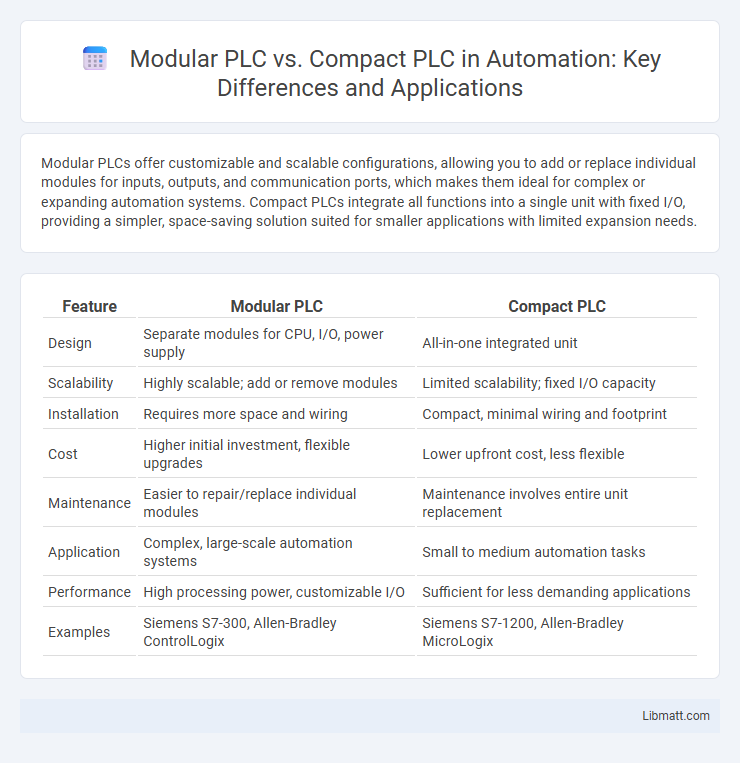
Modular PLCs offer customizable and scalable configurations, allowing you to add or replace individual modules for inputs, outputs, and communication ports, which makes them ideal for complex or expanding automation systems. Compact PLCs integrate all functions into a single unit with fixed I/O, providing a simpler, space-saving solution suited for smaller applications with limited expansion needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modular PLC | Compact PLC |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Separate modules for CPU, I/O, power supply | All-in-one integrated unit |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; add or remove modules | Limited scalability; fixed I/O capacity |
| Installation | Requires more space and wiring | Compact, minimal wiring and footprint |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, flexible upgrades | Lower upfront cost, less flexible |
| Maintenance | Easier to repair/replace individual modules | Maintenance involves entire unit replacement |
| Application | Complex, large-scale automation systems | Small to medium automation tasks |
| Performance | High processing power, customizable I/O | Sufficient for less demanding applications |
| Examples | Siemens S7-300, Allen-Bradley ControlLogix | Siemens S7-1200, Allen-Bradley MicroLogix |
Introduction to PLCs
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are industrial digital computers designed for automation of electromechanical processes, offering precise control and reliability. Modular PLCs provide flexibility with separate modules for power, input/output, and communication, enabling customization for complex systems. Compact PLCs integrate all components into a single unit, ideal for simpler tasks requiring fewer inputs and outputs, making your automation setup efficient and space-saving.
What is a Modular PLC?
A Modular PLC consists of separate, interchangeable modules such as CPU, input/output, power supply, and communication interfaces that can be customized and expanded according to specific automation system requirements. It offers high flexibility, scalability, and easy maintenance in complex industrial processes, enabling users to tailor configurations for various applications. Modular PLCs are typically suited for large-scale operations where adaptability and system growth are critical.
What is a Compact PLC?
A Compact PLC integrates the CPU, power supply, and input/output modules into a single unit, making it ideal for small to medium-sized automation tasks. Its all-in-one design reduces wiring complexity and saves installation space compared to Modular PLCs. Compact PLCs offer fixed I/O configurations with limited expansion options, providing cost-effective and simplified solutions for straightforward control applications.
Key Features of Modular PLCs
Modular PLCs feature separate modules for power supply, CPU, input/output (I/O), and communication, enabling flexible system expansion and customization based on application requirements. Their scalable architecture supports multiple I/O modules, facilitating easy upgrades and maintenance without system downtime. High processing speed, extensive memory capacity, and advanced networking capabilities make modular PLCs ideal for complex industrial automation tasks.
Key Features of Compact PLCs
Compact PLCs feature an integrated design combining the CPU, power supply, and I/O modules into a single unit, optimizing space and simplifying installation. They typically support a fixed number of I/O points and have limited expandability compared to modular PLCs, making them ideal for small to medium automation tasks. Your automation project benefits from easy configuration, cost efficiency, and straightforward maintenance with compact PLCs.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Modular PLCs offer superior scalability by allowing you to add or remove input and output modules based on system requirements, making them ideal for evolving industrial processes. Compact PLCs integrate fixed modules in a single unit, limiting expansion but providing a streamlined, cost-effective solution for smaller applications. Your choice depends on whether future flexibility and system growth are priorities or if a compact design with fixed capabilities suits your current needs.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Modular PLCs offer flexible installation by allowing users to select and add individual modules tailored to specific control tasks, enabling easier upgrades and replacements without dismantling the entire system. In contrast, Compact PLCs integrate all components into a single unit, resulting in simpler initial installation but limited scalability and more complex maintenance when internal parts fail. Maintenance of modular systems is generally more cost-effective due to quick module swaps, while compact PLCs may require complete unit replacement or professional servicing to address internal hardware issues.
Cost Analysis: Modular vs Compact PLC
Modular PLCs typically involve higher upfront costs due to separate components such as CPUs, I/O modules, and power supplies, but offer scalability and flexibility that can lower long-term expenses in expanding systems. Compact PLCs present lower initial investment and simpler installation, making them cost-effective for small to medium-sized applications with fixed I/O requirements. Your choice between modular and compact PLCs should consider the total cost of ownership, including future expansion needs, maintenance, and project complexity to optimize budget allocation.
Application Areas for Each PLC Type
Modular PLCs excel in complex industrial automation systems requiring flexibility and scalability, commonly used in manufacturing plants, process industries, and large-scale production environments. Compact PLCs are ideal for smaller applications with limited space, such as packaging machines, building automation, and simple control tasks in automotive or food processing sectors. Choosing the right PLC depends on your project's size, complexity, and future expansion needs.
Choosing the Right PLC for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate PLC depends on project scale and complexity, with Modular PLCs offering extensive scalability, flexible I/O configurations, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities ideal for large industrial automation systems. Compact PLCs integrate CPU, power supply, and fixed I/O in a single unit, providing cost-effective, space-saving solutions suited for smaller applications with limited expansion needs. Evaluating factors such as system size, I/O requirements, budget constraints, and future expansion plans ensures choosing a PLC that optimizes performance and investment.
Modular PLC vs Compact PLC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com