting in increased fuel efficiency and reduced noise levels, commonly used in commercial jets. Low bypass ratio (LBR) engines have a smaller fan and higher core airflow, producing greater thrust for supersonic speeds and military applications but with higher fuel consumption and noise. Understanding the difference between high bypass and low bypass ratios helps optimize engine selection based on performance, efficiency, and noise considerations for your aviation needs.
How Bypass Ratio Impacts Engine Performance
High bypass ratio engines deliver greater fuel efficiency and lower noise levels by channeling more air around the core, enhancing thrust primarily through bypassed airflow. Low bypass ratio engines generate higher exhaust velocity, resulting in increased specific thrust and faster acceleration, but with higher fuel consumption and noise. Your engine performance choice depends on prioritizing fuel economy and quiet operation versus thrust and speed requirements.
Efficiency Differences: High vs Low Bypass Ratio
High bypass ratio engines deliver superior fuel efficiency by moving a larger volume of air around the core, resulting in greater thrust with less fuel consumption. Low bypass ratio engines generate higher exhaust velocities, which improves performance at supersonic speeds but reduces overall fuel efficiency. Your choice depends on whether priority lies in fuel savings and reduced emissions or in high-speed performance capabilities.
Thrust Output Comparison
High bypass ratio engines generate greater thrust at lower speeds due to increased airflow around the core, improving fuel efficiency and reducing noise. Low bypass ratio engines produce higher thrust at high speeds by maximizing exhaust velocity, making them ideal for supersonic and military applications. Thrust output is heavily influenced by bypass ratio, with high bypass favoring efficiency and low bypass prioritizing raw power and speed.
Fuel Consumption and Environmental Impact
High bypass ratio engines significantly reduce fuel consumption by increasing the mass of air bypassing the core, improving propulsion efficiency. This lower fuel burn results in decreased carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions, contributing to a smaller environmental footprint. Conversely, low bypass ratio engines consume more fuel and produce higher emissions due to their reduced bypass air and reliance on jet velocity for thrust.
Common Applications of High Bypass Ratio Engines
High bypass ratio engines are predominantly used in commercial aviation, specifically for large passenger airliners, due to their superior fuel efficiency and reduced noise levels. These engines optimize thrust by channeling a large volume of air around the core, making them ideal for long-haul flights and cargo planes requiring economical operations. Military transport aircraft and some regional jets also employ high bypass ratio engines to balance performance with operational cost-effectiveness.
Typical Uses for Low Bypass Ratio Engines
Low bypass ratio engines are typically used in military fighter jets and supersonic aircraft due to their ability to produce higher thrust and faster acceleration. These engines prioritize speed and performance over fuel efficiency, making them ideal for combat and high-speed maneuvers. Your aircraft's maneuverability and quick response in demanding conditions benefit greatly from the low bypass ratio design.
Technological Challenges and Innovations
High bypass ratio engines face technological challenges such as managing increased fan blade stress and designing lightweight, durable materials to handle larger diameters efficiently. Innovations in composite materials and advanced aerodynamics have enabled higher thrust-to-weight ratios and improved fuel efficiency in these engines. Your choice between high and low bypass ratios must consider trade-offs in noise reduction, fuel consumption, and engine size dictated by these technological advancements.
Future Trends in Bypass Ratio Engine Design
Future trends in bypass ratio engine design emphasize increasing bypass ratios to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, driven by advances in materials and aerodynamics that enable larger fan diameters without compromising engine weight. Ultra-high bypass ratio engines are becoming central to sustainable aviation goals, leveraging geared turbofan technology to optimize thrust and noise reduction. Conversely, low bypass ratio engines remain relevant for supersonic and military applications, where higher specific thrust and compact size are critical.
High bypass ratio vs Low bypass ratio Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com