IEC 61131-3 defines programming standards for industrial automation and control systems, focusing on the development of PLC software with languages like Ladder Logic and Structured Text to ensure interoperability and maintainability. IEC 61508 addresses functional safety of electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic systems by providing requirements for safety lifecycle management and risk assessment, helping you design systems that reliably prevent hazards and failures.
Table of Comparison
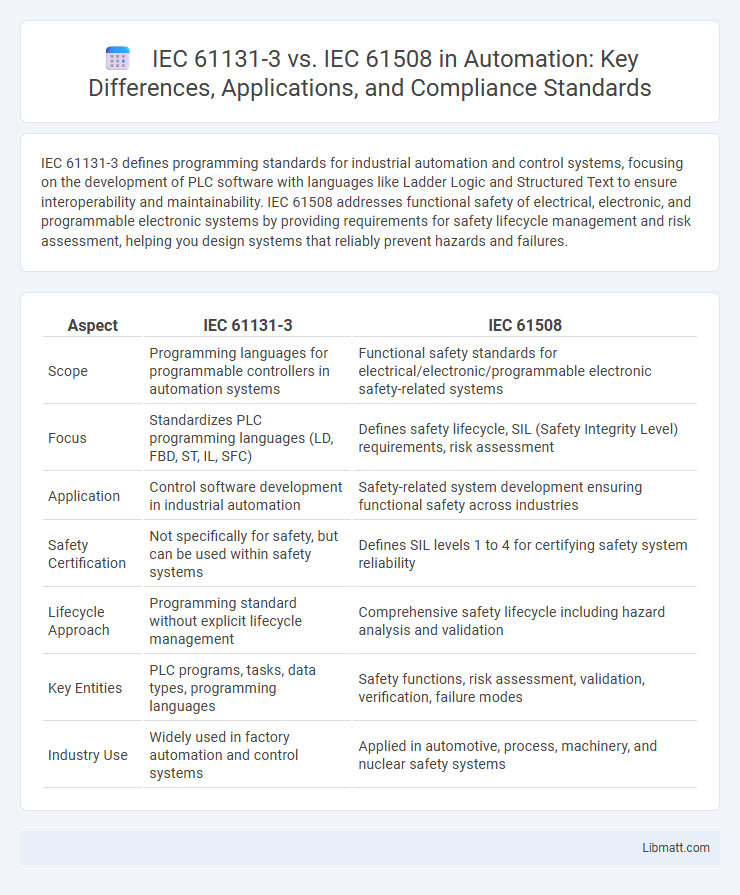
| Aspect | IEC 61131-3 | IEC 61508 |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Programming languages for programmable controllers in automation systems | Functional safety standards for electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems |
| Focus | Standardizes PLC programming languages (LD, FBD, ST, IL, SFC) | Defines safety lifecycle, SIL (Safety Integrity Level) requirements, risk assessment |
| Application | Control software development in industrial automation | Safety-related system development ensuring functional safety across industries |
| Safety Certification | Not specifically for safety, but can be used within safety systems | Defines SIL levels 1 to 4 for certifying safety system reliability |
| Lifecycle Approach | Programming standard without explicit lifecycle management | Comprehensive safety lifecycle including hazard analysis and validation |
| Key Entities | PLC programs, tasks, data types, programming languages | Safety functions, risk assessment, validation, verification, failure modes |
| Industry Use | Widely used in factory automation and control systems | Applied in automotive, process, machinery, and nuclear safety systems |
Introduction to IEC 61131-3 and IEC 61508
IEC 61131-3 defines the international standard for programmable logic controller (PLC) programming languages, providing a structured approach with five programming languages including Ladder Diagram and Structured Text. IEC 61508 is the functional safety standard aimed at ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic systems, particularly in safety-critical applications with risk management throughout the entire system lifecycle. You should understand that IEC 61131-3 focuses on programming industrial automation devices, while IEC 61508 addresses the broader requirements for safety integrity and certification in control systems.
Purpose and Scope Comparison
IEC 61131-3 defines programming languages and software architecture standards for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in industrial automation, focusing on improving software development efficiency and interoperability. IEC 61508 addresses the functional safety of electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic safety-related systems, emphasizing risk reduction throughout the system lifecycle. Understanding both standards' purpose and scope helps you ensure compliance when designing control systems that require both reliable automation and safety integrity.
Key Features of IEC 61131-3
IEC 61131-3 defines a standardized programming environment and language suite for programmable logic controllers (PLCs), emphasizing five programming languages including Ladder Diagram (LD), Structured Text (ST), and Function Block Diagram (FBD). It focuses on enhancing interoperability, reusability, and modularity with features like task management, program organization units, and standardized data types. The standard facilitates efficient automation system development but does not inherently address functional safety requirements, which are covered separately by IEC 61508.
Key Features of IEC 61508
IEC 61508 is a functional safety standard that defines requirements for the entire lifecycle of safety-related systems, emphasizing risk assessment, safety integrity levels (SILs), and rigorous validation and verification processes. Key features include detailed safety lifecycle management, systematic failure avoidance through design and development practices, and quantitative measures for safety performance. Your implementation must align with these criteria to ensure compliance and effective risk mitigation in safety-critical applications.
Differences in Application Areas
IEC 61131-3 is primarily focused on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in industrial automation, defining programming languages and software structures for control systems. IEC 61508 centers on functional safety for electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic safety-related systems across various industries, emphasizing safety lifecycle and risk assessment. The key difference lies in IEC 61131-3 addressing automation programming standards, while IEC 61508 targets comprehensive safety requirements and certification for safety-critical systems.
Programming Languages and Development Approaches
IEC 61131-3 defines standardized programming languages such as Ladder Diagram (LD), Structured Text (ST), Function Block Diagram (FBD), Instruction List (IL), and Sequential Function Chart (SFC) for industrial automation control systems, emphasizing modularity and reusability. IEC 61508 focuses on functional safety, prescribing rigorous development approaches including systematic hazard analysis, safety lifecycle management, and verification to ensure reliability of safety-related systems rather than specifying programming languages. While IEC 61131-3 addresses automation programming with language standards, IEC 61508 mandates development processes to achieve safety integrity levels (SIL) for embedded and programmable electronic systems in safety-critical applications.
Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) Considerations
IEC 61131-3 provides standardized programming languages for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) focusing on industrial automation, while IEC 61508 is a comprehensive functional safety standard addressing Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) requirements across various safety-related systems. SIL considerations in IEC 61508 define rigorous performance criteria and verification processes to ensure safety functions meet targeted failure rates, which are critical for high-risk applications. IEC 61131-3-based systems must be designed and implemented with SIL compliance in mind by integrating IEC 61508 guidelines to achieve required safety integrity levels.
Compliance and Certification Requirements
IEC 61131-3 defines programming languages and software architecture for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) with guidelines for compliance primarily focused on functionality and interoperability, without mandatory certification. IEC 61508 emphasizes functional safety for electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems, requiring rigorous risk assessment, validation, and third-party certification to meet safety integrity levels (SILs). Organizations implementing safety-critical automation must align IEC 61131-3 software development with IEC 61508 certification processes to ensure full compliance with industry safety standards.
Integration Challenges and Best Practices
IEC 61131-3, focused on programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and IEC 61508, centered on functional safety for electrical/electronic/programmable electronic systems, present integration challenges due to differing scopes and requirements. Ensuring compliance with IEC 61508's safety integrity levels (SIL) while implementing IEC 61131-3 programming languages demands rigorous verification, validation, and documentation processes. Best practices include adopting a clear safety lifecycle, leveraging safety-certified tools, and maintaining traceability between design, code, and testing to bridge functional programming with stringent safety standards.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Standard
Selecting between IEC 61131-3 and IEC 61508 depends on the specific requirements of industrial automation versus functional safety applications. IEC 61131-3 centers on programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and software development for control systems, offering standardization in programming languages and design methodologies. IEC 61508 emphasizes safety lifecycle and risk management in safety-related systems, making it essential for environments where functional safety integrity levels (SIL) must be met.
IEC 61131-3 vs IEC 61508 Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com