Push buttons provide momentary contact, making them ideal for temporary actions like starting or stopping a machine, while selector switches offer maintained contact positions for selecting modes or settings. Your choice depends on whether you need brief activation or a sustained, stable selection in your control system.
Table of Comparison
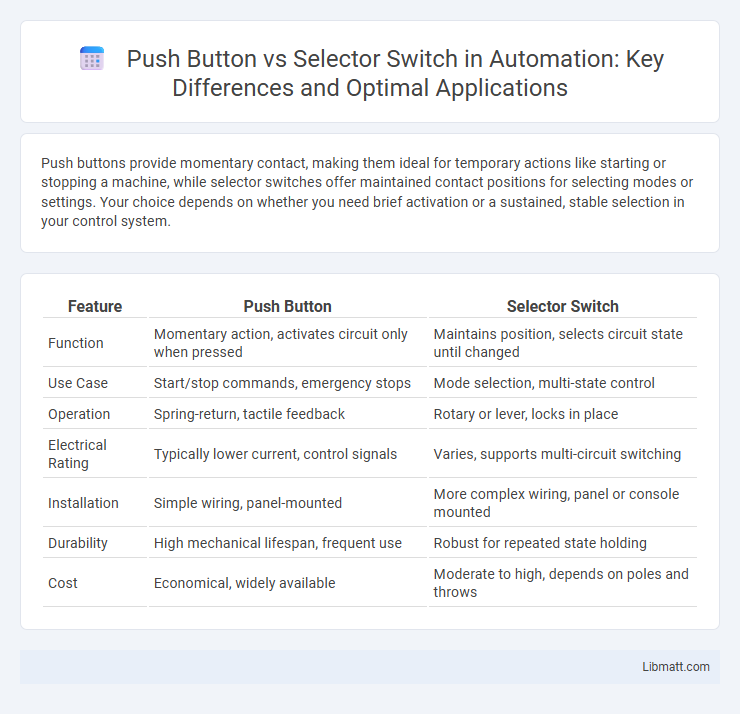
| Feature | Push Button | Selector Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Momentary action, activates circuit only when pressed | Maintains position, selects circuit state until changed |
| Use Case | Start/stop commands, emergency stops | Mode selection, multi-state control |
| Operation | Spring-return, tactile feedback | Rotary or lever, locks in place |
| Electrical Rating | Typically lower current, control signals | Varies, supports multi-circuit switching |
| Installation | Simple wiring, panel-mounted | More complex wiring, panel or console mounted |
| Durability | High mechanical lifespan, frequent use | Robust for repeated state holding |
| Cost | Economical, widely available | Moderate to high, depends on poles and throws |
Introduction to Push Buttons and Selector Switches
Push buttons and selector switches are essential components in industrial control systems, designed to initiate specific machine functions or operations. Push buttons typically provide momentary input by pressing a button that returns to its original position, making them ideal for start-stop control or emergency stops. Selector switches offer a rotational or toggle mechanism, allowing operators to select between multiple functions or modes, ensuring precise control over system settings.
Key Differences Between Push Buttons and Selector Switches
Push buttons provide momentary contact activation, typically used for initiating or stopping machine operations, while selector switches offer maintained contact with multiple positions for selecting modes or functions. Push buttons are designed for quick, transient input, whereas selector switches enable users to choose between settings like ON/OFF, AUTO/MANUAL, or different operational states. The key difference lies in functionality; push buttons control immediate actions, and selector switches allow for mode selection and sustained control changes.
Design and Construction Features
Push button switches feature a compact, spring-loaded design that allows momentary or maintained contact activation, commonly enclosed in a plastic or metal housing for durability. Selector switches incorporate a rotary mechanism with multiple stable positions, often mounted on control panels for easy operational selection among different circuit states. Your choice depends on whether you require a simple momentary action or a multi-position selector with rugged construction designed for precise control tasks.
Functions and Common Applications
Push buttons provide momentary contact for initiating or stopping a process, ideal for start/stop functions in industrial machinery and control panels. Selector switches enable selecting one of several fixed positions, commonly used for mode selection or equipment configuration in automated systems. Both are essential for operator control, with push buttons favoring quick, transient actions and selector switches suited for stable, maintained states.
User Interface and Operation
Push buttons offer a simple, momentary user interface where the operator applies pressure to activate a function, ideal for immediate start-stop commands. Selector switches provide a multi-position interface allowing users to toggle between different modes or settings, offering clearer operational states and preventing accidental changes. The tactile feedback of push buttons ensures quick, decisive actions, while selector switches enhance operational clarity by maintaining a chosen position until manually adjusted.
Electrical and Mechanical Characteristics
Push buttons typically feature momentary electrical contact, designed for short, tactile activation with ratings commonly ranging from 1A to 10A at 120V or 240V AC, providing reliable switching for low to moderate current circuits. Selector switches offer maintained contact positions with mechanical detents, allowing continuous current flow in selected states, often rated for higher loads up to 20A or more, depending on industrial requirements. Mechanically, push buttons emphasize quick actuation and release with minimal travel distance, while selector switches incorporate rotary or lever-based actuation for precise position control and durability under frequent switching.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Push buttons offer straightforward installation, often requiring minimal wiring and panel space, making them ideal for simple control circuits. Selector switches demand more precise alignment and may involve complex mechanical components, resulting in longer installation time and periodic maintenance to ensure proper functionality. Your choice impacts the ease of upkeep, with push buttons generally offering lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
Safety and Reliability Aspects
Push buttons provide quick, immediate response critical for emergency stops, enhancing operational safety by allowing fast machine shutdown. Selector switches offer reliable mode selection with clear position indication, reducing the risk of operator error and ensuring consistent machine settings. Your choice between these devices depends on whether you prioritize rapid safety intervention or dependable operational control.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Push buttons typically offer a more budget-friendly option for basic control needs due to their simple design and lower manufacturing costs. Selector switches, while generally higher in price, provide greater functionality and durability, justifying their cost in applications requiring multi-position control. When managing Your budget, choosing push buttons can reduce upfront expenses, but selector switches may offer better long-term value for complex control systems.
Choosing the Right Option: Push Button or Selector Switch
Choosing the right option between a push button and a selector switch depends on your control needs and application context. Push buttons are ideal for momentary actions like starting or stopping equipment, providing quick and easy user input with a simple press. Selector switches offer multiple stable positions for selecting modes or settings, making them suitable for applications requiring clear, user-selected states.
Push Button vs Selector Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com