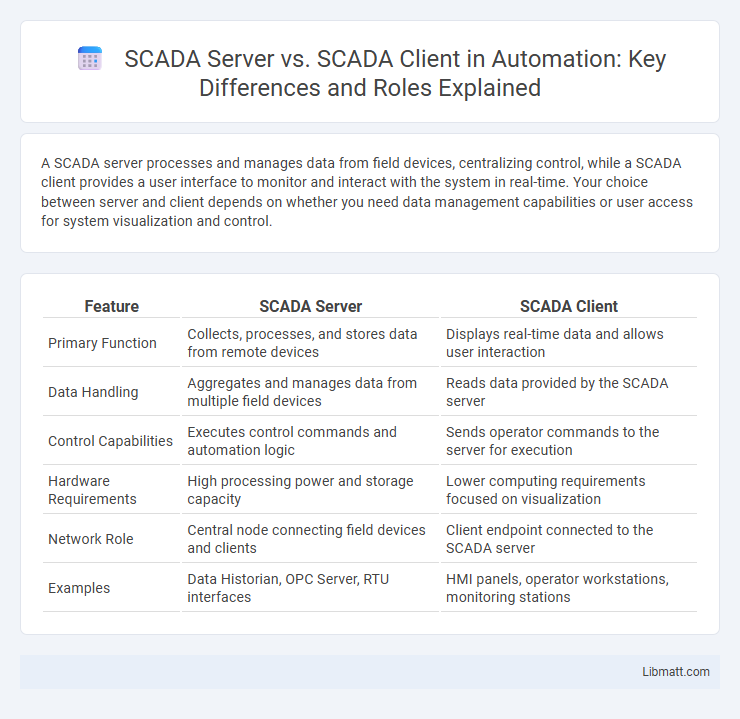
A SCADA server processes and manages data from field devices, centralizing control, while a SCADA client provides a user interface to monitor and interact with the system in real-time. Your choice between server and client depends on whether you need data management capabilities or user access for system visualization and control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SCADA Server | SCADA Client |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Collects, processes, and stores data from remote devices | Displays real-time data and allows user interaction |
| Data Handling | Aggregates and manages data from multiple field devices | Reads data provided by the SCADA server |
| Control Capabilities | Executes control commands and automation logic | Sends operator commands to the server for execution |
| Hardware Requirements | High processing power and storage capacity | Lower computing requirements focused on visualization |
| Network Role | Central node connecting field devices and clients | Client endpoint connected to the SCADA server |
| Examples | Data Historian, OPC Server, RTU interfaces | HMI panels, operator workstations, monitoring stations |
Introduction to SCADA Systems
SCADA servers collect, process, and store real-time data from industrial equipment, enabling centralized control and analysis in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems. SCADA clients serve as user interfaces that display critical operational data, allowing operators to monitor and control processes remotely through graphical dashboards. The interaction between SCADA servers and clients is essential for efficient industrial automation, ensuring data integrity, system reliability, and prompt decision-making.
SCADA Server: Definition and Core Functions
SCADA Server is a centralized system that collects, processes, and stores real-time data from remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) within industrial control networks. It manages data acquisition, executes control commands, and provides a reliable interface for monitoring and analyzing operational statuses. The server's core functions include data logging, alarming, trending, and facilitating communication between field devices and SCADA clients for efficient decision-making.
SCADA Client: Definition and Core Functions
A SCADA Client is a user interface terminal that enables operators to monitor and control industrial processes by visualizing real-time data collected from SCADA Servers. Core functions include displaying graphical representations of process data, issuing control commands, and generating alarms and reports based on server-provided information. It acts as the primary interaction point between human operators and the SCADA system for decision-making and operational oversight.
Key Differences Between SCADA Server and Client
SCADA Server functions as the central hub processing real-time data from field devices, storing historical information, and issuing control commands, while the SCADA Client primarily serves as the user interface for monitoring and interacting with the system. The server manages communication with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and remote terminal units (RTUs), ensuring data integrity and system coordination, whereas the client focuses on visualization, alarms, and report generation for operators. Your understanding of these roles is crucial for optimizing system architecture and ensuring efficient supervision and control in industrial automation.
Data Management in SCADA Server vs Client
SCADA servers play a crucial role in centralized data management, handling the collection, storage, processing, and distribution of real-time operational data from multiple field devices. SCADA clients act primarily as user interfaces, providing visualization, control commands, and access to the processed data without directly managing data storage or system-wide communication. Your system's efficiency depends on the server's ability to manage large datasets reliably, while clients ensure responsive interaction and localized display of critical information.
Communication Protocols and Connectivity
SCADA Server uses standardized communication protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, and OPC to establish reliable data exchange with field devices and SCADA Clients. SCADA Clients typically employ these protocols to connect with the SCADA Server, enabling real-time monitoring and control within industrial networks. Efficient connectivity ensures secure, low-latency communication essential for critical infrastructure management and automation processes.
Security Considerations: Server vs Client
SCADA server security focuses on protecting critical infrastructure by implementing strong access controls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption to prevent unauthorized access and ensure system integrity. SCADA clients require secure authentication mechanisms and endpoint protection to safeguard against malware and unauthorized user actions that could compromise operational control. Your security strategy must balance server-side defenses with client-side measures to maintain a resilient SCADA environment.
Scalability and Performance Implications
SCADA servers handle centralized data processing and control tasks, requiring high scalability to manage numerous connected devices and large data volumes efficiently. SCADA clients, designed for user interaction and visualization, prioritize performance for real-time data rendering but depend on server scalability for overall system responsiveness. Optimizing server scalability directly improves system performance by enabling faster data processing, while client performance is enhanced through efficient UI design and minimal data load.
Use Cases: When to Use Server or Client
SCADA servers are ideal for centralized control systems where real-time data collection, processing, and historical data storage are crucial, such as in power plants or water treatment facilities. SCADA clients are best used for monitoring and managing remote sites or stations, providing operators with interface access to view system status and send commands without handling data processing. Your choice depends on whether you need a central hub for processing and control (server) or a user interface for system interaction (client).
Choosing the Right Architecture for Your SCADA Deployment
SCADA Server manages and processes real-time data from field devices, acting as the central hub responsible for data collection, storage, and control commands. SCADA Client provides user interface access, enabling operators to monitor system status, analyze trends, and issue control instructions without direct data processing responsibilities. Choosing the right architecture depends on your operational scale, with distributed SCADA systems offering enhanced reliability by separating servers and clients, while smaller setups might benefit from integrated solutions for cost-effectiveness and simplicity.
SCADA Server vs SCADA Client Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com