A 3-phase inverter delivers smoother power output and higher efficiency for industrial and large-scale applications by converting DC to three alternating currents with phase shifts, while a single-phase inverter is suitable for residential or small-scale use with simpler design and lower cost. Your choice depends on the power requirements and load type, where 3-phase systems support higher loads and better performance in motors and heavy equipment.
Table of Comparison
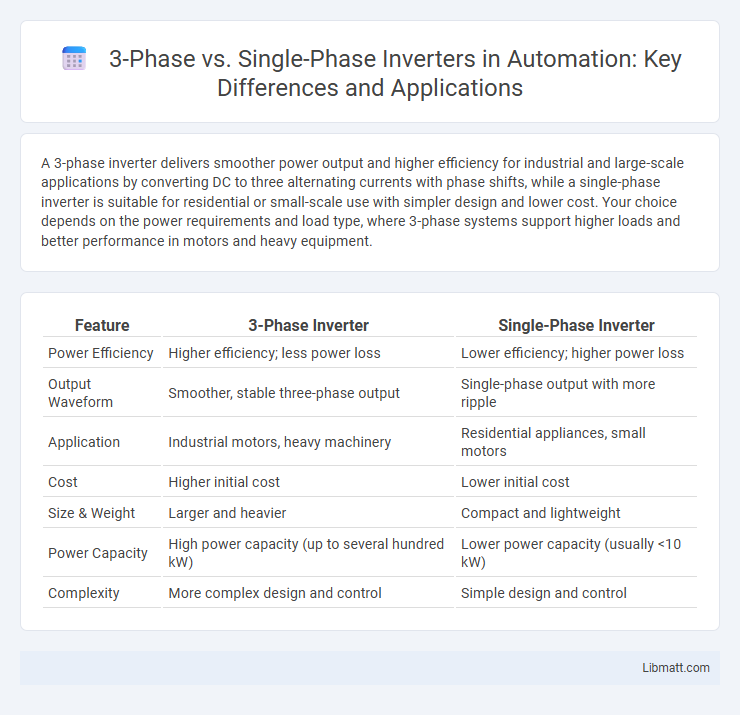
| Feature | 3-Phase Inverter | Single-Phase Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Power Efficiency | Higher efficiency; less power loss | Lower efficiency; higher power loss |
| Output Waveform | Smoother, stable three-phase output | Single-phase output with more ripple |
| Application | Industrial motors, heavy machinery | Residential appliances, small motors |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Power Capacity | High power capacity (up to several hundred kW) | Lower power capacity (usually <10 kW) |
| Complexity | More complex design and control | Simple design and control |
Introduction to Power Inverters
Power inverters convert DC electricity into AC electricity, essential for powering homes and industries. A single-phase inverter supplies power to residential or small commercial loads with simpler design and lower cost, while a 3-phase inverter supports heavy industrial applications by delivering consistent, higher power with improved efficiency and reduced harmonic distortion. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right inverter to optimize energy conversion and system performance.
What is a Single-phase Inverter?
A single-phase inverter converts direct current (DC) into single-phase alternating current (AC), commonly used in residential solar power systems and small appliances. Unlike a 3-phase inverter, which produces three separate AC outputs for industrial or large-scale applications, a single-phase inverter delivers power through just one AC waveform. Your choice between single-phase and 3-phase inverters depends on the power requirement and the complexity of the electrical system.
What is a 3-phase Inverter?
A 3-phase inverter converts direct current (DC) into three alternating currents (AC) that are each 120 degrees out of phase, enabling efficient power delivery to three-phase motors and industrial equipment. Unlike single-phase inverters, which provide power to single-phase loads, 3-phase inverters support balanced loads and higher power capacity, reducing torque ripple and improving performance in heavy-duty applications. These inverters are essential components in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and industrial drives where stable and continuous power output is critical.
Key Differences Between Single-phase and 3-phase Inverters
3-phase inverters provide smoother power output and higher efficiency by delivering three alternating currents with a 120-degree phase shift, while single-phase inverters output a single alternating current. The 3-phase system supports larger loads and is preferred in industrial applications, contrasting with single-phase inverters commonly used in residential or small-scale settings. Voltage stability and reduced harmonic distortion are significant advantages of 3-phase inverters over single-phase models.
Applications of Single-phase Inverters
Single-phase inverters are commonly used in residential solar power systems, small-scale uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and portable electronic devices due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They efficiently convert DC power from solar panels or batteries into AC power suitable for household appliances and light commercial loads. Their compact design and ease of installation make them ideal for low to medium power applications up to about 10 kW.
Applications of 3-phase Inverters
3-phase inverters are widely used in industrial motor drives, renewable energy systems like solar power plants, and electric vehicle propulsion due to their ability to provide smoother torque and higher power output compared to single-phase inverters. Their applications extend to HVAC systems, variable frequency drives, and large-scale uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) where efficient power conversion and balanced load distribution are critical. Your choice of a 3-phase inverter enhances system performance and reliability in high-demand energy environments.
Efficiency Comparison: 3-phase vs Single-phase Inverters
3-phase inverters generally offer higher efficiency compared to single-phase inverters due to better power distribution and reduced harmonic distortion, which leads to lower energy losses. The balanced load in 3-phase systems minimizes the stress on individual components, improving overall system reliability and performance. Single-phase inverters, while simpler and less costly, tend to have higher power losses and lower efficiency under similar load conditions.
Cost Analysis: Single-phase vs 3-phase Solutions
3-phase inverters typically have higher upfront costs compared to single-phase inverters due to their complex design and advanced components required for managing three separate AC outputs. However, 3-phase inverters offer greater efficiency and load balancing, which can reduce long-term operational costs and improve energy reliability in commercial and industrial applications. Single-phase inverters are more cost-effective for residential use with lower power demands but may result in higher energy losses and instability when scaled for larger systems.
Choosing the Right Inverter for Your Needs
Choosing the right inverter depends on your power requirements and application, with 3-phase inverters offering higher efficiency and smoother power delivery for industrial or large-scale systems. Single-phase inverters are more suitable for residential or small-scale use due to their simplicity and lower cost. Consider factors like load capacity, installation complexity, and energy consumption to determine the optimal inverter type for your specific needs.
Conclusion: Making the Best Inverter Choice
A 3-phase inverter offers higher efficiency, smoother power delivery, and better performance for industrial and large-scale applications, while a single-phase inverter is typically more cost-effective and suitable for residential or small commercial use. Your choice should consider the scale of your energy requirements, system complexity, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Evaluating your power load demands and installation environment will help you make the best inverter decision tailored to your needs.
3-phase Inverter vs Single-phase Inverter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com