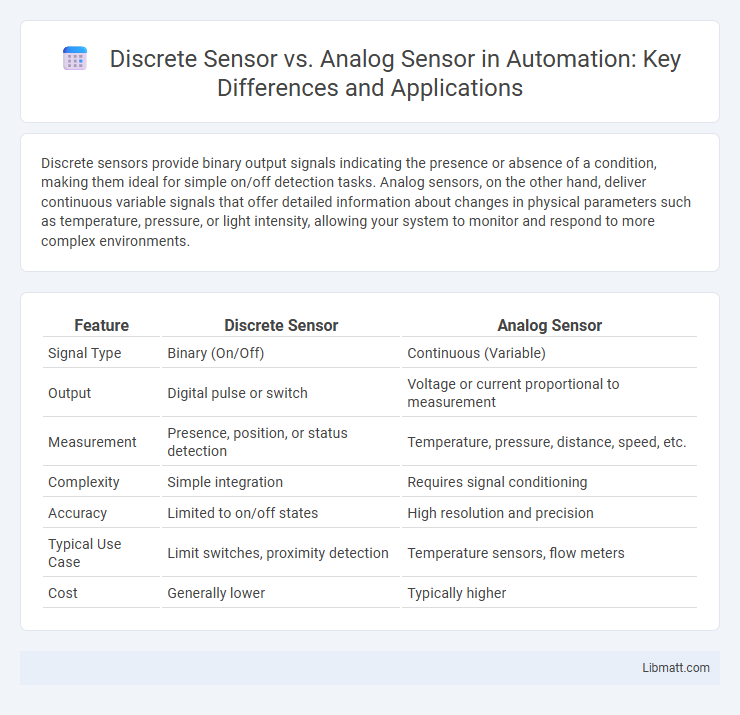
Discrete sensors provide binary output signals indicating the presence or absence of a condition, making them ideal for simple on/off detection tasks. Analog sensors, on the other hand, deliver continuous variable signals that offer detailed information about changes in physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, or light intensity, allowing your system to monitor and respond to more complex environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Discrete Sensor | Analog Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Binary (On/Off) | Continuous (Variable) |
| Output | Digital pulse or switch | Voltage or current proportional to measurement |
| Measurement | Presence, position, or status detection | Temperature, pressure, distance, speed, etc. |
| Complexity | Simple integration | Requires signal conditioning |
| Accuracy | Limited to on/off states | High resolution and precision |
| Typical Use Case | Limit switches, proximity detection | Temperature sensors, flow meters |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
Introduction to Discrete and Analog Sensors
Discrete sensors detect the presence or absence of an object or condition, providing binary output signals such as ON/OFF or HIGH/LOW states. Analog sensors measure continuous physical parameters like temperature, pressure, or light intensity, generating output signals that vary proportionally with the measured quantity. Both sensor types play crucial roles in automation, control systems, and data acquisition by providing distinct types of input data for processing.
What is a Discrete Sensor?
A discrete sensor detects and outputs binary signals, indicating the presence or absence of an object or condition with a simple on/off response. Common examples include proximity sensors, limit switches, and photoelectric sensors, which provide clear, digital signals for automation systems. Your automation setup benefits from discrete sensors when precise, unambiguous detection of specific states is required.
What is an Analog Sensor?
An analog sensor continuously measures physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, or light intensity, producing a variable voltage or current output that corresponds directly to the magnitude of the measured parameter. Unlike discrete sensors that offer binary signals (on/off), analog sensors provide a range of values, enabling more precise and detailed data for monitoring and control applications. Your system gains enhanced accuracy and real-time feedback by integrating analog sensors for continuous sensor data analysis.
Key Differences Between Discrete and Analog Sensors
Discrete sensors provide binary output signals, representing two distinct states such as ON or OFF, while analog sensors deliver continuous signals that vary proportionally to the measured parameter. The key differences lie in signal type, data resolution, and application suitability--discrete sensors excel in detecting specific conditions or changes, whereas analog sensors capture detailed variations in environmental factors like temperature, pressure, or light intensity. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the optimal sensor type for precise monitoring or simple state detection tasks.
Applications of Discrete Sensors
Discrete sensors are widely used in industrial automation for detecting the presence or absence of objects on assembly lines, ensuring precise control in manufacturing processes. They play a crucial role in security systems by monitoring doors and windows for open or closed status, enhancing safety protocols. In robotics, discrete sensors provide binary feedback for position detection and limit switches, enabling accurate and reliable motion control.
Applications of Analog Sensors
Analog sensors are widely used in applications requiring continuous monitoring of physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, and light intensity. They provide real-time, variable output signals that can be directly processed by control systems in industrial automation, environmental sensing, and medical devices. Your choice of an analog sensor ensures precise detection and smooth signal variation essential for accurate measurement in dynamic environments.
Advantages of Discrete Sensors
Discrete sensors offer clear on/off signals that simplify system designs and reduce processing complexity, enhancing reliability in industrial automation. Their robustness against noise and electromagnetic interference provides consistent performance in harsh environments. You benefit from straightforward integration and cost-effective maintenance compared to analog sensors with continuous variable outputs.
Advantages of Analog Sensors
Analog sensors provide continuous and precise measurement of physical parameters, allowing for accurate monitoring of variables such as temperature, pressure, or light intensity. Their ability to detect fine gradations in data supports detailed analysis and real-time responses in applications like environmental sensing and industrial automation. The high resolution and sensitivity of analog sensors make them ideal for scenarios requiring nuanced signal detection beyond simple on/off states.
Limitations and Challenges
Discrete sensors offer simple on/off detection but face limitations in capturing precise variations, leading to less detailed data interpretation. Analog sensors provide continuous output for variable measurements but encounter challenges such as signal noise, calibration drift, and sensitivity to environmental factors. Both sensor types require careful integration and maintenance to ensure accuracy and reliability in complex applications.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate sensor type hinges on the specific requirements of your application, with discrete sensors offering simple on/off detection ideal for straightforward binary states such as presence or absence. Analog sensors provide continuous output data, making them better suited for monitoring variables like temperature, pressure, or light intensity where precise measurement is crucial. Understanding the environmental conditions, signal processing needs, and accuracy demands ensures optimal sensor performance and reliability in your system.
Discrete Sensor vs Analog Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com