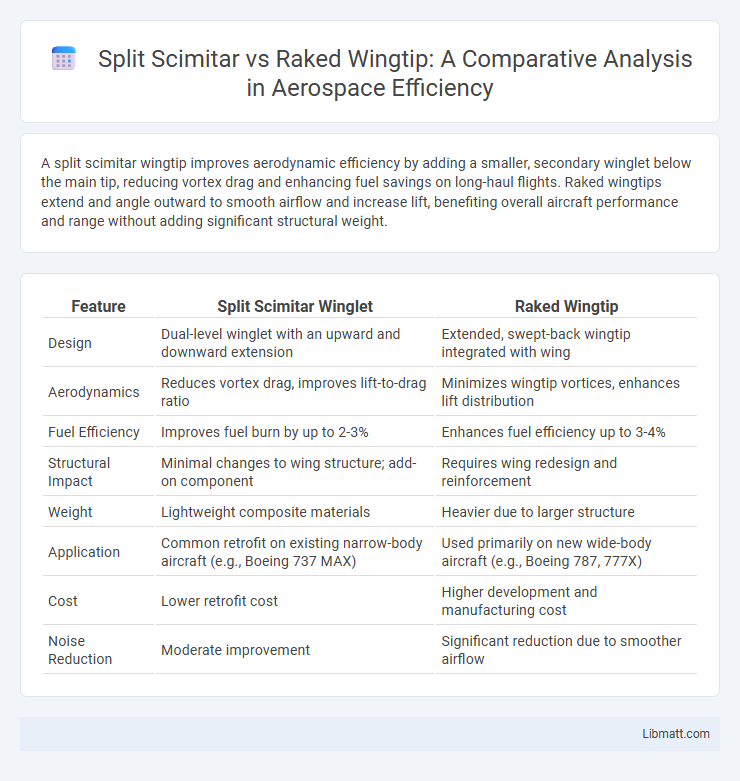
A split scimitar wingtip improves aerodynamic efficiency by adding a smaller, secondary winglet below the main tip, reducing vortex drag and enhancing fuel savings on long-haul flights. Raked wingtips extend and angle outward to smooth airflow and increase lift, benefiting overall aircraft performance and range without adding significant structural weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Split Scimitar Winglet | Raked Wingtip |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Dual-level winglet with an upward and downward extension | Extended, swept-back wingtip integrated with wing |
| Aerodynamics | Reduces vortex drag, improves lift-to-drag ratio | Minimizes wingtip vortices, enhances lift distribution |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves fuel burn by up to 2-3% | Enhances fuel efficiency up to 3-4% |
| Structural Impact | Minimal changes to wing structure; add-on component | Requires wing redesign and reinforcement |
| Weight | Lightweight composite materials | Heavier due to larger structure |
| Application | Common retrofit on existing narrow-body aircraft (e.g., Boeing 737 MAX) | Used primarily on new wide-body aircraft (e.g., Boeing 787, 777X) |
| Cost | Lower retrofit cost | Higher development and manufacturing cost |
| Noise Reduction | Moderate improvement | Significant reduction due to smoother airflow |
Introduction to Aerodynamic Wingtip Designs
Split scimitar and raked wingtips are advanced aerodynamic wingtip designs that enhance aircraft fuel efficiency and performance by reducing drag. The Split scimitar winglet combines an upward and downward winglet for optimal vortex control, while the raked wingtip extends and angles outward for improved lift-to-drag ratio. Your choice between these designs depends on aircraft type and specific fuel-saving goals.
What Is a Split Scimitar Winglet?
A Split Scimitar Winglet features a dual-tip design that improves aerodynamics by reducing drag and enhancing fuel efficiency, compared to traditional wingtips. This winglet consists of an upward wingtip combined with a smaller downward extension, optimizing airflow and stability during flight. Your aircraft can benefit from increased range and lower emissions when equipped with Split Scimitar Winglets versus conventional raked wingtips.
Understanding Raked Wingtips
Raked wingtips are designed with an extended, sharply angled shape that enhances aerodynamic efficiency by reducing drag and increasing lift, improving overall fuel economy and aircraft performance. Unlike split scimitars, which combine upwards and downwards extensions for noise reduction and wingtip vortex control, raked wingtips specifically optimize airflow and stability during flight. Understanding these features helps you appreciate how raked wingtips contribute to smoother, more efficient flights, especially on long-haul aircraft.
Key Differences: Split Scimitar vs Raked Wingtip
Split scimitar wingtips feature an extended winglet with a downward-pointing tip designed to improve aerodynamic efficiency and reduce drag, while raked wingtips are angled extensions of the wing itself, increasing wingspan for better lift and fuel savings. You will notice split scimitar wingtips are more prominent on aircraft like the Boeing 737 MAX, offering noise reduction benefits, whereas raked wingtips are common on wide-body jets like the Boeing 787, enhancing long-range performance. The key difference lies in their shape and aerodynamic purpose: split scimitars optimize fuel efficiency through drag reduction, and raked wingtips maximize lift and stability.
Aerodynamic Efficiency Comparison
Split scimitar winglets improve aerodynamic efficiency by reducing wingtip vortices, lowering drag, and increasing fuel savings compared to traditional wingtip designs. Raked wingtips extend the wingspan with a smooth, angled shape that enhances lift-to-drag ratio and optimizes airflow, particularly at high speeds. Overall, split scimitar winglets offer superior efficiency in fuel reduction and emissions, while raked wingtips excel in maximizing aerodynamic performance on longer-range flights.
Fuel Savings and Operational Costs
Split scimitar winglets improve fuel efficiency by reducing drag, leading to fuel savings of up to 5% compared to traditional wingtip designs. Raked wingtips also enhance aerodynamic performance but typically offer slightly less fuel reduction, around 3-4%. Lower fuel consumption with split scimitar winglets directly contributes to decreased operational costs and extended aircraft range.
Impact on Aircraft Range and Performance
Split scimitar winglets reduce drag by optimizing airflow and decreasing vortex strength, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and extended aircraft range. Raked wingtips enhance lift-to-drag ratio by increasing wingspan without adding weight, leading to better climb performance and lower fuel consumption. Both wingtip designs contribute to aerodynamic efficiency, with split scimitars favoring cruise range and raked wingtips offering a balance between takeoff and cruise performance.
Maintenance and Structural Considerations
Split scimitar wingtips require specialized maintenance due to their unique dual-edge design, which may increase inspection complexity and repair costs compared to traditional wingtips. Raked wingtips, featuring a smooth, elongated shape, offer structural advantages with reduced wingtip vortices, resulting in lower fatigue stress and potentially less frequent maintenance. Your choice between these wingtip designs impacts long-term maintenance schedules and structural integrity management.
Airline Adoption and Aircraft Compatibility
Split scimitar winglets are widely adopted by airlines such as Delta and Southwest for fuel efficiency on Boeing 737 and Airbus A320 families, enhancing aerodynamics on narrow-body jets. Raked wingtips are predominantly used by airlines operating wide-body aircraft like the Boeing 777 and 787, providing improved range and reduced drag on long-haul flights. Your choice between these wingtip designs depends on the aircraft model and operational performance goals prioritizing fuel savings and extended range.
Future Trends in Wingtip Technology
Split scimitar wingtips enhance aerodynamic efficiency by reducing drag through dual-layer design, promoting fuel savings and extended range, while raked wingtips focus on optimizing lift and stability by extending the wing's span with a sleek, angled tip. Emerging trends suggest hybrid designs combining split scimitar and raked elements to maximize performance in next-generation aircraft. Your choice of wingtip technology may impact operational efficiency and environmental sustainability as these innovations evolve.
Split scimitar vs Raked wingtip Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com